QucStioTTIGip Do people walk faster in the airport when they are departing (getting on a plane) or do they walk faster when they are arriving (getting off a plane)? A reputable researcher measured the walking speed of random travelers in two International Airports. His findings are summarized in the table. Complete parts (a)-(c) below Click the icon to view the findings. (a) Is this an observational study or a designed experiment? Why? i Walking Speed A. This is an observational study since the researcher influenced the data B. This is a designed experiment since the researcher influenced the data Direction of Travel Departure Arrival C. This is a designed experiment since the researcher did not influence the data. Mean speed (feet per minute) 251 274 D. This is an observational study since the researcher did not influence the data. Standard deviation 45 38 (feet per minute) Sample size (b) Explain why it is reasonable to use Welch's t-test 35 35 A. The populations are normally distributed. B. The samples are random, large and independent. Print Done C. The samples are random, small and independent. D. The samples are random, large and dependent. (c) Do individuals walk at different speeds depending on whether they are departing or arriving at the a 0.1 level of significance? Let u represent the mean speed of people departing and 2 represent the mean speed of people arriving. State the null and alternative hypothesis. В. Но: Н -12 H1 H2 A. Ho: H С. Но: Н - 12 H1 H2 D. HoH12 Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test. P-value (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion. A. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing. B. Do not reject Ho. There iss not sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing C. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a D. 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing.
QucStioTTIGip Do people walk faster in the airport when they are departing (getting on a plane) or do they walk faster when they are arriving (getting off a plane)? A reputable researcher measured the walking speed of random travelers in two International Airports. His findings are summarized in the table. Complete parts (a)-(c) below Click the icon to view the findings. (a) Is this an observational study or a designed experiment? Why? i Walking Speed A. This is an observational study since the researcher influenced the data B. This is a designed experiment since the researcher influenced the data Direction of Travel Departure Arrival C. This is a designed experiment since the researcher did not influence the data. Mean speed (feet per minute) 251 274 D. This is an observational study since the researcher did not influence the data. Standard deviation 45 38 (feet per minute) Sample size (b) Explain why it is reasonable to use Welch's t-test 35 35 A. The populations are normally distributed. B. The samples are random, large and independent. Print Done C. The samples are random, small and independent. D. The samples are random, large and dependent. (c) Do individuals walk at different speeds depending on whether they are departing or arriving at the a 0.1 level of significance? Let u represent the mean speed of people departing and 2 represent the mean speed of people arriving. State the null and alternative hypothesis. В. Но: Н -12 H1 H2 A. Ho: H С. Но: Н - 12 H1 H2 D. HoH12 Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test. P-value (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Choose the correct conclusion. A. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing. B. Do not reject Ho. There iss not sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing C. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a D. 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 22EQ
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:QucStioTTIGip
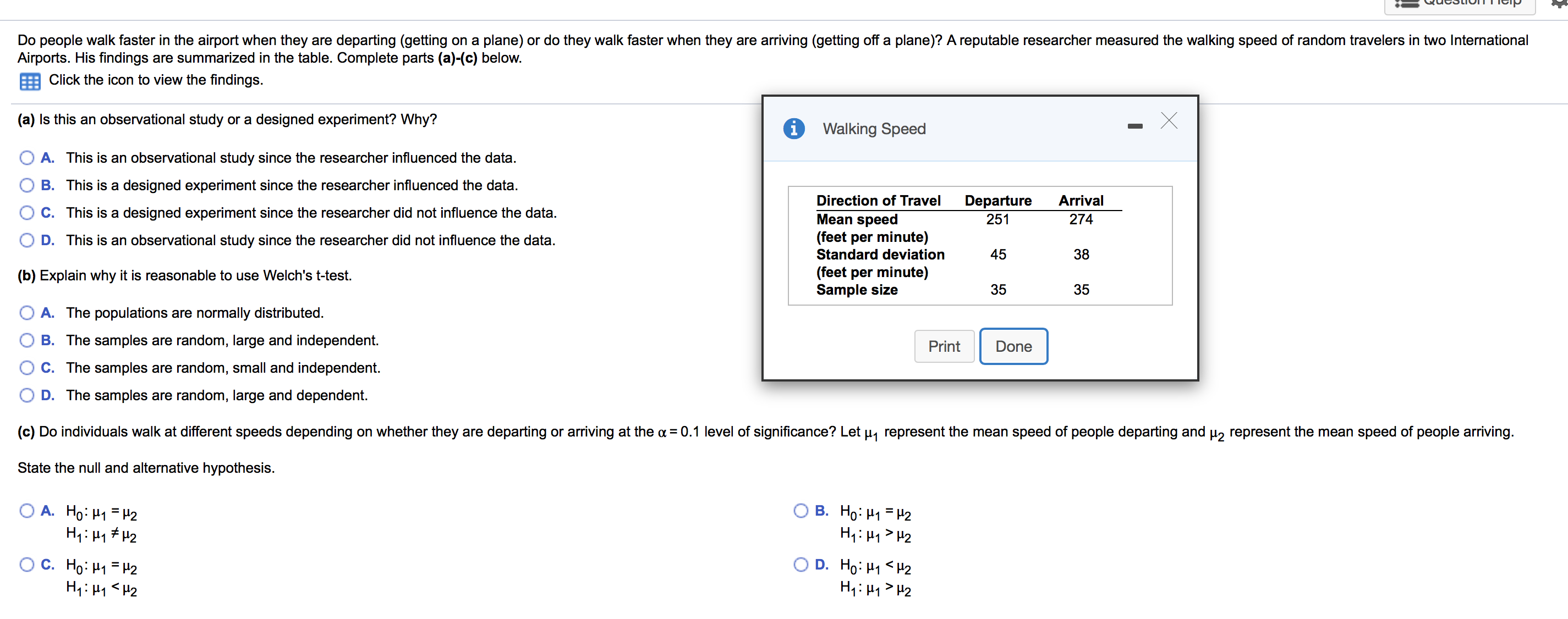
Do people walk faster in the airport when they are departing (getting on a plane) or do they walk faster when they are arriving (getting off a plane)? A reputable researcher measured the walking speed of random travelers in two International
Airports. His findings are summarized in the table. Complete parts (a)-(c) below
Click the icon to view the findings.
(a) Is this an observational study or a designed experiment? Why?
i
Walking Speed
A. This is an observational study since the researcher influenced the data
B. This is a designed experiment since the researcher influenced the data
Direction of Travel
Departure
Arrival
C. This is a designed experiment since the researcher did not influence the data.
Mean speed
(feet per minute)
251
274
D. This is an observational study since the researcher did not influence the data.
Standard deviation
45
38
(feet per minute)
Sample size
(b) Explain why it is reasonable to use Welch's t-test
35
35
A. The populations are normally distributed.
B. The samples are random, large and independent.
Print
Done
C. The samples are random, small and independent.
D. The samples are random, large and dependent.
(c) Do individuals walk at different speeds depending on whether they are departing or arriving at the a 0.1 level of significance? Let u represent the mean speed of people departing and 2 represent the mean speed of people arriving.
State the null and alternative hypothesis.
В. Но: Н -12
H1 H2
A. Ho: H
С. Но: Н - 12
H1 H2
D. HoH12

Transcribed Image Text:Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.
P-value
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Choose the correct conclusion.
A. Reject Ho. There is not sufficient evidence at the a
0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing.
B. Do not reject Ho. There iss not sufficient evidence at the a 0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing
C. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a
0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing
Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence at the a
D.
0.1 level of significance to say that travelers walk at different speeds depending on whether they are arriving or departing.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning