The mean weight of a fire ant worker is 3.11 mg with a standard deviation of 0.49 mg. Let us assume that the weight of any fire ant is independent from the weight of any other fire ant. A typical fire ant colony contains 240,000 fire ant workers. Suppose we look at the weight of each ant in a typical fire ant colony. Let M be the random variable representing the mean weight of all the worker ants in the colony in mg. Let T = the random variable representing the sum of the weights of all the worker ants in the colony in mg. a) What theorem will let us treat T and M as approximately normal random variables? Chebychev's Theorem Law of Large Numbers Convolution Theorem Central Limit Theorem Monte Carlo Theorem b) What is the expected value of T? c) What is the standard deviation of T? d) If TK is T measured in grams (use 1g = 1000mg.), then what is the standard deviation of TK? e) What is the approximate probability that T is greater than 747000? f) What is the standard deviation of M? g) What is the approximate probability M is between 3.111 and 3.112? h) What is the approximate probability that T is within 2 standard deviations of its expected value?
The mean weight of a fire ant worker is 3.11 mg with a standard deviation of 0.49 mg. Let us assume that the weight of any fire ant is independent from the weight of any other fire ant. A typical fire ant colony contains 240,000 fire ant workers. Suppose we look at the weight of each ant in a typical fire ant colony. Let M be the random variable representing the mean weight of all the worker ants in the colony in mg. Let T = the random variable representing the sum of the weights of all the worker ants in the colony in mg.
a) What theorem will let us treat T and M as approximately normal random variables?
b) What is the
c) What is the standard deviation of T?
d) If TK is T measured in grams (use 1g = 1000mg.), then what is the standard deviation of TK?
e) What is the approximate probability that T is greater than 747000?
f) What is the standard deviation of M?
g) What is the approximate probability M is between 3.111 and 3.112?
h) What is the approximate probability that T is within 2 standard deviations of its expected value?
Hello. Since your question has multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts for you. If you want remaining sub-parts to be solved, then please resubmit the whole question and specify those sub-parts you want us to solve.
The provided data is,
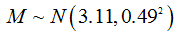
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images




