Transaction costs In late December you decide, for tax purposes, to sell a losing position that you hold in Twitter, which is listed on the NYSE, so that you can capture the loss and use it to offset some capital gains, thus reducing your taxes for the current year. However, since you still believe that Twitter is a good long-term investment, you wish to buy back your position in February the following year. To get this done you call your Charles Schwab brokerage account manager and request that he immediately sell your 1,200 shares of Twitter and then in early February buy them back. CharlesSchwab charges a commission of 54.95 for online stock trades and for broker-assisted trades there is an additional $25 service charge, so the total commission is $29.95 a. Suppose that your total transaction costs for selling the 1,200 shares of Twitter in December were 559.95. What was the bidlask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed? b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not. c. When your February statement arrives in the mail, you see that your total transaction costs for buying the 1,200 shares of Twitter were $47.95. What was the bid/ask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed? d. What are your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares, and what could you have done differently to reduce the total costs? a. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0500. (Round to the nearest cent) b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not. Twitter is listed on the NYSE, a broker market So, had Charles Schwab routed the order to the NYSE, it could have been executed against a buy order, and total transaction costs would have been only the $29.95 brokerage commission. But transaction costs included half the bid/ask spread per share traded, so either: 0) the order went to the NYSE, no public buy order was available, and the market maker bought the 1,200 shares for her inventory (at a cost of half the bid/ask spread per share) or (ii) Charles Schwab routed the order to a dealer market like NASDAQ, and a market maker added the shares to he inventory (at half the spread per share)." This statement is true (Select the best answer from the drop-down menu.) c. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0300. (Round to the nearest cent) d. Your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares is S 107.90. (Round to the nearest cent.) What could you have done differently to reduce the total costs? (Select the best answer below.) OA. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $29.95 Schwab commission per trade. XB. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chanoe of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs ould have been only the S25 Schwab commission per trade. C Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $4.95 Schwab commission per trade. 0 D. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades with a market maker. Had no online trades been necessary, total costs would have been only the S4.95 Schwab commission per trade.
Transaction costs In late December you decide, for tax purposes, to sell a losing position that you hold in Twitter, which is listed on the NYSE, so that you can capture the loss and use it to offset some capital gains, thus reducing your taxes for the current year. However, since you still believe that Twitter is a good long-term investment, you wish to buy back your position in February the following year. To get this done you call your Charles Schwab brokerage account manager and request that he immediately sell your 1,200 shares of Twitter and then in early February buy them back. CharlesSchwab charges a commission of 54.95 for online stock trades and for broker-assisted trades there is an additional $25 service charge, so the total commission is $29.95 a. Suppose that your total transaction costs for selling the 1,200 shares of Twitter in December were 559.95. What was the bidlask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed? b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not. c. When your February statement arrives in the mail, you see that your total transaction costs for buying the 1,200 shares of Twitter were $47.95. What was the bid/ask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed? d. What are your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares, and what could you have done differently to reduce the total costs? a. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0500. (Round to the nearest cent) b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not. Twitter is listed on the NYSE, a broker market So, had Charles Schwab routed the order to the NYSE, it could have been executed against a buy order, and total transaction costs would have been only the $29.95 brokerage commission. But transaction costs included half the bid/ask spread per share traded, so either: 0) the order went to the NYSE, no public buy order was available, and the market maker bought the 1,200 shares for her inventory (at a cost of half the bid/ask spread per share) or (ii) Charles Schwab routed the order to a dealer market like NASDAQ, and a market maker added the shares to he inventory (at half the spread per share)." This statement is true (Select the best answer from the drop-down menu.) c. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0300. (Round to the nearest cent) d. Your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares is S 107.90. (Round to the nearest cent.) What could you have done differently to reduce the total costs? (Select the best answer below.) OA. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $29.95 Schwab commission per trade. XB. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chanoe of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs ould have been only the S25 Schwab commission per trade. C Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $4.95 Schwab commission per trade. 0 D. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades with a market maker. Had no online trades been necessary, total costs would have been only the S4.95 Schwab commission per trade.
SWFT Essntl Tax Individ/Bus Entities 2020
23rd Edition
ISBN:9780357391266
Author:Nellen
Publisher:Nellen
Chapter3: Taxes On The Financial Statements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6RP
Related questions
Question
Despite having the correct answers just wanted to ge explanations for eveything.
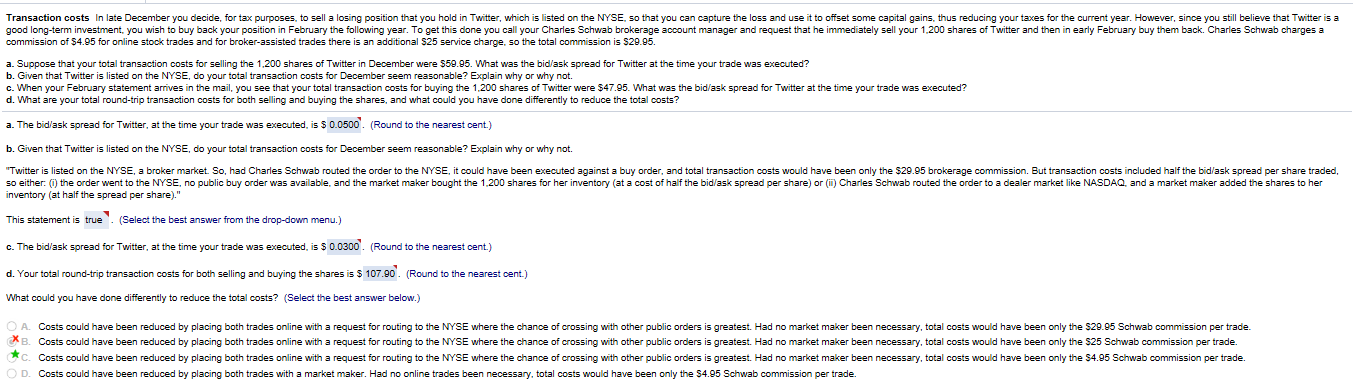
Transcribed Image Text:Transaction costs In late December you decide, for tax purposes, to sell a losing position that you hold in Twitter, which is listed on the NYSE, so that you can capture the loss and use it to offset some capital gains, thus reducing your taxes for the current year. However, since you still believe that Twitter is a
good long-term investment, you wish to buy back your position in February the following year. To get this done you call your Charles Schwab brokerage account manager and request that he immediately sell your 1,200 shares of Twitter and then in early February buy them back. CharlesSchwab charges a
commission of 54.95 for online stock trades and for broker-assisted trades there is an additional $25 service charge, so the total commission is $29.95
a. Suppose that your total transaction costs for selling the 1,200 shares of Twitter in December were 559.95. What was the bidlask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed?
b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not.
c. When your February statement arrives in the mail, you see that your total transaction costs for buying the 1,200 shares of Twitter were $47.95. What was the bid/ask spread for Twitter at the time your trade was executed?
d. What are your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares, and what could you have done differently to reduce the total costs?
a. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0500. (Round to the nearest cent)
b. Given that Twitter is listed on the NYSE, do your total transaction costs for December seem reasonable? Explain why or why not.
Twitter is listed on the NYSE, a broker market So, had Charles Schwab routed the order to the NYSE, it could have been executed against a buy order, and total transaction costs would have been only the $29.95 brokerage commission. But transaction costs included half the bid/ask spread per share traded,
so either: 0) the order went to the NYSE, no public buy order was available, and the market maker bought the 1,200 shares for her inventory (at a cost of half the bid/ask spread per share) or (ii) Charles Schwab routed the order to a dealer market like NASDAQ, and a market maker added the shares to he
inventory (at half the spread per share)."
This statement is true (Select the best answer from the drop-down menu.)
c. The bid/ask spread for Twitter, at the time your trade was executed, is $ 0.0300. (Round to the nearest cent)
d. Your total round-trip transaction costs for both selling and buying the shares is S 107.90. (Round to the nearest cent.)
What could you have done differently to reduce the total costs? (Select the best answer below.)
OA. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $29.95 Schwab commission per trade.
XB. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chanoe of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs ould have been only the S25 Schwab commission per trade.
C Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades online with a request for routing to the NYSE where the chance of crossing with other public orders is greatest. Had no market maker been necessary, total costs would have been only the $4.95 Schwab commission per trade.
0 D. Costs could have been reduced by placing both trades with a market maker. Had no online trades been necessary, total costs would have been only the S4.95 Schwab commission per trade.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning