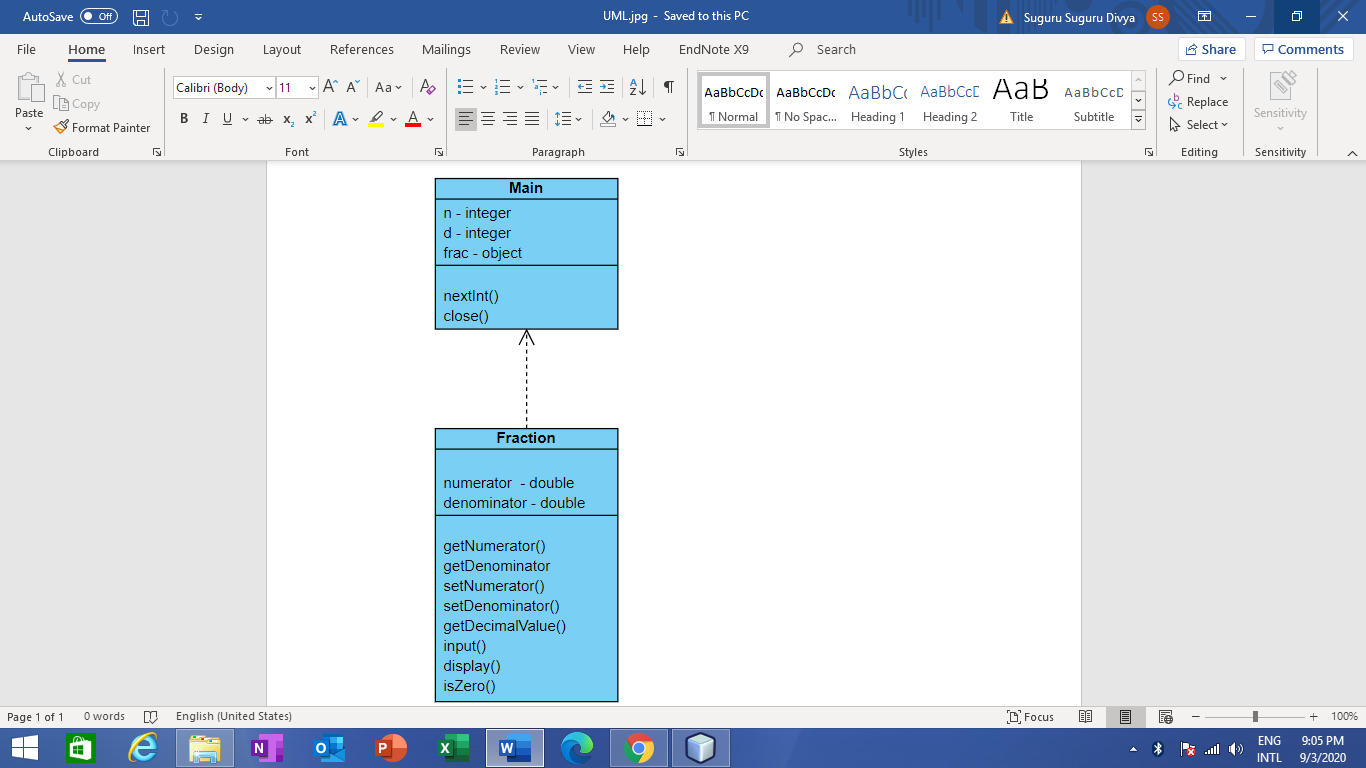
UML class diagram from
Update UML class diagram from the program below to include from the following program.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Fraction
{
private int n, d;
public Fraction()
{
this.n = this.d = 0;
}
public Fraction(int n, int d)
{
this.n = n;
this.d = d;
}
public int getNum()
{
return n;
}
public int getDen()
{
return d;
}
public boolean isZero()
{
return(getNum() == 0 && getDen() != 0);
}
public boolean isequals(Object c)
{
Fraction f = (Fraction) c;
return(Integer.compare(n,f.n))==0 && (Integer.compare(d,f.d)==0);
}
public String getSimplifiedFraction()
{
String result = "";
if(getNum() == 0 && getDen() == 0)
result = "0";
else if(isZero())
result = "0";
else if(getNum() != 0 && getDen() == 0)
result = "Undefined";
else
{
if(getNum() % getDen() == 0)
result = (getNum() / getDen()) + "";
else if(getNum() < 0 && getDen() < 0)
result = (getNum() * -1) + "/" + (getDen() * -1);
else if(getNum() < 0 || getDen() < 0)
{
if(getNum() < 0)
result = "-" + (getNum() * -1) + "/" + getDen(); // appending a sign.
else
result = "-" + getNum() + "/" + (getDen() * -1); // appending a sign.
}
else
result = (getNum() + "/" + getDen());
}
return result;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println(getSimplifiedFraction());
}
public Fraction add(Fraction rhs) {
Fraction sum = new Fraction();
sum.d = d * rhs.d;
sum.n = n * rhs.d + d * rhs.n;
sum.simplify();
return sum;
}
private void simplify()
{
int a,b;
if(Math.abs(n) > Math.abs(d))
{
a = Math.abs(n);
b = Math.abs(d);
}
else
{
a = Math.abs(d);
b = Math.abs(n);
}
int r = a%b;
while(r != 0)
{
a = b;
b = r;
r = a%b;
}
n /= b;
d /= b;
}
}
class TestFraction
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String res;
int num, den, num1, den1;
ArrayList<Fraction> fractions = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
do
{
System.out.print("Enter the num: ");
num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if(num < 0)
break;
System.out.print("Enter the den: ");
den = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
Fraction fraction = new Fraction(num, den);
System.out.print("Enter the num to compare: ");
num1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if(num1 < 0)
break;
System.out.print("Enter the den to compare: ");
den1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
Fraction fraction1 = new Fraction(num1, den1);
if(fraction1.isequals(fraction))
{
System.out.println("\nTrue-> Second fraction is equal to First Fraction");
}
else
System.out.println("\nFalse-> Second fraction is not equal to First Fraction");
fractions.add(fraction);
res = fraction.getSimplifiedFraction();
System.out.println("Fraction added to list as: " + res + "\n"); //result is stored in ‘res’ variable
}while(res != "0");
System.out.println("\nDISPLAYING ALL FRACTIONS:\n" + "-------------------------");
for(Fraction fr : fractions)
fr.display();
System.out.println();
sc.close();
Fraction f = new Fraction(4, 8);
System.out.println("1st fraction: ");
f.display();
Fraction fc = new Fraction(8, 24);
System.out.println("2nd fraction: ");
fc.display();
Fraction res1 = f.add(fc);
System.out.println("Sum: ");
res1.display();
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
class TestMain {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args)
{
do
{
Fraction fraction = takeFractionValues();
if (!fraction.isZero())
{
System.out.println("\nEnter Second Fraction Details: ");
Fraction fraction1 = takeFractionValues();
System.out.println(fraction + " AND " + fraction1);
if (fraction1.isEquals(fraction)) {
System.out.println("\nTrue-> Both Fractions are Equal");
} else
System.out.println("\nFalse-> Both Fractions are not Equal");
Fraction result = fraction.add(fraction1);
result.simplify();
System.out.println("Result of Both Fraction Addition: " + result);
} else
break;
System.out.println("\nEnter First fraction as Zero Fraction to end the Loop");
}
while (true);
System.out.println("\n\nFinished Working with Fractions...");
}
public static Fraction takeFractionValues() {
int num, denom;
System.out.print("Enter the num: ");
num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
while (true) {
String append = "";
System.out.print("Enter the den "+append+": ");
denom = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if (denom == 0) {
System.out.println("Denominator can't be zero");
append = "again";
} else
break;
}
return new Fraction(num, denom);
}
}
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images


