
Concept explainers
The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by a cable BC. A separate cable CG is used to hold up the frame. If AB weighs 120 lb/ft and the column FC has a weight of 180 lb/ft, determine the resultant internal loadings acting on cross sections located at points D and E.
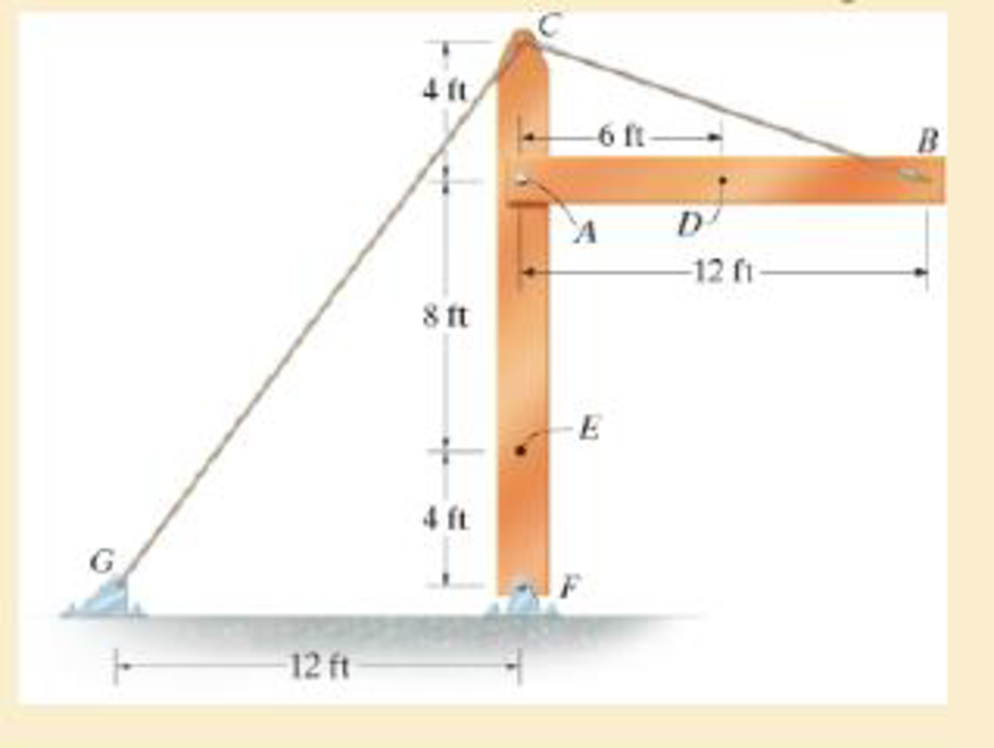
Answer to Problem 1.1RP
The resultant internal loadings at cross section at D are
The resultant internal loadings at cross section at E are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by a cable BC.
The weight of the beam AB is
The weight of the column FC is
Calculation:
Find the loading at the center of the beam AB
Substitute
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the beam AB shown in Figure 1.
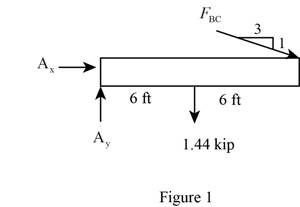
Refer to Figure 1.
Find the angle of cable BC to the horizontal
Find the tension in cable BC as shown below.
Take moment about A is Equal to zero.
Find the support reaction at A as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
Find the loading at the center of the beam AD
Substitute
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the section for point D as shown in Figure 2.
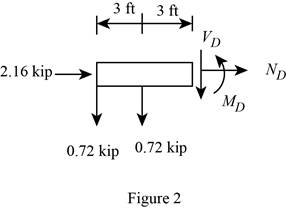
Refer to Figure 2.
Find the internal loadings as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
Take moment about D is Equal to zero.
Hence, the resultant internal loadings at cross section at D are
Find the loading at the center of the column FC
Substitute
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the beam FC shown in Figure 3.
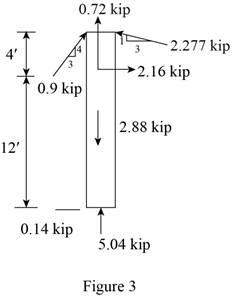
Refer to Figure 3.
Find the angle of cable CG to the horizontal.
Find the tension in cable CG as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
Find the loading at the center of the column FE
Substitute
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the section for point E as shown in Figure 4.
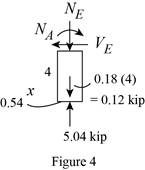
Refer to Figure 4.
Find the internal loadings as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
Take moment about E is Equal to zero.
Therefore, the resultant internal loadings at cross section at E are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
- The beam is supporting a distributed load of w=660 lb/ft. Determine the magnitudes of the resultant internal loadings acting on section b–b through the centroid C on the beam. Show all work and any FBDs that apply.arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant internal loadings at cross-sections at points E and F on the assembly.arrow_forwardThe shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing at A and a smooth journal bearing at B. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-section at C.arrow_forward
- The left half of the simply supported beam carries a uniformlydistributed load of intensity 600 N/m. If E = 10 GPa, determinethe smallest value of I that limits the midspan displacement to1/360th of the span.arrow_forwardHorizontal plates are connected to the bar AB whose length varies linearly from zero to HA, as shown. The total weight of the set of plates is W. Determine: The maximum shear stress in member AB and the torsional rotation at point B. The diameter of member AB is equal to d and its shear modulus is G.arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at point E of the handle arm, and on the cross section of the short link BC.arrow_forward
- Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-sections at points D and E of the frame.arrow_forwardThe beam supports the triangular distributed load shown. Determine the resultant internal loadings on the cross section at point C. Assume the reactions at the supports A and B are vertical.arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-sections at points F and G of the frame.arrow_forward
- 1–1. The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing at B and a journal bearing at C. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at E. Problem 1–1arrow_forwardThe brace and drill bit is used to drill a hole at O. If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected to the forces shown determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-section of the drill bit at A.arrow_forwardThe beam supports the distributed load shown. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross-section at point D. Assume the reactions at the supports A and B are vertical.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
