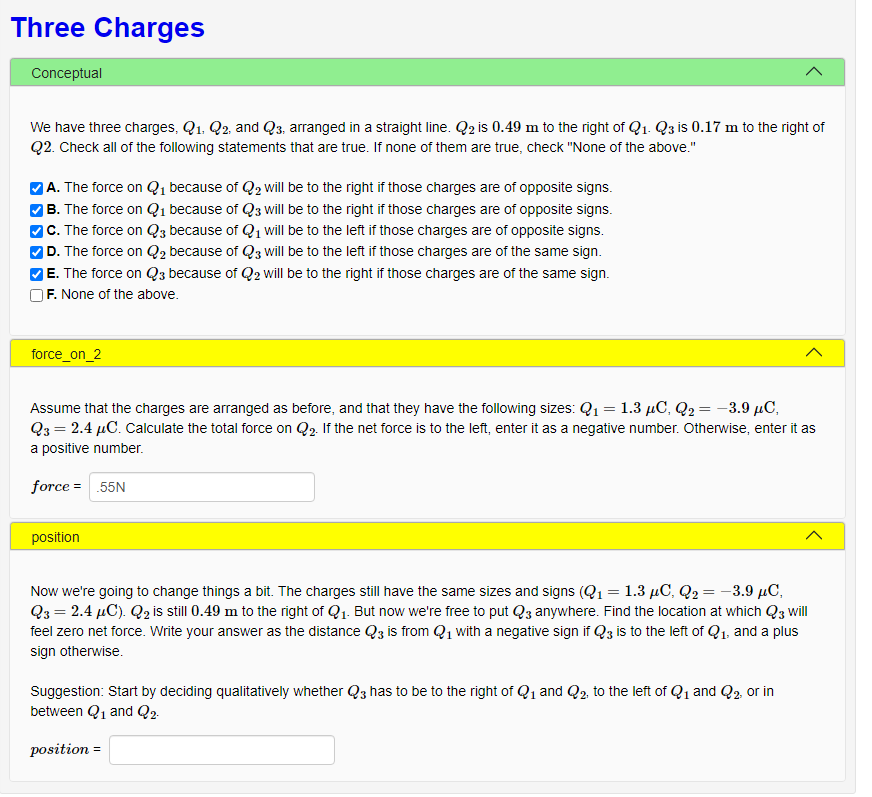
We have three charges, Q1. Q2, and Q3, arranged in a straight line. Q2 is 0.49 m to the right of Q1. Q3 is 0.17 m to the right of Q2. Check all of the following statements that are true. If none of them are true, check "None of the above." A. The force on Q1 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs. B. The force on Q1 because of Q3 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs. MC. The force on Q3 because of Q1 will be to the left if those charges are of opposite signs. D. The force on Q2 because of Q3 will be to the left if those charges are of the same sign. E. The force on Q3 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of the same sign. ) F. None of the above. force_on_2 Assume that the charges are arranged as before, and that they have the following sizes: Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC, Q3 = 2.4 µC. Calculate the total force on Q2. If the net force is to the left, enter it as a negative number. Otherwise, enter it as a positive number. %3D force = .55N position Now we're going to change things a bit. The charges still have the same sizes and signs (Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC, Q3 = 2.4 µC). Q2 is still 0.49 m to the right of Q1. But now we're free to put Q3 anywhere. Find the location at which Q3 will feel zero net force. Write your answer as the distance Q3 is from Q1 with a negative sign if Q3 is to the left of Q1, and a plus sign otherwise. Suggestion: Start by deciding qualitatively whether Q3 has to be to the right of Q1 and Q2, to the left of Q1 and Q2 or in between Q1 and Q2 position =
We have three charges, Q1. Q2, and Q3, arranged in a straight line. Q2 is 0.49 m to the right of Q1. Q3 is 0.17 m to the right of Q2. Check all of the following statements that are true. If none of them are true, check "None of the above." A. The force on Q1 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs. B. The force on Q1 because of Q3 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs. MC. The force on Q3 because of Q1 will be to the left if those charges are of opposite signs. D. The force on Q2 because of Q3 will be to the left if those charges are of the same sign. E. The force on Q3 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of the same sign. ) F. None of the above. force_on_2 Assume that the charges are arranged as before, and that they have the following sizes: Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC, Q3 = 2.4 µC. Calculate the total force on Q2. If the net force is to the left, enter it as a negative number. Otherwise, enter it as a positive number. %3D force = .55N position Now we're going to change things a bit. The charges still have the same sizes and signs (Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC, Q3 = 2.4 µC). Q2 is still 0.49 m to the right of Q1. But now we're free to put Q3 anywhere. Find the location at which Q3 will feel zero net force. Write your answer as the distance Q3 is from Q1 with a negative sign if Q3 is to the left of Q1, and a plus sign otherwise. Suggestion: Start by deciding qualitatively whether Q3 has to be to the right of Q1 and Q2, to the left of Q1 and Q2 or in between Q1 and Q2 position =
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter22: Electric Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12P
Related questions
Question
Already solved the first one but I'm stuck on the last two.
Transcribed Image Text:Three Charges
Conceptual
We have three charges, Q1. Q2, and Q3, arranged in a straight line. Q2 is 0.49 m to the right of Q1. Q3 is 0.17 m to the right of
Q2. Check all of the following statements that are true. If none of them are true, check "None of the above."
A. The force on Q1 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs.
B. The force on Q1 because of Q3 will be to the right if those charges are of opposite signs.
|C. The force on Q3 because of Q1 will be to the left if those charg
D. The force on Q2 because of Q3 will be to the left if those charges are of the same sign.
E. The force on Q3 because of Q2 will be to the right if those charges are of the same sign.
F. None of the above.
are of oppo
sig
force_on_2
Assume that the charges are arranged as before, and that they have the following sizes: Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC,
Q3 = 2.4 µC. Calculate the total force on Q2. If the net force is to the left, enter it as a negative number. Otherwise, enter it as
a positive number.
force = 55N
position
Now we're going to change things a bit. The charges still have the same sizes and signs (Q1 = 1.3 µC, Q2 = -3.9 µC,
Q3 = 2.4 µC). Q2 is still 0.49 m to the right of Q1. But now we're free to put Q3 anywhere. Find the location at which Q3 will
feel zero net force. Write your answer as the distance Q3 is from Q1 with a negative sign if Q3 is to the left of Q1, and a plus
sign otherwise.
Suggestion: Start by deciding qualitatively whether Q3 has to be to the right of Q1 and Q2, to the left of Q1 and Q2, or in
between Q1 and Q2-
position =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning