Problem 4 (counts as two problems): Let X1, X2, ., X,be a collection of independent discrete random variables that all take the value 1 with probability p and take the value 0 with probability (1-p). The following set of steps illustrates the Law of Large Numbers at work. a) Compute the mean and the variance of X1 (which is the same for X2, X3, etc.) b) Use your answer to (a) to compute the mean and variance of p == (X, + X2 + ….+ Xn), which is the proportion of “ones" observed in the n instances of X.
Problem 4 (counts as two problems): Let X1, X2, ., X,be a collection of independent discrete random variables that all take the value 1 with probability p and take the value 0 with probability (1-p). The following set of steps illustrates the Law of Large Numbers at work. a) Compute the mean and the variance of X1 (which is the same for X2, X3, etc.) b) Use your answer to (a) to compute the mean and variance of p == (X, + X2 + ….+ Xn), which is the proportion of “ones" observed in the n instances of X.
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
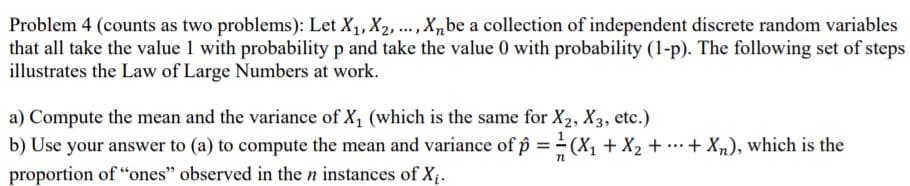
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4 (counts as two problems): Let X1, X2, ., X,be a collection of independent discrete random variables
that all take the value 1 with probability p and take the value 0 with probability (1-p). The following set of steps
illustrates the Law of Large Numbers at work.
a) Compute the mean and the variance of X1 (which is the same for X2, X3, etc.)
b) Use your answer to (a) to compute the mean and variance of p == (X, + X2 + ….+ Xn), which is the
proportion of “ones" observed in the n instances of X.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Solution:
4.
From the given information, X1, X2,………, Xn be the independent discrete random variables that take the value 1 with probability p and take the value 0 with probability (1-p).
Then, the mean of X1 is
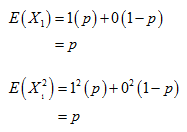
Then, the variance of X1 is
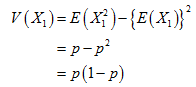
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
