Two lakes are connected to each other as shown in the figure below. Each lake has a volume of 106 m³ and an initial concentration of 10 g/m³. Lake 1 receives an inflow of 105 m³/day and a concentration of 100 g/m³. In addition to the Lake 1 outflow, Lake 2 receives an inflow of 1x105 m³/day with a concentration of 100 g/m³. The chemical undergoes first-order decay with a rate constant of 0.1 /day. (i) Calculate the steady-state concentrations (in g/m³) in the effluent from the lakes. (Include the mass balance equations in your solution.)
Two lakes are connected to each other as shown in the figure below. Each lake has a volume of 106 m³ and an initial concentration of 10 g/m³. Lake 1 receives an inflow of 105 m³/day and a concentration of 100 g/m³. In addition to the Lake 1 outflow, Lake 2 receives an inflow of 1x105 m³/day with a concentration of 100 g/m³. The chemical undergoes first-order decay with a rate constant of 0.1 /day. (i) Calculate the steady-state concentrations (in g/m³) in the effluent from the lakes. (Include the mass balance equations in your solution.)
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter11: Rate Of Reaction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 81QAP: The hypothetical reaction QR+Xproductswas monitored at 27C as a function of time. The following...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:2)
Two lakes are connected to each other as shown in the figure below. Each lake
has a volume of 106 m³ and an initial concentration of 10 g/m³. Lake 1 receives
an inflow of 105 m³/day and a concentration of 100 g/m³. In addition to the Lake
1 outflow, Lake 2 receives an inflow of 1x105 m³/day with a concentration of 100
g/m³. The chemical undergoes first-order decay with a rate constant of 0.1 /day.
(i)
Calculate the steady-state concentrations (in g/m³) in the effluent from the
lakes. (Include the mass balance equations in your solution.)
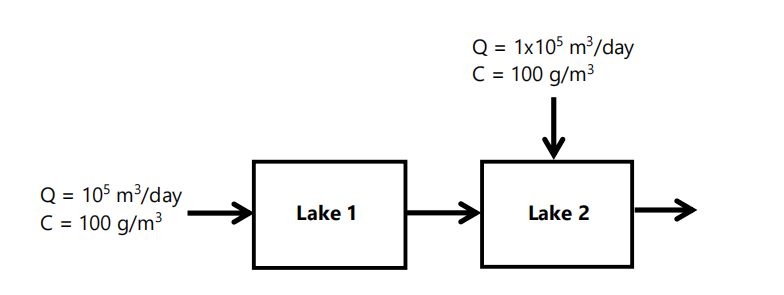
Transcribed Image Text:Q = 105 m³/day
C = 100 g/m³
Lake 1
Q = 1x105 m³/day
C = 100 g/m³
Lake 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning