The amino group can be protonated (that is, it has an extra proton attached) in a strongly acidic solution. This produces a diprotic acid of the form as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine. H2A+, as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine.
The amino group can be protonated (that is, it has an extra proton attached) in a strongly acidic solution. This produces a diprotic acid of the form as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine. H2A+, as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine.
Chapter14: Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10RQ: For oxyacids, how does acid strength depend on a. the strength of the bond to the acidic hydrogen...
Related questions
Question
this question also please help. this topic is very difficult for me
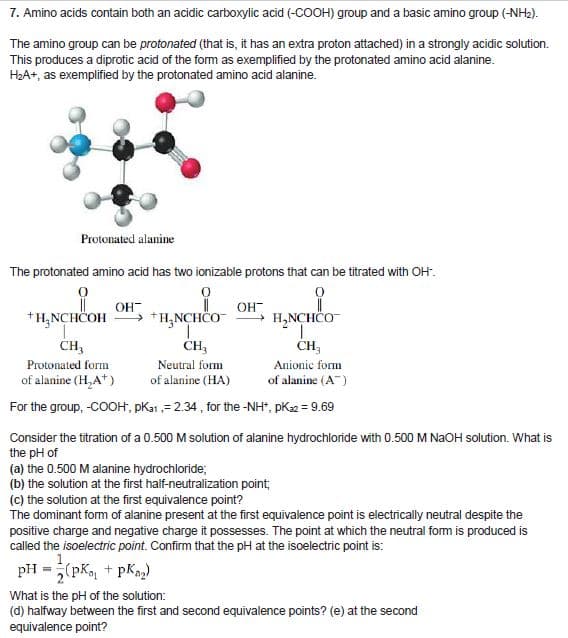
Transcribed Image Text:7. Amino acids contain both an acidic carboxylic acid (-COOH) group and a basic amino group (-NH2).
The amino group can be protonated (that is, it has an extra proton attached) in a strongly acidic solution.
This produces a diprotic acid of the form as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine.
H2A+, as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine.
Protonated alanine
The protonated amino acid has two ionizable protons that can be titrated with OH".
OH
+H;NCHČOH
OH
+H,NCHCO
+ H,NCHČO
CH,
CH,
CH;
Protonated form
Neutral form
Anionic form
of alanine (H,A*)
of alanine (HA)
of alanine (A)
For the group, -COOH, pKa1,= 2.34, for the -NH", pK2 = 9.69
Consider the titration of a 0.500 M solution of alanine hydrochloride with 0.500 M NAOH solution. What is
the pH of
(a) the 0.500 M alanine hydrochloride;
(b) the solution at the first half-neutralization point;
(c) the solution at the first equivalence point?
The dominant form of alanine present at the first equivalence point is electrically neutral despite the
positive charge and negative charge it possesses. The point at which the neutral form is produced is
called the isoelectric point. Confirm that the pH at the isoelectric point is:
pH =(pK, + pKaz)
What is the pH of the solution:
(d) halfway between the first and second equivalence points? (e) at the second
equivalence point?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning