
Concept explainers
Zingerone gives ginger its pungent taste.
a. What is the molecular formula of zingerone?
b. How many lone pairs are present?
c. Draw a skeletal structure.
d. How many
e. What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Answer to Problem 1.38P
The molecular formula of zingerone is
Explanation of Solution
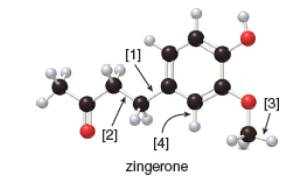
The given ball-and-stick model of zingerone is,
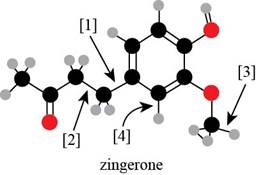
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
In the above model,
• There are three red balls. Thus, there are three
• There are eleven black balls. Thus, there are eleven
• There are fourteen grey balls. Thus, there are fourteen
Hence, the molecular formula of zingerone is
The molecular formula of zingerone is
(b)
Interpretation: The number of lone pairs in zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In a compound or molecule, the lone pairs represent number of unshared electrons on atom. An atom may or may not have unshared electrons. For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms have no lone pair but each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are total
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of citric acid is
There are total
(c)
Interpretation: A skeletal structure of zingerone is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
Answer to Problem 1.38P
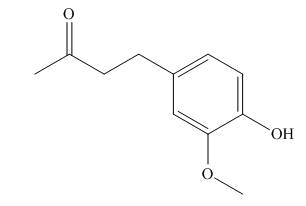
A skeletal structure of zingerone is,
Explanation of Solution
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
A skeletal structure of zingerone is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond.
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are seven
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of zingerone is,
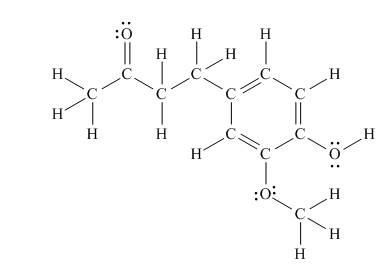
Figure 3
According to the rules of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
The
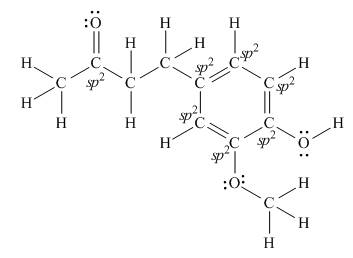
Figure 4
Thus, there are seven
There are seven
(e)
Interpretation: The orbitals that are used to form each indicated bond is to be stated.
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
Bond [1] represents bonding between the carbon atom of benzene
Thus,
Bond
Bond
Thus,
Bond
Thus, bond
The number of surrounded group around any atom predicts the hybridization of that atom, which is further helpful in predicting the orbitals involved in the bond formation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STUDY GDE...-W/ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
General Chemistry: Atoms First
Chemistry
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
- Consider the following computer-generated model of caffeine: Complete a Lewis structure for caffeine in which all atoms have a formal charge of zero (as is typical with most organic compounds). How many C and N atoms are sp2 hybridized? How many C and N atoms are sp3 hybridized? sp hybridized? How many and bonds are there?arrow_forwardMinoxidil (C9H15N15O) is a compound produced by the Pharmacia Upjohn Company that has been approved as a treatment for some types of male pattern baldness. Note that in such shorthand ring structures, each point where lines meet is a carbon atom and that the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms in the rings have been omitted. There will be four bonds to each carbon atom. a. Give the hybridization of the five nitrogen atoms in minoxidil. b. Give the hybridization of each of the nine carbon atoms in minoxidil. c. Give the approximate values for the bond angles marked a, b, c, d, e, and f. d. Including all the hydrogen atoms, how many bonds exist in minoxidil? e. How many bonds exist in minoxidil?arrow_forwardAllene (1,2-propadicne), a gas, has the following structure: What is the hybridization at each carbon atom? What is the geometry about each carbon atom? Using valencebond theory, describe the bonding about the center carbon atom. 1,3-dichloroallene is a derivative of allene with the following structure: Is this a polar molecule? (If you have difficulty visualizing the structure of this molecule, you might build a molecular model of it.)arrow_forward
- Pelargondin is the molecule responsible for the red color of the geranium flower. It also contributes to the color of ripe strawberries and raspberries. The structure of pelargondin is: How many and bonds exist in pelargondin? What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms marked 14?arrow_forwardPhosphoserine is a less-common amino acid. (a) Identify the hybridizations of atoms I through 5. (b) What are the approximate values of the bond angles A, B. C, and D? (c) What are the most polar bonds in the molecule?arrow_forwardWhat hybridization is required for central atoms that have a tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs? A trigonal planar arrangement of electron pairs? A linear arrangement of e lectron pairs? How many unhybridized p atomic orbitals are present when a central atom exhibits tetrahedral geometry? Trigonal planar geometry? Linear geometry? What are the unhybridized p atomic orbitals used for? Describe the bonding in H2S, CH4, H2CO, and HCN, using the localized electron model.arrow_forward
- Draw orbital diagrams (boxes with arrows in them) to represent the electron configurations—without hybridization—for all the atoms in SF2. Circle the electrons involved in bonding. Draw a three-dimensional sketch of the molecule and show orbital overlap. What bond angle do you expect from the unhybridized orbitals? How well does valence bond theory agree with theexperimentally measured bond angle of 98.2°?arrow_forwarda) Consider a molecule of acetone cyanohydrin, shown below. What is the hybridization and molecular geometry at CA, CB, and O? (b) For Carbon B (CB) and nitrogen (N), draw orbital energy diagrams showing the orbitals involved in bonding after hybridization. Be sure to fill the orbitals appropriately with valence electrons. c) In your diagrams in part (b), which orbitals are involved in sigma and pi bonding? Orbitals Involved in Sigma Bonding Orbitals Involved in Pi Bonding 2p sp sp2 sp3 2p sp sp2 sp3 (d) In a sample containing many molecules of acetone cyanohydrin (and no other substances), what type(s) of intermolecular forces could be present? Choose all that apply. Covalent Bonds Hydrogen Bonds Dipole-Dipole Forces London Dispersion Forcesarrow_forwardIn the hydrocarbon(a) What is the hybridization at each carbon atom in themolecule? (b) How many s bonds are there in the molecule?(c) How many p bonds? (d) Identify all the 120° bond anglesin the molecule. [Section 9.6]arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





