To understand the dynamics of a series R-C circuit. Consider a series circuit containing a resistor of resistance R and a capacitor of capacitance C connected to a source of EMF & with negligible internal resistance. The wires are also assumed to have zero resistance. Initially, the switch is open and the capacitor discharged. (Figure 1) Let us try to understand the processes that take place after the switch is closed. The charge of the capacitor, the current in the circuit, and, correspondingly, the voltages across the resistor and the capacitor will be changing. Note that at any moment in time during the life of our circuit, Kirchhoff's loop rule holds and, indeed, it is helpful: - VR - Vc = 0. where VR is the voltage across the resistor and Vc is the voltage across the capacitor. Figure R ww i=0 C=40=0 1 of 1 Submit Previous Answere ✓ Correct ▾ Part F In the steady state, what is the charge q of the capacitor? Express your answer in terms of any or all of E, R. and C. ▸ ▸ View Available Hint(s) q= Submit ▾ Part G fe Parts for PS do for Part redo foart F refor Part F keyboard shortcuts for Part F help for Part F How much work W is done by the voltage source by the time the steady state is reached? Express your answer in terms of any or all of E. R. and C. ▸ View Available Hint(s) W = for Part for Part Go for Part&redo forrt Gres VAC Submit Provide Feedback Part G keyboard shortcuts for Part G help for Part G
To understand the dynamics of a series R-C circuit. Consider a series circuit containing a resistor of resistance R and a capacitor of capacitance C connected to a source of EMF & with negligible internal resistance. The wires are also assumed to have zero resistance. Initially, the switch is open and the capacitor discharged. (Figure 1) Let us try to understand the processes that take place after the switch is closed. The charge of the capacitor, the current in the circuit, and, correspondingly, the voltages across the resistor and the capacitor will be changing. Note that at any moment in time during the life of our circuit, Kirchhoff's loop rule holds and, indeed, it is helpful: - VR - Vc = 0. where VR is the voltage across the resistor and Vc is the voltage across the capacitor. Figure R ww i=0 C=40=0 1 of 1 Submit Previous Answere ✓ Correct ▾ Part F In the steady state, what is the charge q of the capacitor? Express your answer in terms of any or all of E, R. and C. ▸ ▸ View Available Hint(s) q= Submit ▾ Part G fe Parts for PS do for Part redo foart F refor Part F keyboard shortcuts for Part F help for Part F How much work W is done by the voltage source by the time the steady state is reached? Express your answer in terms of any or all of E. R. and C. ▸ View Available Hint(s) W = for Part for Part Go for Part&redo forrt Gres VAC Submit Provide Feedback Part G keyboard shortcuts for Part G help for Part G
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter21: Circuits And Dc Instruments
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 33CQ: Draw two graphs of charge versus time on a capacitor. Draw one for charging an initially uncharged...
Related questions
Question
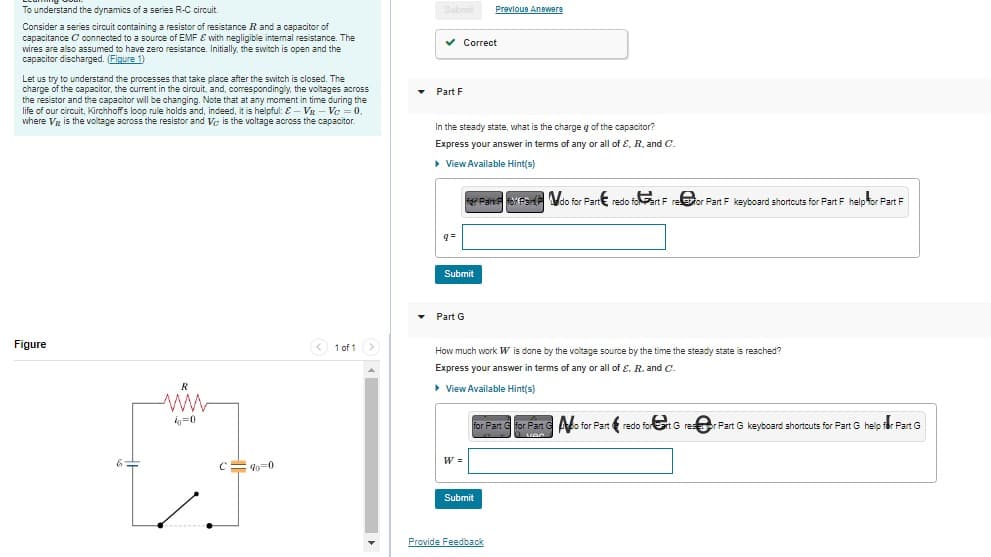
Transcribed Image Text:To understand the dynamics of a series R-C circuit.
Consider a series circuit containing a resistor of resistance R and a capacitor of
capacitance C connected to a source of EMF & with negligible internal resistance. The
wires are also assumed to have zero resistance. Initially, the switch is open and the
capacitor discharged. (Figure 1)
Let us try to understand the processes that take place after the switch is closed. The
charge of the capacitor, the current in the circuit, and, correspondingly, the voltages across
the resistor and the capacitor will be changing. Note that at any moment in time during the
life of our circuit, Kirchhoff's loop rule holds and, indeed, it is helpful: - VR - Vc = 0.
where VR is the voltage across the resistor and Vc is the voltage across the capacitor.
Figure
R
ww
i=0
C=40=0
1 of 1
Submit Previous Answere
✓ Correct
▾ Part F
In the steady state, what is the charge q of the capacitor?
Express your answer in terms of any or all of E, R. and C.
▸
▸ View Available Hint(s)
q=
Submit
▾ Part G
fe Parts for PS do for Part redo foart F refor Part F keyboard shortcuts for Part F help for Part F
How much work W is done by the voltage source by the time the steady state is reached?
Express your answer in terms of any or all of E. R. and C.
▸ View Available Hint(s)
W =
for Part for Part Go for Part&redo forrt Gres
VAC
Submit
Provide Feedback
Part G keyboard shortcuts for Part G help for Part G
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 19.57
A fully charged 8.0 μP capacitor is connected in series with a 1.8x10 12 resistor
Part A
What percentage of the original charge is left on the capacitor after 1.7 s of discharging?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
F Parts for Pan do for Part redo foart A refor Part A keyboard shortcuts for Part A help for Part A
Submit
Request Answer
< Return to Assignment
Provide Feedback
%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning