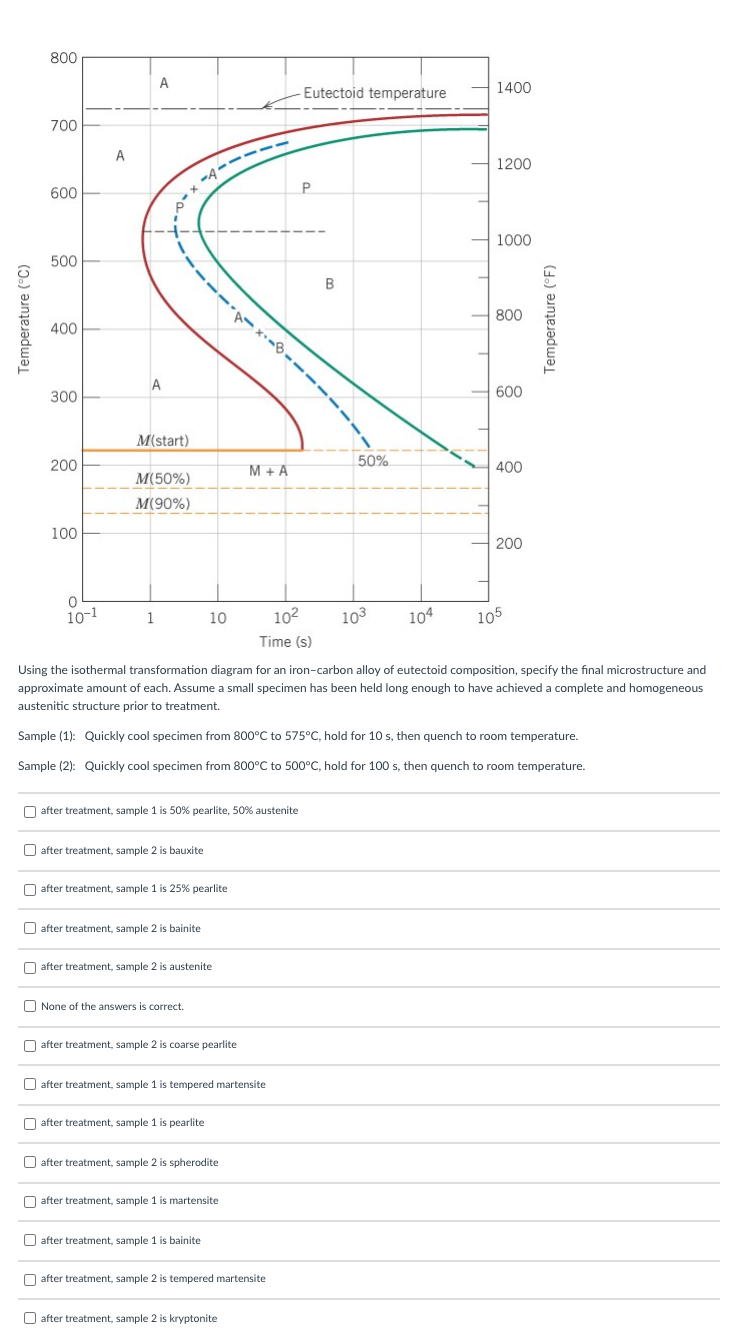
Using the isothermal transformation diagram for an iron-carbon alloy of eutectoid composition, specify the final microstructure and approximate amount of each. Assume a small specimen has been held long enough to have achieved a complete and homogeneous austenitic structure prior to treatment. Sample (1): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 575°C, hold for 10 s, then quench to room temperature. Sample (2): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 500°C, hold for 100 s, then quench to room temperature.
Using the isothermal transformation diagram for an iron-carbon alloy of eutectoid composition, specify the final microstructure and approximate amount of each. Assume a small specimen has been held long enough to have achieved a complete and homogeneous austenitic structure prior to treatment. Sample (1): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 575°C, hold for 10 s, then quench to room temperature. Sample (2): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 500°C, hold for 100 s, then quench to room temperature.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:800
A
Eutectoid temperature
H 1400
700
A
H 1200
600
1000
500
B
800
400
A
300
600
M(start)
200
M + A
50%
400
M(50%)
M(90%)
100
200
10-1
1
10
102
103
104
105
Time (s)
Using the isothermal transformation diagram for an iron-carbon alloy of eutectoid composition, specify the final microstructure and
approximate amount of each. Assume a small specimen has been held long enough to have achieved a complete and homogeneous
austenitic structure prior to treatment.
Sample (1): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 575°C, hold for 10 s, then quench to room temperature.
Sample (2): Quickly cool specimen from 800°C to 500°C, hold for 100 s, then quench to room temperature.
O after treatment, sample 1 is 50% pearlite, 50% austenite
O after treatment, sample 2 is bauxite
O after treatment, sample 1 is 25% pearlite
O after treatment, sample 2 is bainite
O after treatment, sample 2 is austenite
O None of the answers is correct.
O after treatment, sample 2 is coarse pearlite
O after treatment, sample 1 is tempered martensite
O after treatment, sample 1 is pearlite
O after treatment, sample 2 is spherodite
O after treatment, sample 1 is martensite
O after treatment, sample 1 is bainite
O after treatment, sample 2 is tempered martensite
O after treatment, sample 2 is kryptonite
Temperature (°C)
Temperature (°F)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY