Problem. 9: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral || F. dS, where S F(x, y, z) = xz² i + 3 + cos(2) ) j+ (æ²z+ y²) k and S is the top half of the sphere x² + y? + z? = 9. Note that S is not a closed surface. First, compute the integrals over Si and S2, where Si is the disk a? + y² < 9, oriented downward, and S2 = S1 U S is a closed surface. F. dS = ? dy dx z²+y²<9 ?
Problem. 9: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral || F. dS, where S F(x, y, z) = xz² i + 3 + cos(2) ) j+ (æ²z+ y²) k and S is the top half of the sphere x² + y? + z? = 9. Note that S is not a closed surface. First, compute the integrals over Si and S2, where Si is the disk a? + y² < 9, oriented downward, and S2 = S1 U S is a closed surface. F. dS = ? dy dx z²+y²<9 ?
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12T
Related questions
Question
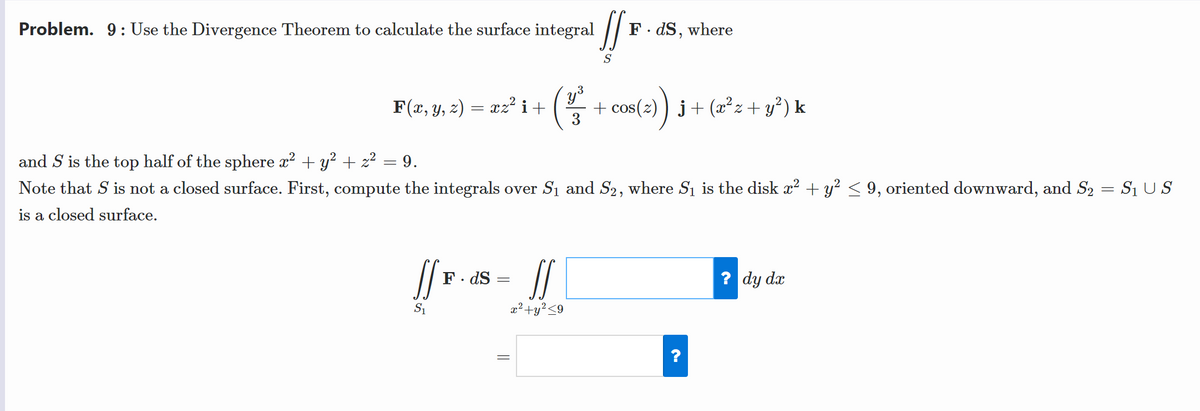
Transcribed Image Text:Problem. 9: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral
F. dS, where
F(x, y, z) = xz² i+
3
+ cos(2) ) j+ (² z + y?) k
and S is the top half of the sphere x2 + y² + z² = 9.
Note that S is not a closed surface. First, compute the integrals over S1 and S2, where Sı is the disk x? + y? < 9, oriented downward, and S2 = S1 US
is a closed surface.
F. dS
? dy dx
S1
a?+y?<9
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage