Suppose we have a binomial experiment in which success is defined to be a particular quality or attribute that interests us. (a) Suppose n = 27 and p = 0.23. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.) np = 6.21 nq = 20.79 Yes be approximated by a normal random variable because np exceeds 5 can What are the values of u, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.) (b) Suppose n = 25 and p = 0.15. Can we safely approximate p by a normal distribution? Why or why not? No p cannot be approximated by a normal random variable because np does not exceed 5 (c) Suppose n = 43 and p = 0.20. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.) np = ng = Yes p can be approximated by a normal random variable because both np and nq exceed What are the values of u, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.) Hp =
Suppose we have a binomial experiment in which success is defined to be a particular quality or attribute that interests us. (a) Suppose n = 27 and p = 0.23. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.) np = 6.21 nq = 20.79 Yes be approximated by a normal random variable because np exceeds 5 can What are the values of u, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.) (b) Suppose n = 25 and p = 0.15. Can we safely approximate p by a normal distribution? Why or why not? No p cannot be approximated by a normal random variable because np does not exceed 5 (c) Suppose n = 43 and p = 0.20. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.) np = ng = Yes p can be approximated by a normal random variable because both np and nq exceed What are the values of u, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.) Hp =
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Suppose we have a binomial experiment in which success is defined to be a particular quality or attribute that interests us.
From part A I need help with the last blank:
Yes, p can be approximated by a normal random variable because (, np and nq do not exceed, nq exceeds, nq does not exceed, both np and nq exceed, np does not exceed) - np exceeds is incorrect for this blank
I need help with
What are the values of ?p̂ and ?p̂? (Use 3 decimal places.) - it is below the fill in the blank above
(c) Suppose n = 43 and p = 0.20. Can we approximate p̂ by a
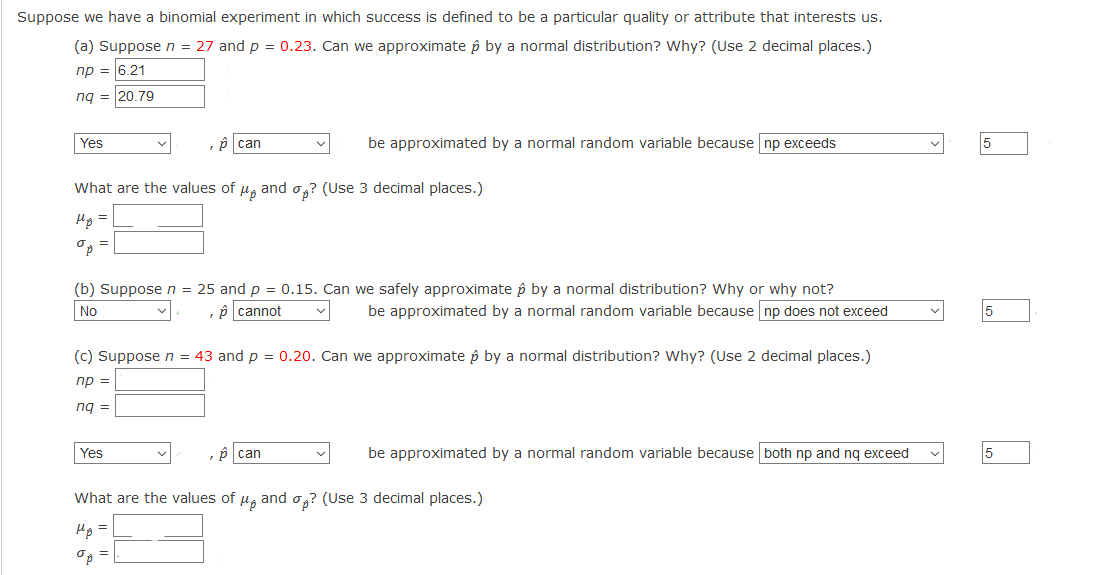
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose we have a binomial experiment in which success is defined to be a particular quality or attribute that interests us.
(a) Suppose n = 27 and p = 0.23. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.)
np = 6.21
ng = 20.79
Yes
p can
be approximated by a normal random variable because np exceeds
What are the values of u, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.)
Hg =
(b) Suppose n = 25 and p = 0.15. Can we safely approximate p by a normal distribution? Why or why not?
No
p cannot
be approximated by a normal random variable because np does not exceed
5
(c) Suppose n = 43 and p = 0.20. Can we approximate p by a normal distribution? Why? (Use 2 decimal places.)
np =
nq =
Yes
p can
be approximated by a normal random variable because both np and ng exceed
5
What are the values of µ, and o,? (Use 3 decimal places.)
Hp =
Op =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman