
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed formula for the first Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
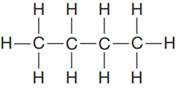
In the given Lewis structure, there are two
The condensed formula for the first Lewis structure is shown as:
(b)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
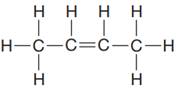
In the structure above, there are two
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown as:
(c)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
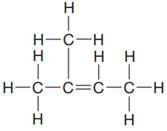
In the structure above, there are two
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown as:
(d)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
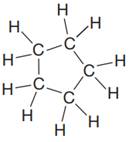
The structure above is a five carbon ring structure. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is:
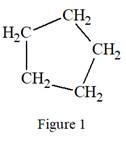
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown in Figure 1.
(e)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
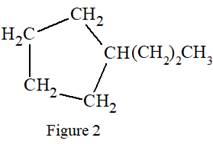
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
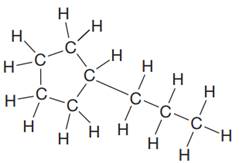
In the structure above, there is a five membered ring on the left side and a branch of three carbon atoms. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. On one of the carbon atoms in the five membered ring, two
Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is:

The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown in Figure 2.
(f)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
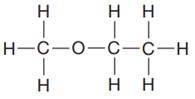
In the structure above, a
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- For the following molecule, give, according to IUPAC standards, it's name. Follow the rules for commas, spaces and dashes.arrow_forwardDraw a second resonance structure of the following structures with the arrow showing movement of electrons and bonds.arrow_forwardQuestion: In organic chemistry, is it possible to synthesize a molecule that violates the octet rule? If so, provide an example and explain the underlying principles. .arrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds contains a triple bond?arrow_forwardFor the structure below, draw the resonance structure that is indicated by the curved arrow(s). Be sure to include formal charges.Draw the second structure given to draw the new resonance structure. Include lone pairs and charges in your structure. Use the + and - to add/remove charges to an atom, and use the single bond to add/remove double bonds.arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the following compoundarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
