
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
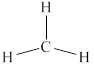
Figure 1
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around carbon atom is
The valence electrons of carbon atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on carbon atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
(b)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
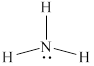
Figure 2
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around nitrogen atom is
The valence electrons of nitrogen atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on nitrogen atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
(c)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
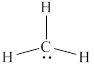
Figure 3
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around carbon atom is
The valence electrons of carbon atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on carbon atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
(d)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
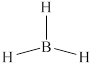
Figure 4
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around boron atom is
The valence electrons of boron atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on boron atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
(e)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
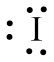
Figure 5
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around iodine atom is
The valence electrons of iodine atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on iodine atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
(f)
Interpretation:
The non-hydrogen atom from the given species having a complete octet is to be stated. The formal charge on the atom is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical compounds contain two types of bonds. These are known as ionic and covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the ions are held by the electrostatic interaction between them. In covalent bonds, the atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons. The formal charge is the charge on the constituent atoms in a molecule. It is calculated by using valence electrons of the atom.
Answer to Problem 1.22AP
The non-hydrogen atom in
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
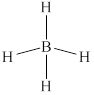
Figure 6
From the above figure, it is clear that number of electrons around boron atom is
The valence electrons of boron atom in the
Thus, the formal charge on boron atom in
The non-hydrogen atom in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Write a Lewis electron dot diagram for phosphoryl chloride,POCl3 (Fig. 3.29). Assign formal charges to all the atoms.arrow_forwardHow many resonance structures can be drawn for the hydrogen tellurate ion (HTeO4–) in which the central tellurium atom bears a –1 formal charge and the oxygens bear formal charges of either zero or –1? Enter your answer as a whole number.arrow_forwardThe hypochlorite ion, ClO-, is the active ingredient inbleach. The perchlorate ion, ClO4-, is a main componentof rocket propellants. Draw Lewis structures for both ions. (a) What is the formal charge of Cl in the hypochlorite ion?(b) What is the formal charge of Cl in the perchlorate ion, assumingthe Cl—O bonds are all single bonds? (c) What is theoxidation number of Cl in the hypochlorite ion? (d) Whatis the oxidation number of Cl in the perchlorate ion, assumingthe Cl—O bonds are all single bonds? (e) In a redox reaction,which ion would you expect to be more easily reduced?arrow_forward
- What is the formal charge on the anionic molecule (BrO3)-?arrow_forwardGiven the bonds C N, C H, C Br, and S O, (a) which atom in each is the more electronegative? (b) which of these bonds is the most polar?arrow_forwardWrite the correct Lewis structure and assign a formal charge to each atom in fulminate ion, CNO.arrow_forward
- Write all resonance structures of chlorobenzene, C6H5Cl, a molecule with the same cyclic structure as benzene. In all structures, keep the CCl bond as a single bond. Which resonance structures are the most important?arrow_forwardDefine formal charge and explain how to calculate it. What is the purpose of the formal charge? Organic compounds are composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen but also may have oxygen, nitrogen, and/or halogens in the formula. Formal charge arguments work very well for organic compounds when drawing the best Lewis structure. How do C, H, N, O, and Cl satisfy the octet rule in organic compounds so as to have a formula charge of zero?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





