Suppose b is any integer. If b mod 12 = 7, what is 8b mod 12? In other words, if division of b by 12 gives a remainder of 7, what is the remainder when 8b is divided by 12? Fill in the blanks to show that the same answer will be obtained no matter what integer is used for b at the start. Because b mod 12 = 7, there is an integer m such that b = 12m + 7 8b = 129 + r with 0 sr< 12. The result is Multiply both sides of this equation by 8 and then simplify the right-hand side to find values of q and r such that q = 7m + 2 and r= 4 Now 0 sr< 12, and q is an integer because products and sums of integers are integers So the uniqueness part of the quotient remainder theorem guarantees that the remainder obtained when 8b is divided by 12 is 4
Suppose b is any integer. If b mod 12 = 7, what is 8b mod 12? In other words, if division of b by 12 gives a remainder of 7, what is the remainder when 8b is divided by 12? Fill in the blanks to show that the same answer will be obtained no matter what integer is used for b at the start. Because b mod 12 = 7, there is an integer m such that b = 12m + 7 8b = 129 + r with 0 sr< 12. The result is Multiply both sides of this equation by 8 and then simplify the right-hand side to find values of q and r such that q = 7m + 2 and r= 4 Now 0 sr< 12, and q is an integer because products and sums of integers are integers So the uniqueness part of the quotient remainder theorem guarantees that the remainder obtained when 8b is divided by 12 is 4
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter2: The Integers
Section2.7: Introduction To Coding Theory (optional)
Problem 18E
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
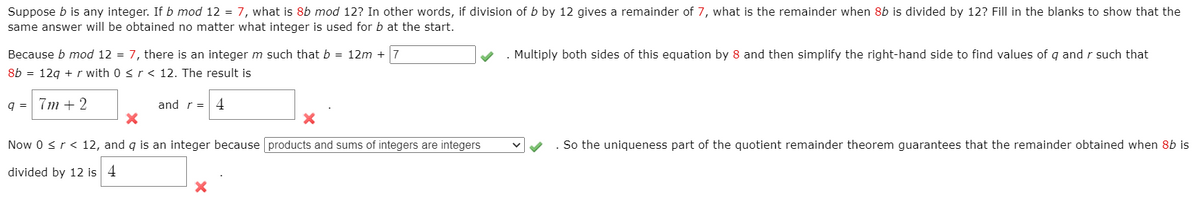
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose b is any integer. If b mod 12 = 7, what is 8b mod 12? In other words, if division of b by 12 gives a remainder of 7, what is the remainder when 8b is divided by 12? Fill in the blanks to show that the
same answer will be obtained no matter what integer is used for b at the start.
. Multiply both sides of this equation by 8 and then simplify the right-hand side to find values of q and r such that
Because b mod 12 = 7, there is an integer m such that b = 12m + 7
8b = 12g + r with 0 <r < 12. The result is
q = 7m + 2
and r = 4
Now 0 <r< 12, and q is an integer because products and sums of integers are integers
So the uniqueness part of the quotient remainder theorem guarantees that the remainder obtained when 8b is
divided by 12 is 4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell


Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell
