
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
![]()
Figure 1
The bond angle for V-shaped geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
(b)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
![]()
Figure 2
The bond angle for linear geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
(c)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
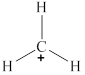
Figure 3
The bond angle for planar geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
(d)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
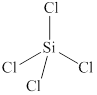
Figure 4
The bond angle for tetrahedral geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
(e)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is shown in figure 5.
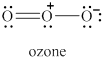
Figure 5
In the given molecule, the oxygen atoms are bonded to each other. The geometry of the given molecule is V-shaped. This geometry of molecule is shown in figure 6.
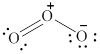
Figure 6
The bond angle for V-shaped geometry in case of ozone is more than the usual bond angle. This is because of the repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons. Thus, the bond angle in the given molecule is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
(f)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule for
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is shown in figure 7.
![]()
Figure 7
In the given molecule, the carbon atoms are bonded to each other in the linear fashion. Thus, it has only bond pair of electrons. Therefore, the geometry of the given molecule is linear. This geometry of molecule is shown in figure 8.
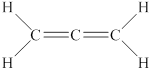
Figure 8
The bond angle for linear geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule for
(g)
Interpretation:
The bond angle in the given molecule is to be stated. The answer is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
There are various theories which explain the geometry of the molecules. The geometry is decided on the basis of specific position of atom in the molecule. The bond lengths and bond angles between the bonded atoms play a major role in this. The bond angle is specific for a specific geometry of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1.28AP
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is shown in figure 9.
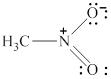
Figure 9
In the given molecule, the nitrogen atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom. Thus, it has three bond pairs of electrons and nitrogen carries a positive charge. Therefore, the geometry of the given molecule is planar. This geometry of molecule is shown in figure 10.
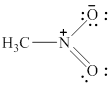
Figure 10
The bond angle for planar geometry is
The bond angle in the given molecule is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Compounds such as NaBH4, Al(BH4)3, and LiAlH4 are complex hydrides used as reducing agents in many syntheses. (a) Give the oxidation state of each element in these compounds. (b) Write a Lewis structure for the polyatomic anion in NaBH4, and predict its shape.arrow_forwardFor each of the following molecules, write a Lewis structure, predict the molecular structure (including bond angles), and give the expected hydra orbitals for sulfur d. S2O3^2-arrow_forwardIn many ways, arsenate (AsO4 3−) is very similar to phosphate (PO4 3-), yet it does not substitute for phosphate in biomolecules. After reviewing the essential atomic characteristics of the element arsenic, explain this phenomenon.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

