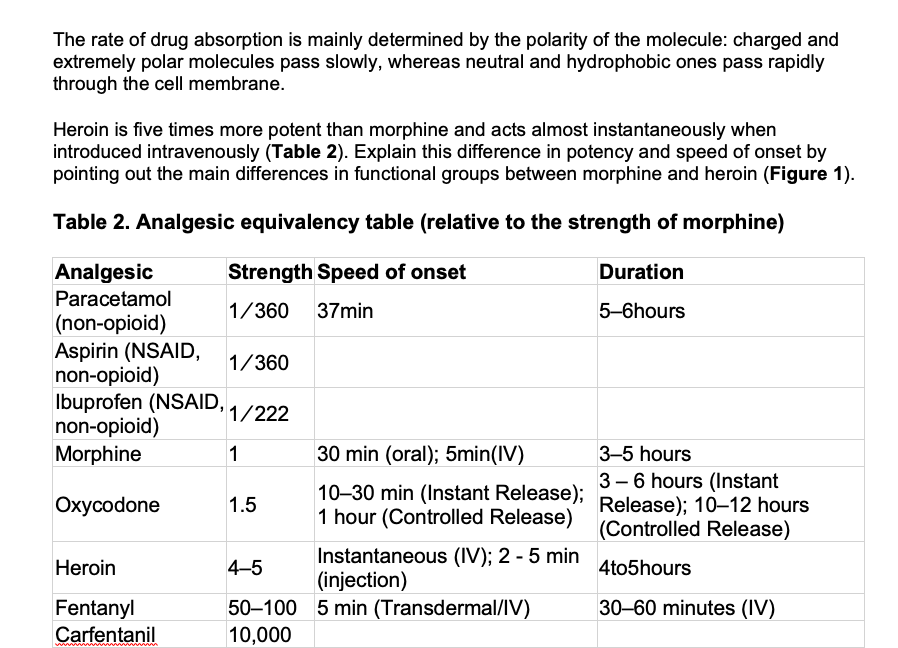
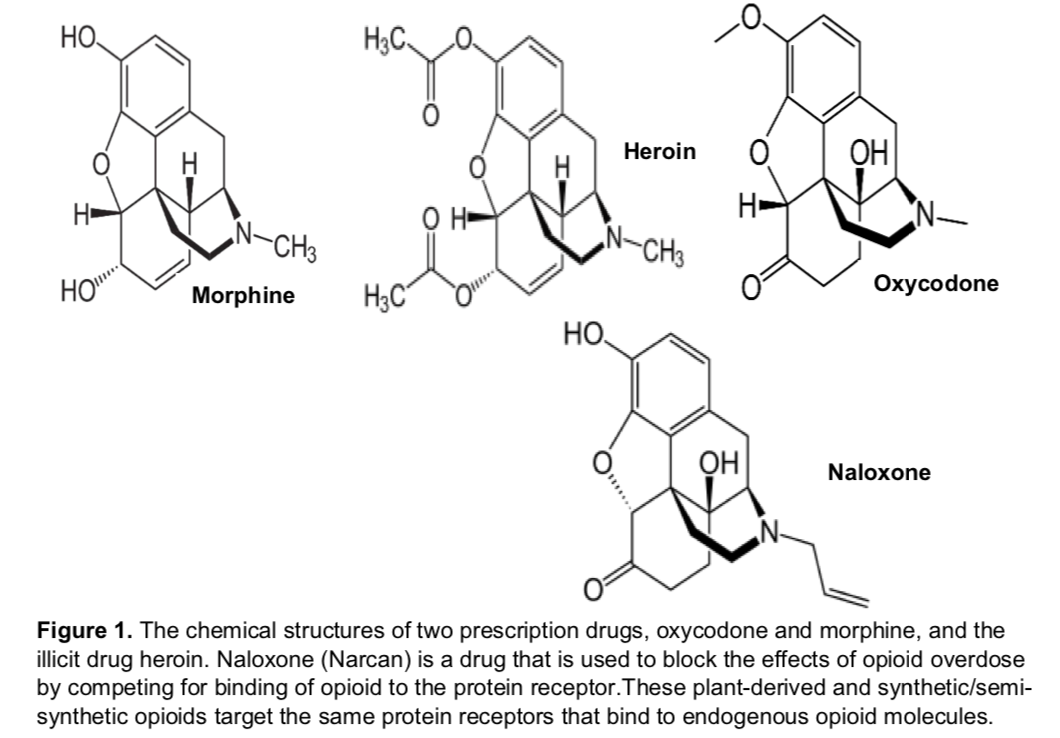
The rate of drug absorption is mainly determined by the polarity of the molecule: charged and extremely polar molecules pass slowly, whereas neutral and hydrophobic ones pass rapidly through the cell membrane. Heroin is five times more potent than morphine and acts almost instantaneously when introduced intravenously (Table 2). Explain this difference in potency and speed of onset by pointing out the main differences in functional groups between morphine and heroin (Figure 1) Table 2. Analgesic equivalency table (relative to the strength of morphine) Strength Speed of onset Analgesic Duration Paracetamol 1/360 37min 5-6hours (non-opioid) Aspirin (NSAID, non-opioid) Ibuprofen (NSAID, 1/222 non-opioid) 1/360 30 min (oral); 5min(IV) 3-5 hours Morphine 1 3-6 hours (Instant 10-30 min (Instant Release); Release); 10-12 hours Охусodone 1.5 1 hour (Controlled Release)(Controlled Release) Instantaneous (IV); 2 -5 min (injection) 4to5hours Heroin 4-5 50-100 5 min (Transdermal/IV) 10,000 30-60 minutes (IV) Fentanyl Carfentanil НО. HаС о ОН Heroin H H Ни N- На H N-CHs CH3 Охусodone Hас Ноне Morphine НО. ОН Naloxone Figure 1. The chemical structures of two prescription drugs, oxycodone and morphine, and the illicit drug heroin. Naloxone (Narcan) is a drug that is used to block the effects of opioid overdose by competing for binding of opioid to the protein receptor.These plant-derived and synthetic/semi- synthetic opioids target the same protein receptors that bind to endogenous opioid molecules.
The rate of drug absorption is mainly determined by the polarity of the molecule: charged and extremely polar molecules pass slowly, whereas neutral and hydrophobic ones pass rapidly through the cell membrane. Heroin is five times more potent than morphine and acts almost instantaneously when introduced intravenously (Table 2). Explain this difference in potency and speed of onset by pointing out the main differences in functional groups between morphine and heroin (Figure 1) Table 2. Analgesic equivalency table (relative to the strength of morphine) Strength Speed of onset Analgesic Duration Paracetamol 1/360 37min 5-6hours (non-opioid) Aspirin (NSAID, non-opioid) Ibuprofen (NSAID, 1/222 non-opioid) 1/360 30 min (oral); 5min(IV) 3-5 hours Morphine 1 3-6 hours (Instant 10-30 min (Instant Release); Release); 10-12 hours Охусodone 1.5 1 hour (Controlled Release)(Controlled Release) Instantaneous (IV); 2 -5 min (injection) 4to5hours Heroin 4-5 50-100 5 min (Transdermal/IV) 10,000 30-60 minutes (IV) Fentanyl Carfentanil НО. HаС о ОН Heroin H H Ни N- На H N-CHs CH3 Охусodone Hас Ноне Morphine НО. ОН Naloxone Figure 1. The chemical structures of two prescription drugs, oxycodone and morphine, and the illicit drug heroin. Naloxone (Narcan) is a drug that is used to block the effects of opioid overdose by competing for binding of opioid to the protein receptor.These plant-derived and synthetic/semi- synthetic opioids target the same protein receptors that bind to endogenous opioid molecules.
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter23: Amines
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 23.21P
Related questions
Question
Explain this difference in potency and speed of onset by pointing out the main differences in
Transcribed Image Text:The rate of drug absorption is mainly determined by the polarity of the molecule: charged and
extremely polar molecules pass slowly, whereas neutral and hydrophobic ones pass rapidly
through the cell membrane.
Heroin is five times more potent than morphine and acts almost instantaneously when
introduced intravenously (Table 2). Explain this difference in potency and speed of onset by
pointing out the main differences in functional groups between morphine and heroin (Figure 1)
Table 2. Analgesic equivalency table (relative to the strength of morphine)
Strength Speed of onset
Analgesic
Duration
Paracetamol
1/360
37min
5-6hours
(non-opioid)
Aspirin (NSAID,
non-opioid)
Ibuprofen (NSAID, 1/222
non-opioid)
1/360
30 min (oral); 5min(IV)
3-5 hours
Morphine
1
3-6 hours (Instant
10-30 min (Instant Release); Release); 10-12 hours
Охусodone
1.5
1 hour (Controlled Release)(Controlled Release)
Instantaneous (IV); 2 -5 min
(injection)
4to5hours
Heroin
4-5
50-100 5 min (Transdermal/IV)
10,000
30-60 minutes (IV)
Fentanyl
Carfentanil
Transcribed Image Text:НО.
HаС
о
ОН
Heroin
H
H
Ни
N-
На
H
N-CHs
CH3
Охусodone
Hас
Ноне
Morphine
НО.
ОН
Naloxone
Figure 1. The chemical structures of two prescription drugs, oxycodone and morphine, and the
illicit drug heroin. Naloxone (Narcan) is a drug that is used to block the effects of opioid overdose
by competing for binding of opioid to the protein receptor.These plant-derived and synthetic/semi-
synthetic opioids target the same protein receptors that bind to endogenous opioid molecules.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305081079
Author:
STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning