Suppose you have an experiment where you draw three cards (with replacement) from a standard deck of 52 cards. You then count the number of aces drawn. Use this experiment to address each of the following questions. Round solutions to four decimal places, if necessary. a) State the random variable. X = the number of aces observed when you draw three random cards ✓ b) Construct a probability distribution table for the number of aces obtained when three cards are randomly drawn (with replacement). Enter the c-values from smallest to largest. C P(x) 0 0.7865 1 0.1966 2 0.0164 3 0.0005 c) Determine the shape of the probability distribution of x. V The probability distribution of x is Right-skewed
Suppose you have an experiment where you draw three cards (with replacement) from a standard deck of 52 cards. You then count the number of aces drawn. Use this experiment to address each of the following questions. Round solutions to four decimal places, if necessary. a) State the random variable. X = the number of aces observed when you draw three random cards ✓ b) Construct a probability distribution table for the number of aces obtained when three cards are randomly drawn (with replacement). Enter the c-values from smallest to largest. C P(x) 0 0.7865 1 0.1966 2 0.0164 3 0.0005 c) Determine the shape of the probability distribution of x. V The probability distribution of x is Right-skewed
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 4ECP: Show that the probability of drawing a club at random from a standard deck of 52 playing cards is...
Related questions
Question
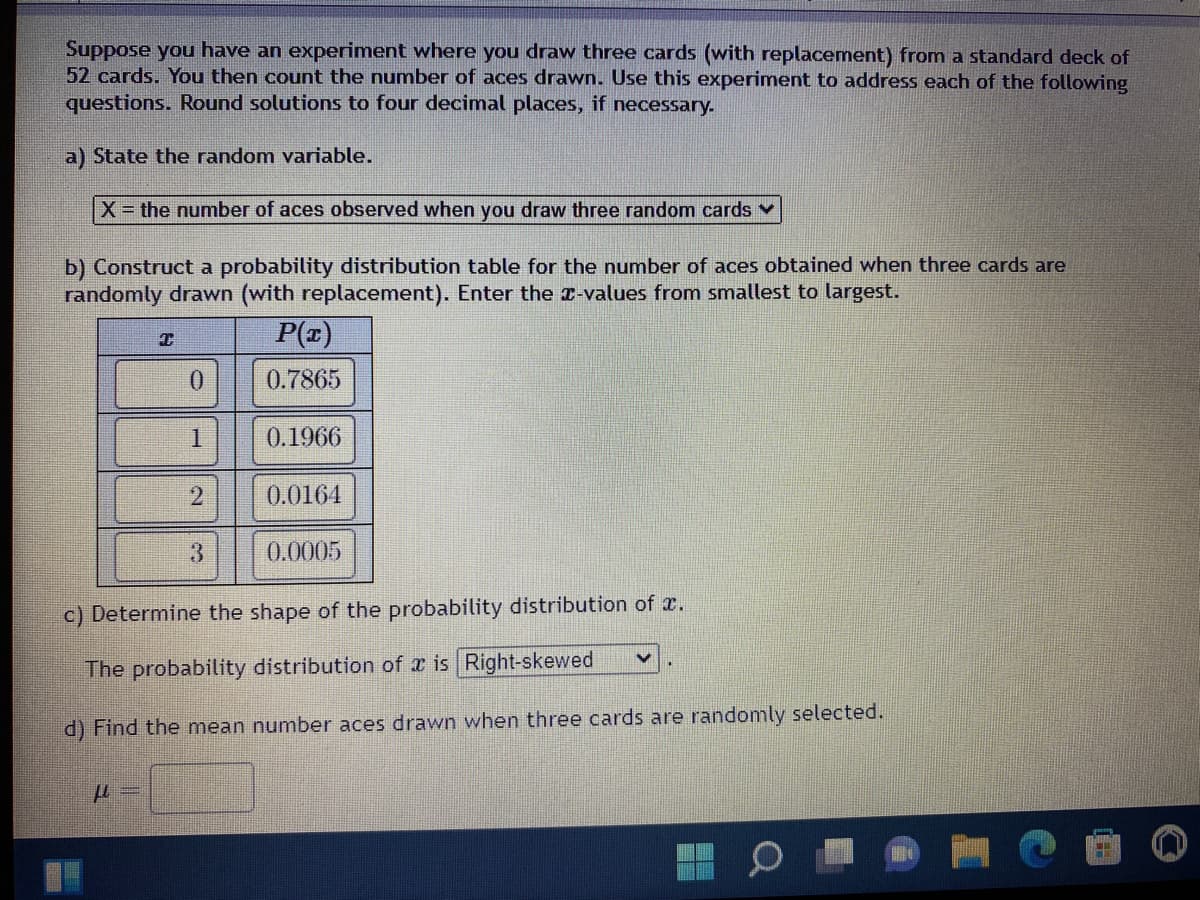
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose you have an experiment where you draw three cards (with replacement) from a standard deck of
52 cards. You then count the number of aces drawn. Use this experiment to address each of the following
questions. Round solutions to four decimal places, if necessary.
a) State the random variable.
X = the number of aces observed when you draw three random cards ✓
b) Construct a probability distribution table for the number of aces obtained when three cards are
randomly drawn (with replacement). Enter the x-values from smallest to largest.
T
P(x)
0
0.7865
1
0.1966
2
0.0164
3
0.0005
c) Determine the shape of the probability distribution of .
V
The probability distribution of x is Right-skewed
d) Find the mean number aces drawn when three cards are randomly selected.
μ=
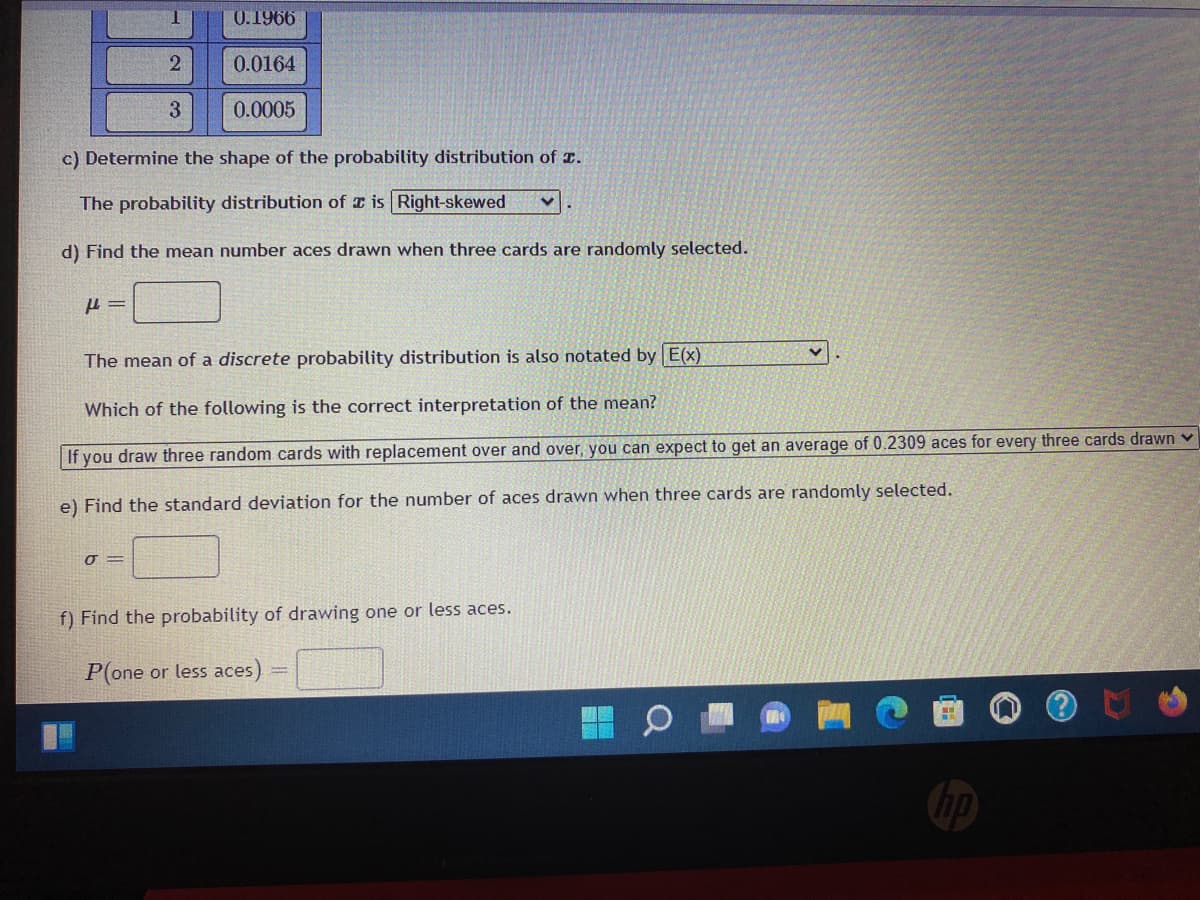
Transcribed Image Text:0.1966
2
0.0164
3
0.0005
c) Determine the shape of the probability distribution of .
The probability distribution of a is Right-skewed
d) Find the mean number aces drawn when three cards are randomly selected.
P=
The mean of a discrete probability distribution is also notated by E(x)
Which of the following is the correct interpretation of the mean?
If you draw three random cards with replacement over and over, you can expect to get an average of 0.2309 aces for every three cards drawn ✓
e) Find the standard deviation for the number of aces drawn when three cards are randomly selected.
0 =
f) Find the probability of drawing one or less aces.
P(one or less aces)
hp
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

