We are interested in when the second derivative is equal to zero. This actually happens a few times with our data set, but there is only one equivalence point. With our data there are a number of consecutive places early on where the second derivative is zero. To figure out why this happens, suppose we have a function whose second derivative is always zero. So we have dy 0. What is for this function? fip dx dy dr? With that derivative, what kind of function must y be? Conclusion: If f(x) is a function on an interval, then f"(x) = on that interval.
We are interested in when the second derivative is equal to zero. This actually happens a few times with our data set, but there is only one equivalence point. With our data there are a number of consecutive places early on where the second derivative is zero. To figure out why this happens, suppose we have a function whose second derivative is always zero. So we have dy 0. What is for this function? fip dx dy dr? With that derivative, what kind of function must y be? Conclusion: If f(x) is a function on an interval, then f"(x) = on that interval.
Chapter5: Exponential And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.5: Exponential And Logarithmic Models
Problem 3ECP: Estimate the age of a newly discovered fossil for which the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 is...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Left Column is mL of NaOH
Right Column is pH level

Transcribed Image Text:We are interested in when the second derivative is equal to zero. This actually happens a few
times with our data set, but there is only one equivalence point. With our data there are a
number of consecutive places early on where the second derivative is zero. To figure out why
this happens, suppose we have a function whose second derivative is always zero. So we have
dy
= 0. What is
dx?
dy
for this function?
dx
With that derivative, what kind of function must y be? Conclusion: If f(x) is a
function on an interval, then f"(x) =
on that interval.
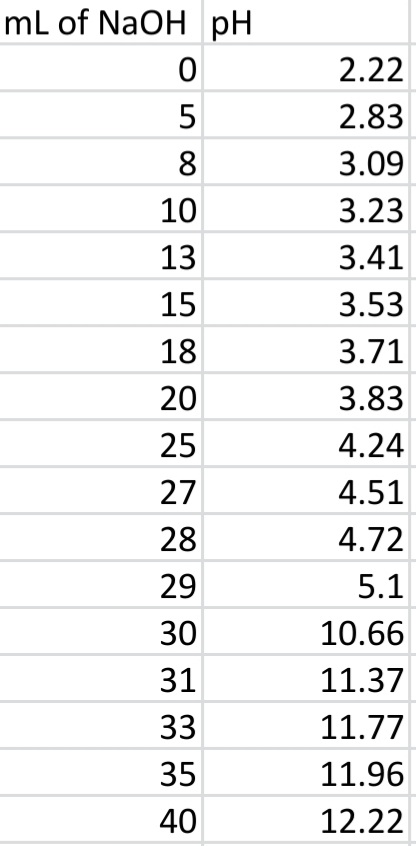
Transcribed Image Text:mL of NaOH pH
2.22
5
2.83
3.09
10
3.23
13
3.41
15
3.53
18
3.71
20
3.83
25
4.24
27
4.51
28
4.72
29
5.1
30
10.66
31
11.37
33
11.77
35
11.96
40
12.22
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell