y Part A The average kinetic energy of the molecules of an ideal gas at 10°C has the value K10. At what temperature T₁ (in degrees Celsius) will the average kinetic energy of the same gas be twice this value, 2K10? Express the temperature to the nearest integer. ▸ View Available Hint(s) T₁ = Submit Part B - ΑΣΦ ? °C The molecules in an ideal gas at 10°C have a root-mean-square (rms) speed Urms. At what temperature T₂ (in degrees Celsius) will the molecules have twice the rms speed, 20rms?
y Part A The average kinetic energy of the molecules of an ideal gas at 10°C has the value K10. At what temperature T₁ (in degrees Celsius) will the average kinetic energy of the same gas be twice this value, 2K10? Express the temperature to the nearest integer. ▸ View Available Hint(s) T₁ = Submit Part B - ΑΣΦ ? °C The molecules in an ideal gas at 10°C have a root-mean-square (rms) speed Urms. At what temperature T₂ (in degrees Celsius) will the molecules have twice the rms speed, 20rms?
Chapter2: The Kinetic Theory Of Gases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 81AP: One process for decaffeinating coffee uses carbon dioxide ( M=44.0 g/mol) at a molar density of...
Related questions
Question
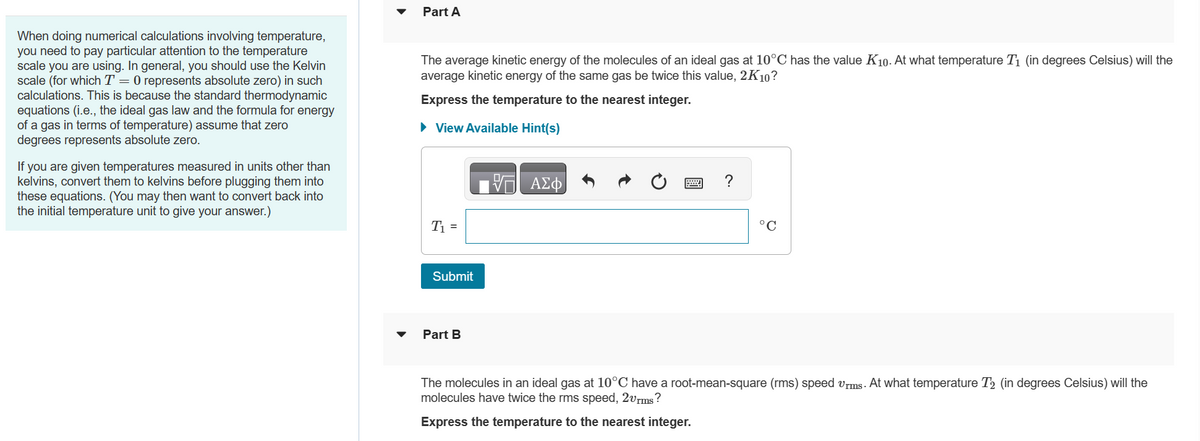
Transcribed Image Text:When doing numerical calculations involving temperature,
you need to pay particular attention to the temperature
scale you are using. In general, you should use the Kelvin
scale (for which T = 0 represents absolute zero) in such
calculations. This is because the standard thermodynamic
equations (i.e., the ideal gas law and the formula for energy
of a gas in terms of temperature) assume that zero
degrees represents absolute zero.
If you are given temperatures measured in units other than
kelvins, convert them to kelvins before plugging them into
these equations. (You may then want to convert back into
the initial temperature unit to give your answer.)
Part A
The average kinetic energy of the molecules of an ideal gas at 10°C has the value K10. At what temperature T₁ (in degrees Celsius) will the
average kinetic energy of the same gas be twice this value, 2K10?
Express the temperature to the nearest integer.
► View Available Hint(s)
T₁ =
Submit
Part B
V
ΑΣΦ
Ć
wwwwww
?
°C
The molecules in an ideal gas at 10°C have a root-mean-square (rms) speed urms. At what temperature T₂ (in degrees Celsius) will the
molecules have twice the rms speed, 2vrms?
Express the temperature to the nearest integer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning