
Concept explainers
(a)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1.18P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The value of
The value of
The expression for
is 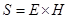
Concept used:
Write the expression for cross product of two
Here,
is the component of vector 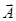 along
along 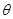 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
is the component of vector 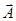 along
along 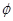 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
along 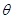 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
along 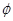
Calculation:
Substitute
for 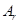 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
for 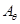 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
for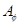 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
for 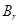
 for
for 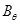 m:math display='block'>
m:math display='block'>
for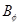
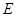 for
for 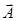 and
and 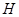 for
for
Write the expression of
Here,
is 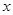 component for
component for
Substitute
Simplify further.
Write the expression of
Here,
component for 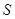
Substitute
Simplify further.
Write the expression of
Here,
component for 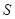
Substitute
Simplify further.
So the rectangular expression for
Conclusion:
Thus,the value of
(b)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1.18P
Thevalue of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From equation (3) the value of
So the value of
From equation (5) the value of
So the value of
From equation (7) the value of
So the value of
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Engineering Electromagnetics
- 1. Polarization a. causes charging by induction b. redistributes charges c. affects dielectrics d. all of the above 2. Around a dipole, the electric field lines a. originate from the negative to the positive charge b. hit the equipotential surfaces at any angle c. form a vector field d. form a scalar field 3. Plots of potential V (vertical axis) as a function of distance (horizontal) a. are on the positive V side of the horizontal for a positive charge b. are on the negative V side for a negative potential c. could be different for many charges d. all of the above 4. When moving from point A to B to calculate potential difference, a. the result is dependent on the path taken b. the increase or decrease in potential energy does not depend on the path c. you may go to infinity then come back d. all of the abovearrow_forwardobtain the spherical coordinates of 10a, at the point p(x 3.y 2,24). with unit vectorarrow_forwardFind the total surface area of a sphere with diameter 130 marrow_forward
- Calculate the divergence theorem for the vector function in the circular cylindrical region surrounded by r = 5, z = 0 and z = 4.arrow_forwardElectromagnetics. A spherical surface has following range. Find volume of spherical surface.arrow_forwardIn a scalar field v, v=xy-2yz, find at point p(2,3,6) the direction and the magnitude of maximum increase of v.arrow_forward
- A point in spherical coordinate is located at (2, 60°, 70°). The distance of this point to a point (9, 50°, 17), which is in cylindrical coordinate, is ________ units?arrow_forwardDescribe the surfaces, in the spherical coordinates, defined by the following equations:a) ρ=13b) θ=2π/3c) φ=π/4arrow_forwardGiven a scalar field V=2xy-yz+xz i.Find the vector representing the direction and magnitude of the maximum rate of increase of V at pointp(2,-1,0) and ii. find the rate of increase of V at point pin the direction toward pointQ(0,2.6)arrow_forward
- Evaluate the expression for Area of the cone using appropriate “dS” from spherical coordinate system and also discuss values by choosing accurate limits.arrow_forwardPoint P in cylindrical coordinates is P(ρ = 7.4, ϕ=0.8, z = 3.5). Determine the θ, in radians, for the same point. (Round your answers to 4 decimal places.)arrow_forward6 The area to be considered in using Gauss's Law should be the one where the electric field is perpendicular. This surface is referred to as __________ . Select one: a. PLANE AREA SURFACE b. SPHERICAL SURFACE c. CYLINDRICAL SURFACE d. GAUSSIAN SURFACEarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





