Step 1: Determine the total positive charge on the hexapeptide when all acidic and basic groups are fully protonated. Enter your answer without the sign. charge: Step 2: Determine the pK value of the group that loses a proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge pK = of zero. Step 3: Determine the pK value of the group that gains a proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge pK = of zero. Step 4: Estimate the pl value of the hexapeptide. pI =
Step 1: Determine the total positive charge on the hexapeptide when all acidic and basic groups are fully protonated. Enter your answer without the sign. charge: Step 2: Determine the pK value of the group that loses a proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge pK = of zero. Step 3: Determine the pK value of the group that gains a proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge pK = of zero. Step 4: Estimate the pl value of the hexapeptide. pI =
Chapter26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, And Proteins
Section26.SE: Something Extra
Problem 50AP: The -helical parts of myoglobin and other proteins stop whenever a proline residue is encountered in...
Related questions
Question
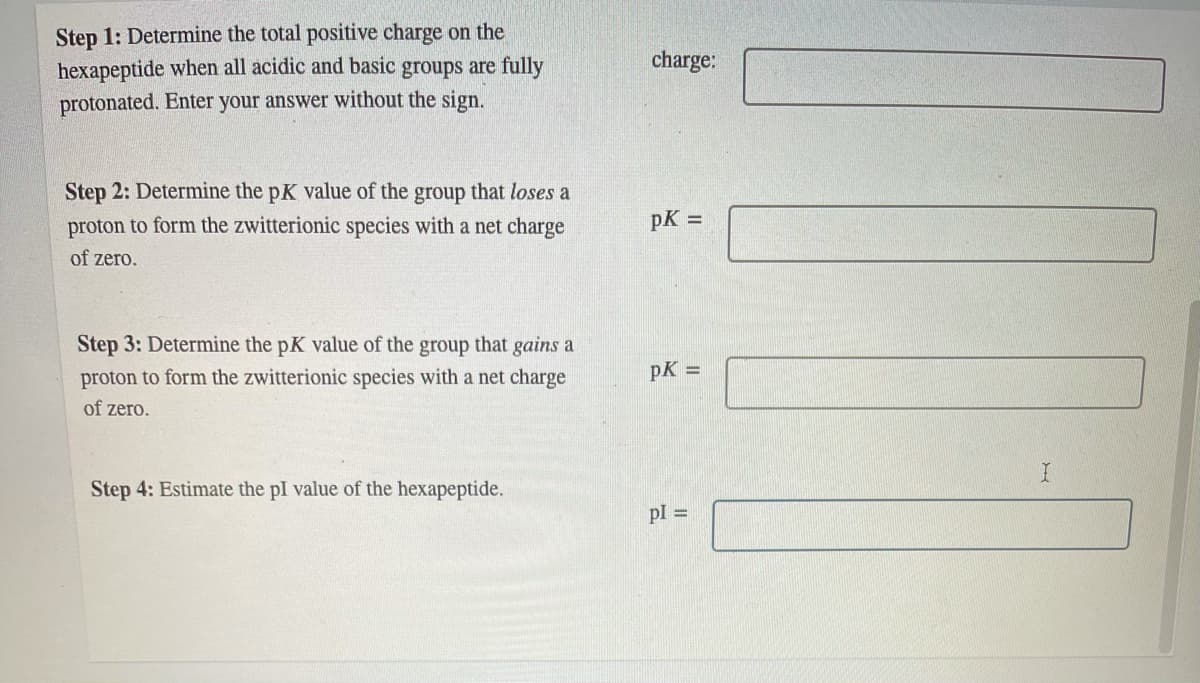
Transcribed Image Text:Step 1: Determine the total positive charge on the
hexapeptide when all acidic and basic groups are fully
charge:
protonated. Enter your answer without the sign.
Step 2: Determine the pK value of the group that loses a
proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge
pK =
of zero.
Step 3: Determine the pK value of the group that gains a
proton to form the zwitterionic species with a net charge
pK =
of zero.
Step 4: Estimate the pI value of the hexapeptide.
pl =
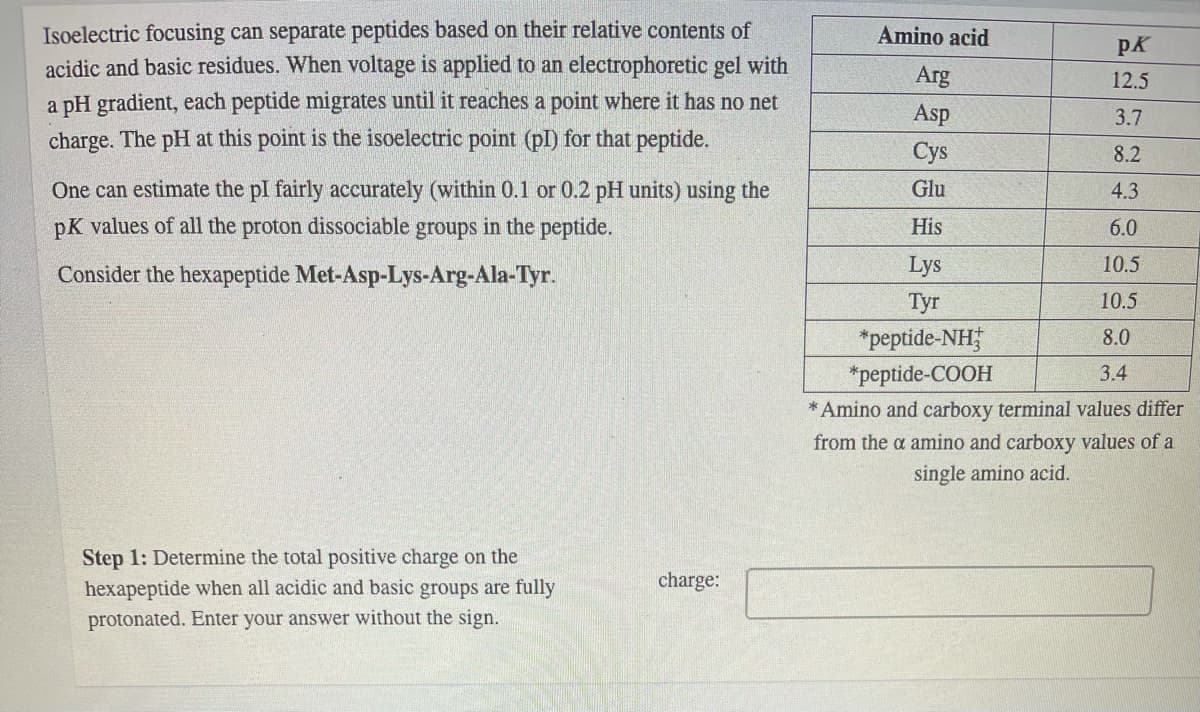
Transcribed Image Text:Isoelectric focusing can separate peptides based on their relative contents of
acidic and basic residues. When voltage is applied to an electrophoretic gel with
Amino acid
pK
Arg
12.5
a pH gradient, each peptide migrates until it reaches a point where it has no net
charge. The pH at this point is the isoelectric point (pl) for that peptide.
Asp
3.7
Cys
8.2
One can estimate the pl fairly accurately (within 0.1 or 0.2 pH units) using the
Glu
4.3
pK values of all the proton dissociable groups in the peptide.
His
6.0
Consider the hexapeptide Met-Asp-Lys-Arg-Ala-Tyr.
Lys
10.5
Tyr
10.5
*peptide-NH;
8.0
*peptide-COOH
3.4
* Amino and carboxy terminal values differ
from the a amino and carboxy values of a
single amino acid.
Step 1: Determine the total positive charge on the
hexapeptide when all acidic and basic groups are fully
charge:
protonated. Enter your answer without the sign.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

