Problem 2 The figure below shows the same long straight wire with current i to the right and wire loops that we have been examining for the past few homework sets. In this problem, we will focus just on loop (a), the larger square loop on the left. At the time depicted in the figure, the upper edge is at some distance a from the long wire, the loop has edge length L, and has resistance R. Note that this is essentially the same situation as presented in example 27.2 in the text PHY 205 Homework 11- Due November 20, 2019 2 b The loop has clockwise current iL flowing around it, but this time the source of the current in the loop is a changing magnetic flux through it. The flux may be changing because the straight-line current, i, is changing in time while the loops remain in the locations shown (and therefore the field is changing at the location of the loops) or because the loops are moving while the straight wire current remains constant (a) At the time depicted by the diagram, what is the flux through the square loop, as a function of the parameters listed in the problem statement? (Note that the field is NOT uniform so you do have to set up an integral similar to the one in the example.) (b) If the currents in the straight wire and loop are as shown above, and the loop current is due to the wire current changing, is that wire current increasing in magnitude or decreasing? (c) Use the flux you worked out in part (a), which is a function of the wire current i, to answer the following: If the the loop current is due to a wire current that is changing at a constant rate di/dt, what is the magnitude of the induced EMF and the induced current i in the loop? (d) If the loop current is, instead, due to the motion of the loop, in which of the following directions could the loop be moving: toward the wire, away from the wire, to the left, or to the right? (e) If the loop current is due to the motion of the loop, and it is moving with speed v = what is the EMF and current il (again, in terms of the parameters given) in the loop? Note a is now the variable that is changing in time, and we have flux in terms of a - don't forget the chain rule in taking derivatives. da/dt,
Problem 2 The figure below shows the same long straight wire with current i to the right and wire loops that we have been examining for the past few homework sets. In this problem, we will focus just on loop (a), the larger square loop on the left. At the time depicted in the figure, the upper edge is at some distance a from the long wire, the loop has edge length L, and has resistance R. Note that this is essentially the same situation as presented in example 27.2 in the text PHY 205 Homework 11- Due November 20, 2019 2 b The loop has clockwise current iL flowing around it, but this time the source of the current in the loop is a changing magnetic flux through it. The flux may be changing because the straight-line current, i, is changing in time while the loops remain in the locations shown (and therefore the field is changing at the location of the loops) or because the loops are moving while the straight wire current remains constant (a) At the time depicted by the diagram, what is the flux through the square loop, as a function of the parameters listed in the problem statement? (Note that the field is NOT uniform so you do have to set up an integral similar to the one in the example.) (b) If the currents in the straight wire and loop are as shown above, and the loop current is due to the wire current changing, is that wire current increasing in magnitude or decreasing? (c) Use the flux you worked out in part (a), which is a function of the wire current i, to answer the following: If the the loop current is due to a wire current that is changing at a constant rate di/dt, what is the magnitude of the induced EMF and the induced current i in the loop? (d) If the loop current is, instead, due to the motion of the loop, in which of the following directions could the loop be moving: toward the wire, away from the wire, to the left, or to the right? (e) If the loop current is due to the motion of the loop, and it is moving with speed v = what is the EMF and current il (again, in terms of the parameters given) in the loop? Note a is now the variable that is changing in time, and we have flux in terms of a - don't forget the chain rule in taking derivatives. da/dt,
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter27: Direct-current Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 22P: For the circuit shown in Figure P27.22, we wish to find the currents I1, I2, and I3. Use Kirchhoffs...
Related questions
Question
Could you answer A-C, Thank you

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2
The figure below shows the same long straight wire with current i to the right and wire loops that
we have been examining for the past few homework sets. In this problem, we will focus just on loop
(a), the larger square loop on the left. At the time depicted in the figure, the upper edge is at some
distance a from the long wire, the loop has edge length L, and has resistance R. Note that this is
essentially the same situation as presented in example 27.2 in the text
PHY 205
Homework 11- Due November 20, 2019
2
b
The loop has clockwise current iL flowing around it, but this time the source of the current in the
loop is a changing magnetic flux through it. The flux may be changing because the straight-line
current, i, is changing in time while the loops remain in the locations shown (and therefore the field
is changing at the location of the loops) or because the loops are moving while the straight wire
current remains constant
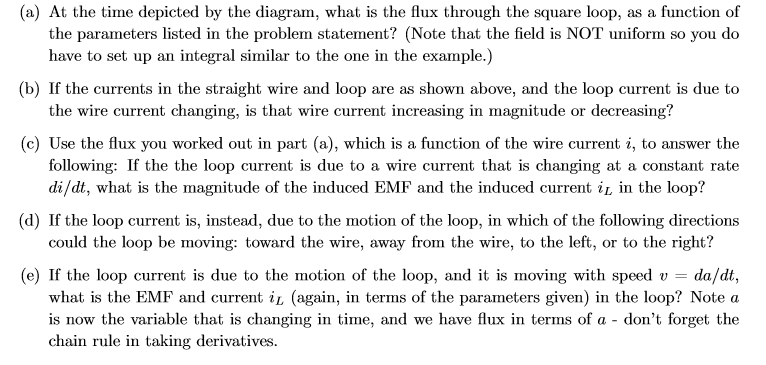
Transcribed Image Text:(a) At the time depicted by the diagram, what is the flux through the square loop, as a function of
the parameters listed in the problem statement? (Note that the field is NOT uniform so you do
have to set up an integral similar to the one in the example.)
(b) If the currents in the straight wire and loop are as shown above, and the loop current is due to
the wire current changing, is that wire current increasing in magnitude or decreasing?
(c) Use the flux you worked out in part (a), which is a function of the wire current i, to answer the
following: If the the loop current is due to a wire current that is changing at a constant rate
di/dt, what is the magnitude of the induced EMF and the induced current i in the loop?
(d) If the loop current is, instead, due to the motion of the loop, in which of the following directions
could the loop be moving: toward the wire, away from the wire, to the left, or to the right?
(e) If the loop current is due to the motion of the loop, and it is moving with speed v =
what is the EMF and current il (again, in terms of the parameters given) in the loop? Note a
is now the variable that is changing in time, and we have flux in terms of a - don't forget the
chain rule in taking derivatives.
da/dt,
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning