• Set A₁A₁ (HbAA) • Set A₁A₂ (HbAS) • Set A₂A₂ (Hbss) Using your simulations as examples, explain why the HbS allele is more common in some parts of the world than others. Include information about the genotypes in your response.
• Set A₁A₁ (HbAA) • Set A₁A₂ (HbAS) • Set A₂A₂ (Hbss) Using your simulations as examples, explain why the HbS allele is more common in some parts of the world than others. Include information about the genotypes in your response.
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter19: Population Genetics And Human Evolution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9QP: Using the HardyWeinberg Law in Human Genetics Suppose you are monitoring the allelic and genotypic...
Related questions
Question

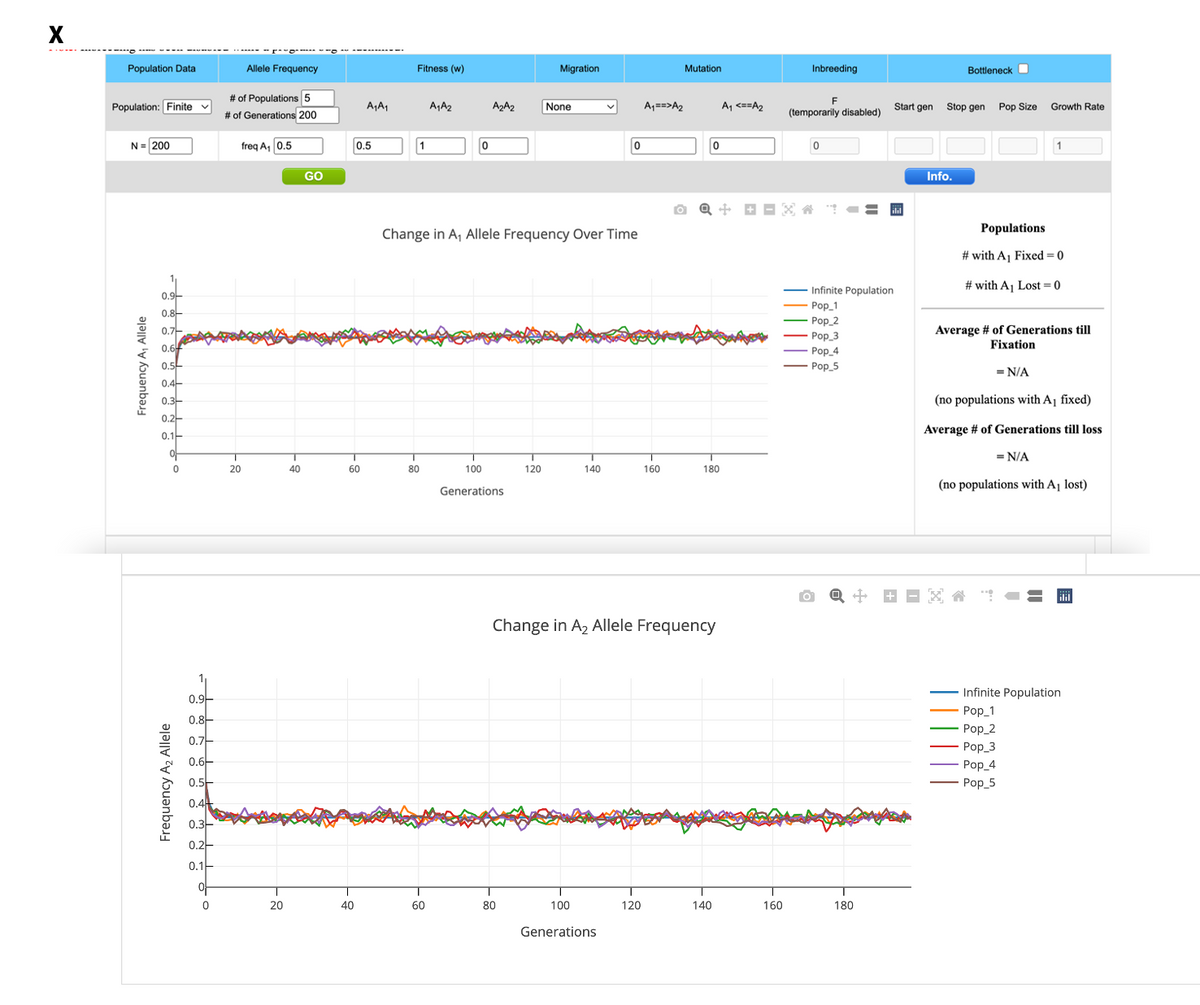
Transcribed Image Text:• Set A₁A₁ (HbAA)
• Set A₁A₂ (HbAS)
• Set A₂A₂ (Hbss)
Using your simulations as examples, explain why the HbS allele is more common in
some parts of the world than others. Include information about the genotypes in
your response.
Transcribed Image Text:X
Population Data
Population: Finite
N = 200
Frequency A, Allele
0.7-
0.6
0.1
Frequency A₂ Allele
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
-8°
0
Allele Frequency
# of Populations 5
# of Generations 200
20
freq A₁ 0.5
T
20
40
GO
60
40
A₁A₁
0.5
Fitness (w)
80
A₁ A₂
60
0
A₂A2
Change in A₁ Allele Frequency Over Time
100
Generations
Migration
120
80
None
140
100
0
Generations
A₁ ==>A₂
120
160
Change in A₂ Allele Frequency
Mutation
0
180
140
A₁ <==A₂
Inbreeding
160
+ += 84
(temporarily disabled)
0
F
Infinite Population
Pop_1
Pop_2
Pop_3
Pop_4
Pop_5
180
Bottleneck
Start gen Stop gen Pop Size
Info.
Growth Rate
1
Populations
# with A₁ Fixed=0
# with A₁ Lost = 0
Average # of Generations till
Fixation
=N/A
=N/A
(no populations with A₁ fixed)
Average # of Generations till loss
(no populations with A₁ lost)
Infinite Population
Pop_1
Pop_2
Pop_3
Pop_4
Pop 5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning