Requirement 1. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transacti been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Cost of Goods Sold Inventory on Hand More info Unit Cost Date Quantity Dec. 1 11 23 26 29 Purchases Unit Cost Total Cost Unit Quantity Cost Total Cost Quantity Total Cost Dec. 1 Beginning merchandise inventory Dec. 11 Purchase Dec. 23 Sale Dec. 26 Purchase Dec. 29 Sale Requirements 1. 22 tires @ $53 each 14 tires @ $71 each 18 tires @ $82 each 10 tires @ $74 each 19 tires @ $82 each Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory corting method X - X
Requirement 1. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transacti been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.) Cost of Goods Sold Inventory on Hand More info Unit Cost Date Quantity Dec. 1 11 23 26 29 Purchases Unit Cost Total Cost Unit Quantity Cost Total Cost Quantity Total Cost Dec. 1 Beginning merchandise inventory Dec. 11 Purchase Dec. 23 Sale Dec. 26 Purchase Dec. 29 Sale Requirements 1. 22 tires @ $53 each 14 tires @ $71 each 18 tires @ $82 each 10 tires @ $74 each 19 tires @ $82 each Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory corting method X - X
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337690881
Author:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Chapter6: Cost Of Goods Sold And Inventory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 67APSA: Inventory Costing Methods Andersons Department Store has the following data for inventory,...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
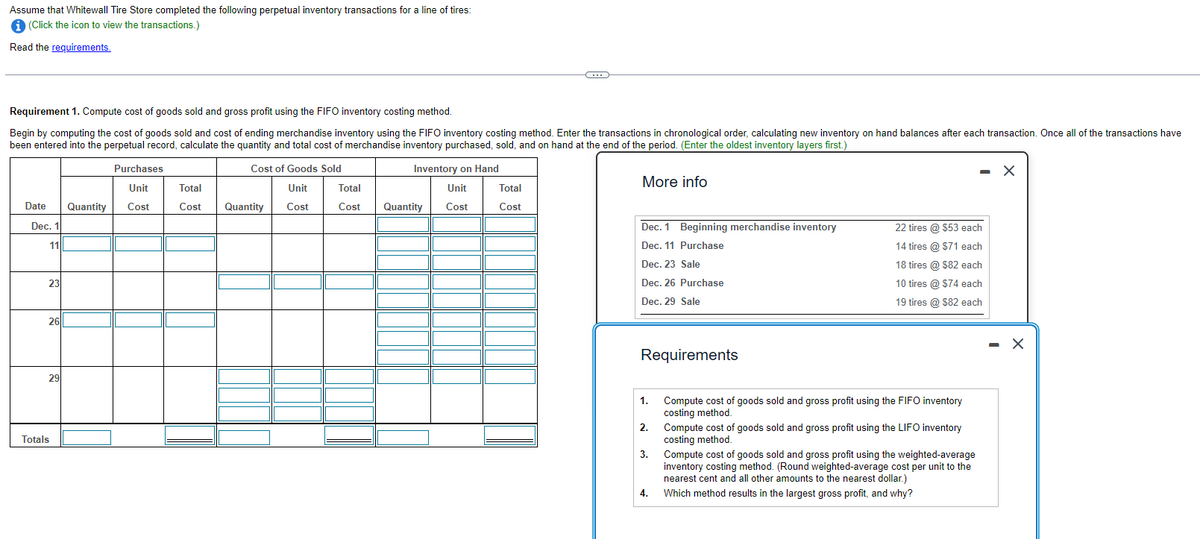
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that Whitewall Tire Store completed the following perpetual inventory transactions for a line of tires:
i (Click the icon to view the transactions.)
Read the requirements.
Requirement 1. Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method.
Begin by computing the cost of goods sold and cost of ending merchandise inventory using the FIFO inventory costing method. Enter the transactions in chronological order, calculating new inventory on hand balances after each transaction. Once all of the transactions have
been entered into the perpetual record, calculate the quantity and total cost of merchandise inventory purchased, sold, and on hand at the end of the period. (Enter the oldest inventory layers first.)
Date Quantity
Dec. 1
11
23
261
29
Totals
Purchases
Unit
Cost
Cost of Goods Sold
Total
Unit
Cost Quantity Cost
Total
Cost
Inventory on Hand
Unit
Quantity Cost
C
Total
Cost
More info
Dec. 1 Beginning merchandise inventory
Dec. 11 Purchase
Dec. 23 Sale
Dec. 26 Purchase
Dec. 29 Sale
Requirements
1.
2.
3.
4.
22 tires @ $53 each
14 tires @ $71 each
18 tires @ $82 each
10 tires @ $74 each
19 tires @ $82 each
Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the FIFO inventory
costing method.
Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the LIFO inventory
costing method.
- X
Compute cost of goods sold and gross profit using the weighted-average
inventory costing method. (Round weighted-average cost per unit to the
nearest cent and all other amounts to the nearest dollar.)
Which method results in the largest gross profit, and why?
-
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305088436
Author:
Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,