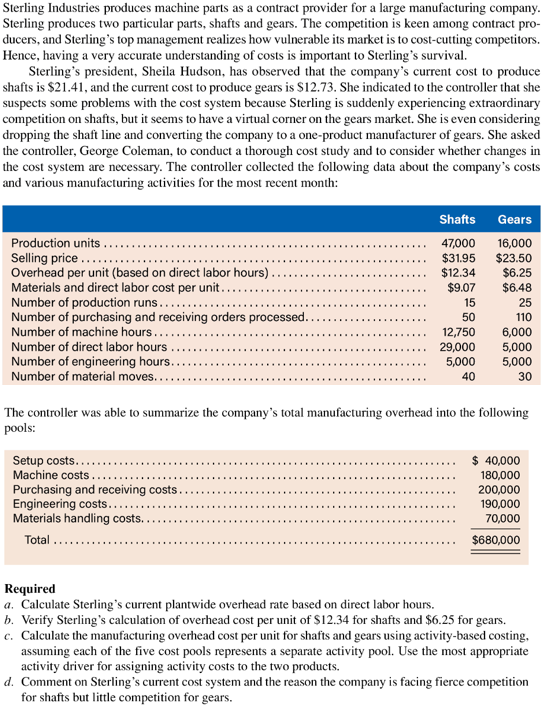
Sterling Industries produces machine parts as a contract provider for a large manufacturing company Sterling produces two particular parts, shafts and gears. The competition is keen among contract pro- ducers, and Sterling's top management realizes how vulnerable its market is to cost-cutting competitors Hence, having a very accurate understanding of costs is important to Sterling's survival Sterling's president, Sheila Hudson, has observed that the company's current cost to produce shafts is $21.41, and the current cost to produce gears is S12.73. She indicated to the controller that she suspects some problems with the cost system because Sterling is suddenly experiencing extraordinary competition on shafts, but it seems to have a virtual corner on the gears market. She is even considering dropping the shaft line and converting the company to a one-product manufacturer of gears. She asked the controller, George Coleman, to conduct a thorough cost study and to consider whether changes in the cost system are necessary. The controller collected the following data about the company's costs and various manufacturing activities for the most recent month Shafts Gears Production units Selling price Overhead per unit (based on direct labor hours). Materials and direct labor cost per unit.... Number of production runs......... Number of purchasing and receiving orders processed.. Number of machine hours... 47,000 $31.95 $12.34 $9.07 16,000 $23.50 $6.25 $6.48 15 25 110 6,000 5,000 5,000 50 12,750 29,000 5,000 Number of direct labor hours Number of engineering hours.. Number of material moves.. 40 30 The controller was able to summarize the company's total manufacturing overhead into the following pools: Setup costs... Machine costs Purchasing and receiving costs Engineering costs.. Materials handling costs.. 40,000 180,000 200,000 190,000 70,000 Total $680,000 Required a. Calculate Sterling's current plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours b. Verify Sterling's calculation of overhead cost per unit of $12.34 for shafts and $6.25 for gears. c. Calculate the manufacturing overhead cost per unit for shafts and gears using activity-based costing assuming each of the five cost pools represents a separate activity pool. Use the most appropriate activity driver for assigning activity costs to the two products. d. Comment on Sterling 's current cost system and the reason the company is facing fierce competition for shafts but little competition for gears
Sterling Industries produces machine parts as a contract provider for a large manufacturing company Sterling produces two particular parts, shafts and gears. The competition is keen among contract pro- ducers, and Sterling's top management realizes how vulnerable its market is to cost-cutting competitors Hence, having a very accurate understanding of costs is important to Sterling's survival Sterling's president, Sheila Hudson, has observed that the company's current cost to produce shafts is $21.41, and the current cost to produce gears is S12.73. She indicated to the controller that she suspects some problems with the cost system because Sterling is suddenly experiencing extraordinary competition on shafts, but it seems to have a virtual corner on the gears market. She is even considering dropping the shaft line and converting the company to a one-product manufacturer of gears. She asked the controller, George Coleman, to conduct a thorough cost study and to consider whether changes in the cost system are necessary. The controller collected the following data about the company's costs and various manufacturing activities for the most recent month Shafts Gears Production units Selling price Overhead per unit (based on direct labor hours). Materials and direct labor cost per unit.... Number of production runs......... Number of purchasing and receiving orders processed.. Number of machine hours... 47,000 $31.95 $12.34 $9.07 16,000 $23.50 $6.25 $6.48 15 25 110 6,000 5,000 5,000 50 12,750 29,000 5,000 Number of direct labor hours Number of engineering hours.. Number of material moves.. 40 30 The controller was able to summarize the company's total manufacturing overhead into the following pools: Setup costs... Machine costs Purchasing and receiving costs Engineering costs.. Materials handling costs.. 40,000 180,000 200,000 190,000 70,000 Total $680,000 Required a. Calculate Sterling's current plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours b. Verify Sterling's calculation of overhead cost per unit of $12.34 for shafts and $6.25 for gears. c. Calculate the manufacturing overhead cost per unit for shafts and gears using activity-based costing assuming each of the five cost pools represents a separate activity pool. Use the most appropriate activity driver for assigning activity costs to the two products. d. Comment on Sterling 's current cost system and the reason the company is facing fierce competition for shafts but little competition for gears
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter10: Evaluating Decentralized Operations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17E: Materials used by the Instrument Division of Ziegler Inc. are currently purchased from outside...
Related questions
Question
Please answer last subpart labeled D.
Comment on Sterling's current cost system and the reason the company is facing fierce competition for shafts but little competition for gears.
Transcribed Image Text:Sterling Industries produces machine parts as a contract provider for a large manufacturing company
Sterling produces two particular parts, shafts and gears. The competition is keen among contract pro-
ducers, and Sterling's top management realizes how vulnerable its market is to cost-cutting competitors
Hence, having a very accurate understanding of costs is important to Sterling's survival
Sterling's president, Sheila Hudson, has observed that the company's current cost to produce
shafts is $21.41, and the current cost to produce gears is S12.73. She indicated to the controller that she
suspects some problems with the cost system because Sterling is suddenly experiencing extraordinary
competition on shafts, but it seems to have a virtual corner on the gears market. She is even considering
dropping the shaft line and converting the company to a one-product manufacturer of gears. She asked
the controller, George Coleman, to conduct a thorough cost study and to consider whether changes in
the cost system are necessary. The controller collected the following data about the company's costs
and various manufacturing activities for the most recent month
Shafts
Gears
Production units
Selling price
Overhead per unit (based on direct labor hours).
Materials and direct labor cost per unit....
Number of production runs.........
Number of purchasing and receiving orders processed..
Number of machine hours...
47,000
$31.95
$12.34
$9.07
16,000
$23.50
$6.25
$6.48
15
25
110
6,000
5,000
5,000
50
12,750
29,000
5,000
Number of direct labor hours
Number of engineering hours..
Number of material moves..
40
30
The controller was able to summarize the company's total manufacturing overhead into the following
pools:
Setup costs...
Machine costs
Purchasing and receiving costs
Engineering costs..
Materials handling costs..
40,000
180,000
200,000
190,000
70,000
Total
$680,000
Required
a. Calculate Sterling's current plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours
b. Verify Sterling's calculation of overhead cost per unit of $12.34 for shafts and $6.25 for gears.
c. Calculate the manufacturing overhead cost per unit for shafts and gears using activity-based costing
assuming each of the five cost pools represents a separate activity pool. Use the most appropriate
activity driver for assigning activity costs to the two products.
d. Comment on Sterling 's current cost system and the reason the company is facing fierce competition
for shafts but little competition for gears
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning