Problem 15-2A Recording, adjusting, and reporting available-for-sale debt securities LO P3 Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Mead Inc. began operations in Year 1, following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities. Year 1 Jan. 20 Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $25,000. Feb. 9 Purchased notes of Sony for $59,490. June 12 Purchased bonds of Mattel for $45,000. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $26,900; Sony, $49,050; and Mattel, $55,950. Year 2 Apr. 15 Sold all of the bonds of Johnson & Johnson for $28,000. July 5 Sold all of the bonds of Mattel for $39,000. July 22 Purchased notes of Sara Lee for $17,100. Aug. 19 Purchased bonds of Kodak for $18,450. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $18,900; Sara Lee, $16,500; and Sony, $63,000. Year 3 Feb. 27 Purchased bonds of Microsoft for $161,000. June 21 Sold all of the notes of Sony for $61,200. June 30 Purchased bonds of Black & Decker for $54,900. Aug. 3 Sold all of the notes of Sara Lee for $13,800. Nov. 1 Sold all of the bonds of Kodak for $23,400. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Black & Decker, $57,300; and Microsoft, $159,500.
Problem 15-2A Recording, adjusting, and reporting available-for-sale debt securities LO P3 Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Mead Inc. began operations in Year 1, following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities. Year 1 Jan. 20 Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $25,000. Feb. 9 Purchased notes of Sony for $59,490. June 12 Purchased bonds of Mattel for $45,000. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $26,900; Sony, $49,050; and Mattel, $55,950. Year 2 Apr. 15 Sold all of the bonds of Johnson & Johnson for $28,000. July 5 Sold all of the bonds of Mattel for $39,000. July 22 Purchased notes of Sara Lee for $17,100. Aug. 19 Purchased bonds of Kodak for $18,450. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $18,900; Sara Lee, $16,500; and Sony, $63,000. Year 3 Feb. 27 Purchased bonds of Microsoft for $161,000. June 21 Sold all of the notes of Sony for $61,200. June 30 Purchased bonds of Black & Decker for $54,900. Aug. 3 Sold all of the notes of Sara Lee for $13,800. Nov. 1 Sold all of the bonds of Kodak for $23,400. Dec. 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Black & Decker, $57,300; and Microsoft, $159,500.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter13: Investments And Long-term Receivables
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2MC: During 2021, Anthony Company purchased debt securities as a long-term investment and classified them...
Related questions
Question
Problem 15-2A Recording, adjusting, and reporting available-for-sale debt securities LO P3
Skip to question
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
Mead Inc. began operations in Year 1, following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities.
Year 1
| Jan. | 20 | Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $25,000. | ||
| Feb. | 9 | Purchased notes of Sony for $59,490. | ||
| June | 12 | Purchased bonds of Mattel for $45,000. | ||
| Dec. | 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $26,900; Sony, $49,050; and Mattel, $55,950. |
Year 2
| Apr. | 15 | Sold all of the bonds of Johnson & Johnson for $28,000. | ||
| July | 5 | Sold all of the bonds of Mattel for $39,000. | ||
| July | 22 | Purchased notes of Sara Lee for $17,100. | ||
| Aug. | 19 | Purchased bonds of Kodak for $18,450. | ||
| Dec. | 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $18,900; Sara Lee, $16,500; and Sony, $63,000. |
Year 3
| Feb. | 27 | Purchased bonds of Microsoft for $161,000. | ||
| June | 21 | Sold all of the notes of Sony for $61,200. | ||
| June | 30 | Purchased bonds of Black & Decker for $54,900. | ||
| Aug. | 3 | Sold all of the notes of Sara Lee for $13,800. | ||
| Nov. | 1 | Sold all of the bonds of Kodak for $23,400. | ||
| Dec. | 31 | Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Black & Decker, $57,300; and Microsoft, $159,500. |
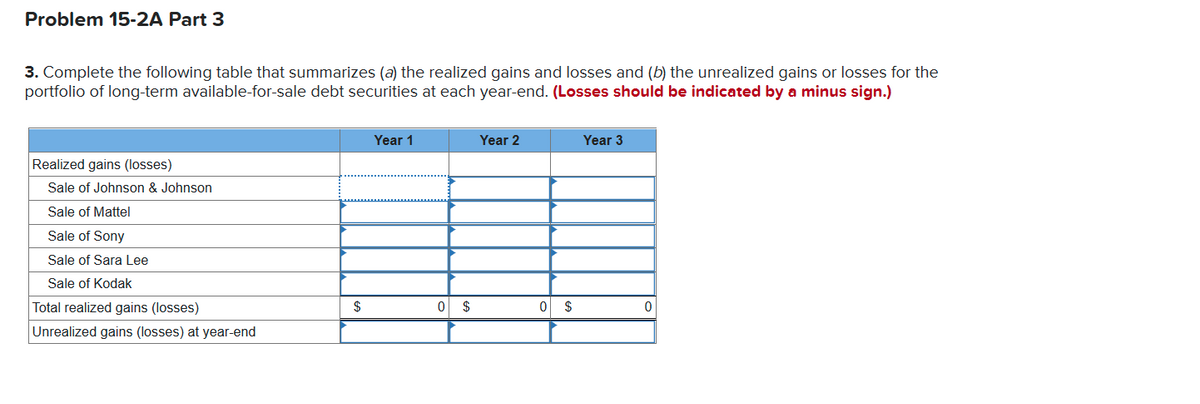
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 15-2A Part 3
3. Complete the following table that summarizes (a) the realized gains and losses and (b) the unrealized gains or losses for the
portfolio of long-term available-for-sale debt securities at each year-end. (Losses should be indicated by a minus sign.)
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Realized gains (losses)
Sale of Johnson & Johnson
Sale of Mattel
Sale of Sony
Sale of Sara Lee
Sale of Kodak
Total realized gains (losses)
$
$
0 $
Unrealized gains (losses) at year-end
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285866307
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
