ure of 40 mol% benzene and 60 mol% ethylene dichloride in a distillation column with a partial reboiler and a total condenser. The feed rate is 750 mol/h, and feed is a saturated vapor. We desire a distillate product of 99.2 mol % benzene and a bottoms product that is 0.5 mol % benzene. Reflux is a saturated liquid, and CMO can be used. Equilibrium data can be approximated with an average relative volatility of 1.11 (benzene is more volatile). Note: You could also use (check) Raoult's Law modeling for the system as another source of equilibrium information. ) Find the minimum external reflux ratio. ) Use the Fenske equation to find the number of stages required at total reflux. :) Estimate the total number of stages required for this separation, using the Gilliland correlation for R = 1.2 Rmin.
ure of 40 mol% benzene and 60 mol% ethylene dichloride in a distillation column with a partial reboiler and a total condenser. The feed rate is 750 mol/h, and feed is a saturated vapor. We desire a distillate product of 99.2 mol % benzene and a bottoms product that is 0.5 mol % benzene. Reflux is a saturated liquid, and CMO can be used. Equilibrium data can be approximated with an average relative volatility of 1.11 (benzene is more volatile). Note: You could also use (check) Raoult's Law modeling for the system as another source of equilibrium information. ) Find the minimum external reflux ratio. ) Use the Fenske equation to find the number of stages required at total reflux. :) Estimate the total number of stages required for this separation, using the Gilliland correlation for R = 1.2 Rmin.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
Solve this problem.
An example of the calculation is provided.

Transcribed Image Text:1) Distillation of a binary mixture and comparisons of methods.
We wish to separate a mixture of 40 mol % benzene and 60 mol% ethylene dichloride in a distillation
column with a partial reboiler and a total condenser. The feed rate is 750 mol/h, and feed is a saturated
vapor. We desire a distillate product of 99.2 mol % benzene and a bottoms product that is 0.5 mol % benzene.
Reflux is a saturated liquid, and CMO can be used. Equilibrium data can be approximated with an average
relative volatility of 1.11 (benzene is more volatile). Note: You could also use (check) Raoult's Law
modeling for the system as another source of equilibrium information.
a) Find the minimum external reflux ratio.
b)
Use the Fenske equation to find the number of stages required at total reflux.
c) Estimate the total number of stages required for this separation, using the
Gilliland correlation for R = 1.2 Rmin.
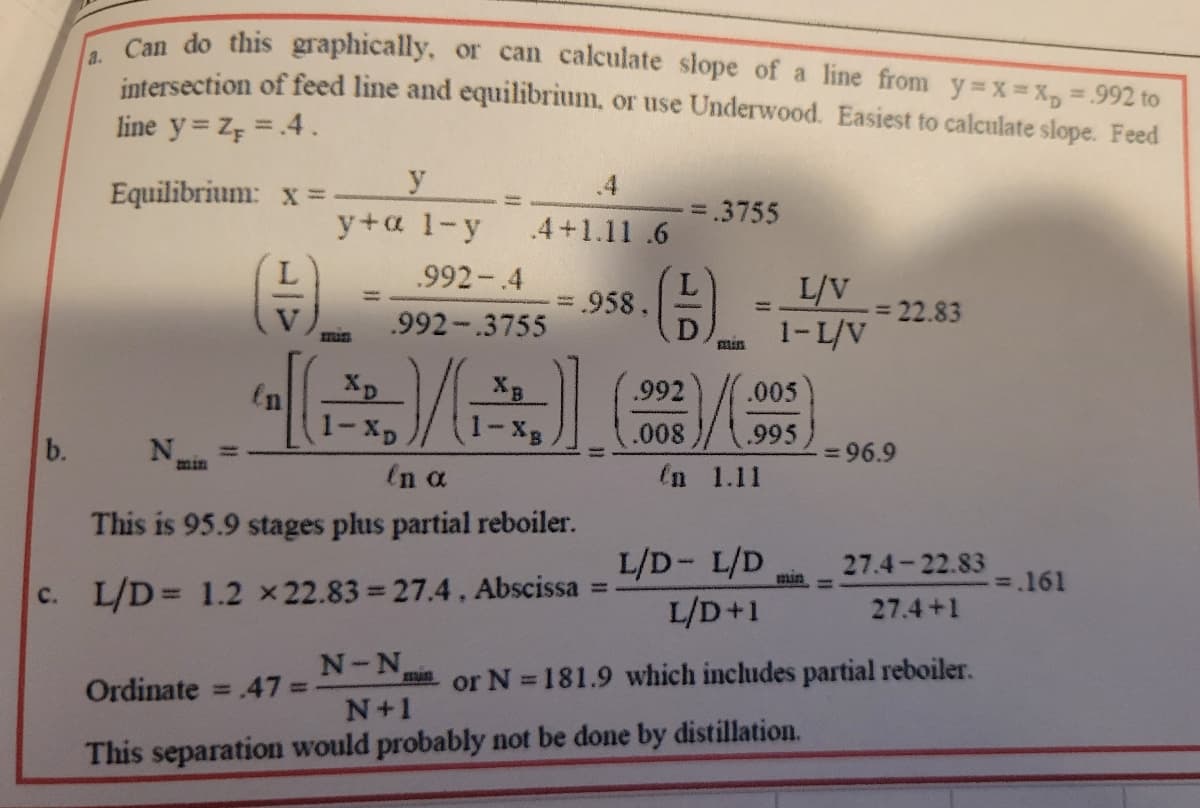
Transcribed Image Text:a.
b.
Can do this graphically, or can calculate slope of a line from y=x= x₁ = .992 to
intersection of feed line and equilibrium, or use Underwood. Easiest to calculate slope. Feed
line y = Z, = .4.
Equilibrium:
x =
y
y+ a 1-y
.992-.4
.992-.3755
XD
1-XD
N-N
Nin
in α
This is 95.9 stages plus partial reboiler.
c. L/D = 1.2 x 22.83=27.4, Abscissa
mun
4+1.11.6
XB
N+1
.958.
-
.992
.008
= .3755
mais
.005
.995
en 1.11
L/V
1-L/V
L/D- L/D
L/D+1
133343
Ordinate = .47 =
This separation would probably not be done by distillation.
= 22.83
= 96.9
27.4-22.83
27.4+1
or N=181.9 which includes partial reboiler.
=.161
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The