When an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force called friction. This force has a magnitude of μN, where μ is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 50 kg is released from the top of an inclined plane that is inclined 60° to the horizontal. Assume the gravitational force is constant, air resistance is negligible, and the coefficient of kinetic friction μ = 0.1. Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. If the top surface of the plane is 7 m long, what is the velocity of the object when it reaches the bottom? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/sec². Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. x(t) = mg sin 60° 60° N mg -KAN x(t) mg cos 60° x(0) = 0
When an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force called friction. This force has a magnitude of μN, where μ is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 50 kg is released from the top of an inclined plane that is inclined 60° to the horizontal. Assume the gravitational force is constant, air resistance is negligible, and the coefficient of kinetic friction μ = 0.1. Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. If the top surface of the plane is 7 m long, what is the velocity of the object when it reaches the bottom? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/sec². Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. x(t) = mg sin 60° 60° N mg -KAN x(t) mg cos 60° x(0) = 0
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter5: More Applications Of Newton’s Laws
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 61P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
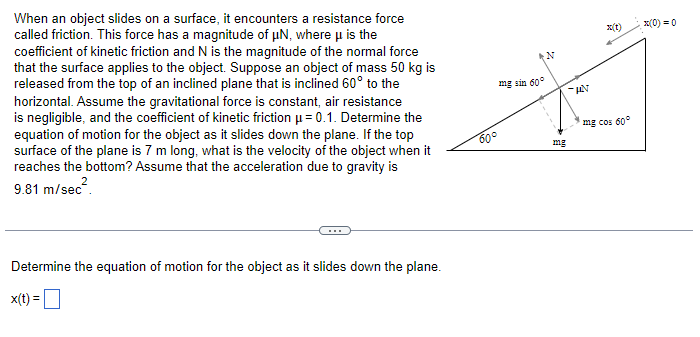
Transcribed Image Text:When an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force
called friction. This force has a magnitude of μN, where μ is the
coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of the normal force
that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 50 kg is
released from the top of an inclined plane that is inclined 60° to the
horizontal. Assume the gravitational force is constant, air resistance
is negligible, and the coefficient of kinetic friction μ = 0.1. Determine the
equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane. If the top
surface of the plane is 7 m long, what is the velocity of the object when it
reaches the bottom? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is
9.81 m/sec².
Determine the equation of motion for the object as it slides down the plane.
x(t) =
mg sin 60°
شت
60°
N
mg
x(t)
-KAN
x(0) = 0
mg cos 60°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University