STERLING TIRE COMPANY Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2013 Sales (30,000 tires at $80 each).. $2,400,000 Less: Variable costs (30,000 tires at $40).. 1,200,000 Fixed costs 500,000 Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). $ 700,000 Interest expense.. 55,000 Earnings before taxes (EBT). $ 645,000 Income tax expense (20%). 129,000 Earnings after taxes (EAT). $ 516,000 Given this income statement, compute the following: a. Degree of operating leverage. b. Degree of financial leverage. c. Degree of combined leverage. d. Break-even point in units.
STERLING TIRE COMPANY Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2013 Sales (30,000 tires at $80 each).. $2,400,000 Less: Variable costs (30,000 tires at $40).. 1,200,000 Fixed costs 500,000 Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). $ 700,000 Interest expense.. 55,000 Earnings before taxes (EBT). $ 645,000 Income tax expense (20%). 129,000 Earnings after taxes (EAT). $ 516,000 Given this income statement, compute the following: a. Degree of operating leverage. b. Degree of financial leverage. c. Degree of combined leverage. d. Break-even point in units.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter8: Inventories: Special Valuation Issues
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11RE: Johnson Corporation had beginning inventory of 20,000 at cost and 35,000 at retail. During the year,...
Related questions
Question
100%
Please, use these formulas that are in the image only.
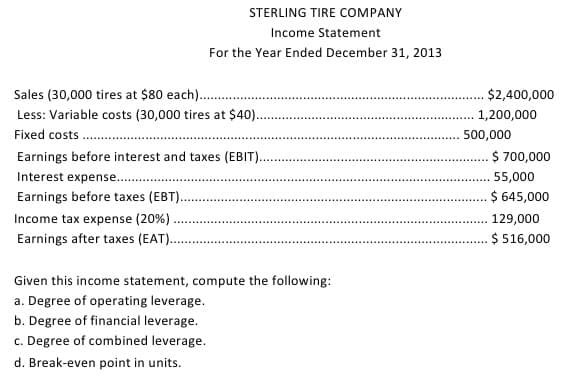
Transcribed Image Text:STERLING TIRE COMPANY
Income Statement
For the Year Ended December 31, 2013
Sales (30,000 tires at $80 each)..
$2,400,000
Less: Variable costs (30,000 tires at $40).
1,200,000
Fixed costs .
500,000
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)..
$ 700,000
Interest expense..
55,000
Earnings before taxes (EBT)..
$ 645,000
Income tax expense (20%)
129,000
Earnings after taxes (EAT)..
$ 516,000
Given this income statement, compute the following:
a. Degree of operating leverage.
b. Degree of financial leverage.
c. Degree of combined leverage.
d. Break-even point in units.

Transcribed Image Text:Using these formulas:
1-Breakeven Point Formula:
FC
Q =p- vc
2-Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL):
Percentage change in EBIT
Percentage change in sales
DOL
3-The formula for calculating the degree of operating
leverage at a base sales level, Q, is the following:
eX (P – vc)
DOL(Q) = Qx (P –- vc) – FC
Q: the sales level. P: sale price. vc: variable operating costs per unit.
FC: fixed operating costs.
4-The Degree Of Financial Leverage (DFL):
Percentage change in EPS
Percentage change in EBIT
DFL
EBIT
DFL at base level EBIT =
EBIT - I - (PD x
5-degree of total leverage (DTL)
Percentage change in EPS
Percentage change in sales
DTL
ex (P – vc)
PD
DTL at Q units =
ex (P – vc) – FC – 1 –(2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning