ter 10 em 15 15 of 24 > Part A A fuel cell differs from a battery because the current is being generated from a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which the reactant is consumed. A classic example of a fuel cell is the phosphoric acid fuel cell (PAFC), which have been used in stationary power generators, buses, and even submarines. Fuel cells require an electrolyte (similar to batteries) to carry electrically charged species between the electrodes, and a PAFC utilizes phosphoric acid (H3 PO4) as its electrolyte. The weak acid phosphoric acid has three acidic protons, highlighted in red here: H3 PO4. As a weak acid, some of the acid will remain in molecular form when dissolved in water. Write the net ionic equation that depicts the dissociation of the first proton including charges for any ions produced. Express you answer as net ionic equation including phases. View Available Hint(s) ΑΣφ ? Submit Net ionic equations for neutralization reactions Acids and bases can react with each other to form water, and that process is called neutralization. Net ionic equations are equations that depict only the reaction between participating ions. From the example in the introduction, if equal amounts (in moles) of HCI and NaOH were added to water, the acid and base would neutralize each other to form water and salt. The molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the neutralization between a strong acid and strong base are presented below. P Pearson Contact Us Permissions 2019 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved.| Terms of Use | Privacy Policy Copyright t
ter 10 em 15 15 of 24 > Part A A fuel cell differs from a battery because the current is being generated from a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which the reactant is consumed. A classic example of a fuel cell is the phosphoric acid fuel cell (PAFC), which have been used in stationary power generators, buses, and even submarines. Fuel cells require an electrolyte (similar to batteries) to carry electrically charged species between the electrodes, and a PAFC utilizes phosphoric acid (H3 PO4) as its electrolyte. The weak acid phosphoric acid has three acidic protons, highlighted in red here: H3 PO4. As a weak acid, some of the acid will remain in molecular form when dissolved in water. Write the net ionic equation that depicts the dissociation of the first proton including charges for any ions produced. Express you answer as net ionic equation including phases. View Available Hint(s) ΑΣφ ? Submit Net ionic equations for neutralization reactions Acids and bases can react with each other to form water, and that process is called neutralization. Net ionic equations are equations that depict only the reaction between participating ions. From the example in the introduction, if equal amounts (in moles) of HCI and NaOH were added to water, the acid and base would neutralize each other to form water and salt. The molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the neutralization between a strong acid and strong base are presented below. P Pearson Contact Us Permissions 2019 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved.| Terms of Use | Privacy Policy Copyright t
Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305264434
Author:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Chapter32: Voltaic Cell Measurements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2ASA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ter 10
em 15
15 of 24
>
Part A
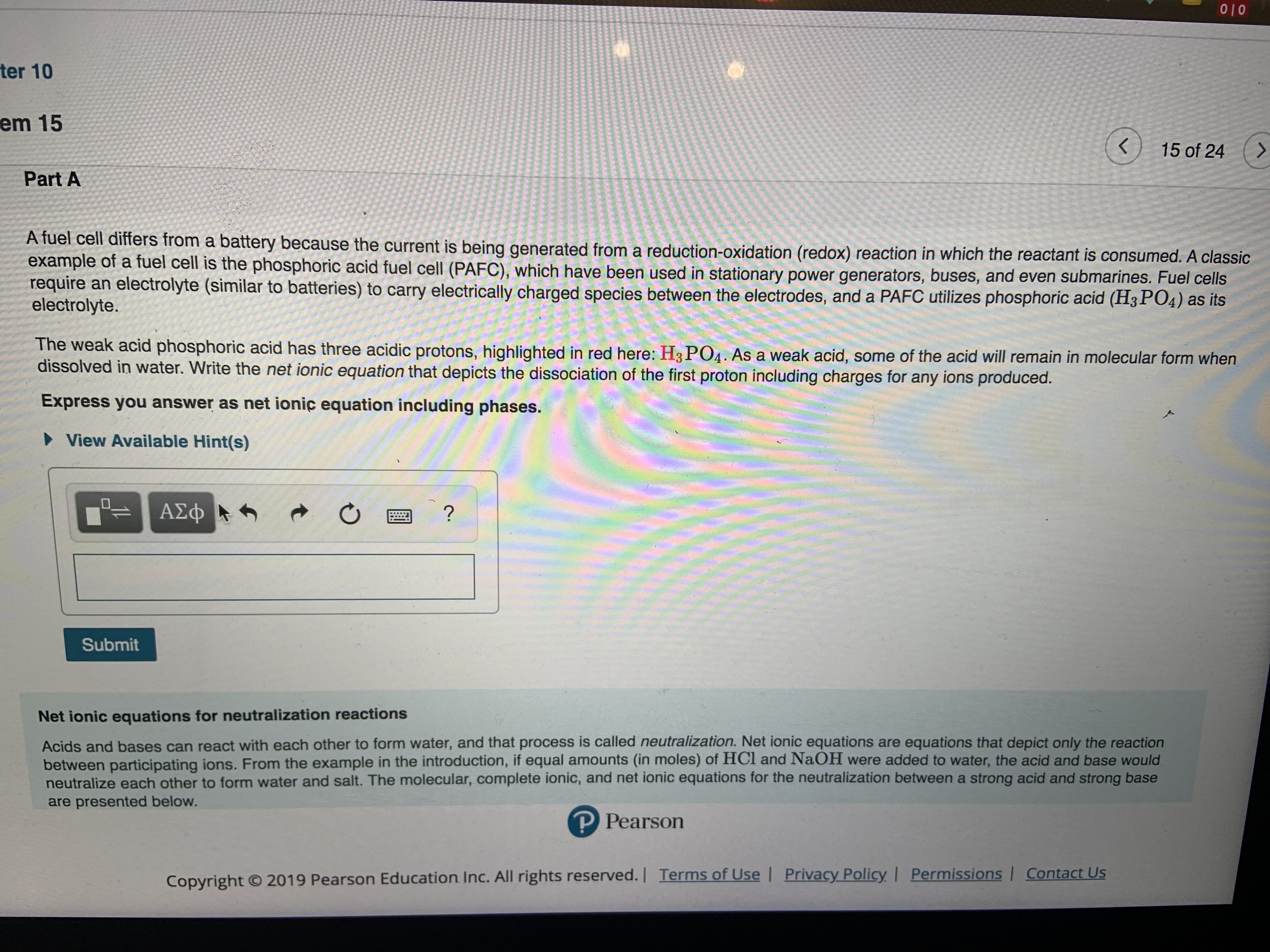
A fuel cell differs from a battery because the current is being generated from a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which the reactant is consumed. A classic
example of a fuel cell is the phosphoric acid fuel cell (PAFC), which have been used in stationary power generators, buses, and even submarines. Fuel cells
require an electrolyte (similar to batteries) to carry electrically charged species between the electrodes, and a PAFC utilizes phosphoric acid (H3 PO4) as its
electrolyte.
The weak acid phosphoric acid has three acidic protons, highlighted in red here: H3 PO4. As a weak acid, some of the acid will remain in molecular form when
dissolved in water. Write the net ionic equation that depicts the dissociation of the first proton including charges for any ions produced.
Express you answer as net ionic equation including phases.
View Available Hint(s)
ΑΣφ
?
Submit
Net ionic equations for neutralization reactions
Acids and bases can react with each other to form water, and that process is called neutralization. Net ionic equations are equations that depict only the reaction
between participating ions. From the example in the introduction, if equal amounts (in moles) of HCI and NaOH were added to water, the acid and base would
neutralize each other to form water and salt. The molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the neutralization between a strong acid and strong base
are presented below.
P Pearson
Contact Us
Permissions
2019 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved.| Terms of Use | Privacy Policy
Copyright
t
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Step 1
VIEWTrending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 1 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemical Principles in the Laboratory
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305264434
Author:
Emil Slowinski, Wayne C. Wolsey, Robert Rossi
Publisher:
Brooks Cole

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
