
a.
Record the eight events in the
a.
Explanation of Solution
The eight events are recorded using
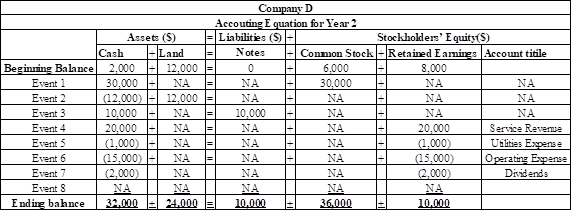
Table (1)
b.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in equity, year-end balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for the year 2.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity:
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity records the changes in the owners’ equity during the end of an accounting period by explaining about the increase or decrease in the capital reserves of shares.
Balance sheet:
Balance is the financial statement that reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (
Statement of cash flows:
Statement of cash flows is one among the financial statement of a Company statement that
Shows aggregate data of all
Income statement for the year 2 is prepared as follows:
| Company D | |
| Income Statement | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Service Revenue | $20,000 |
| Utilities Expense | (1,000) |
| Operating Expense | ($15,000) |
| Net Income | 4,000 |
Table (2)
Statement of changes in equity for the year 2 is prepared is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Beginning Common Stock | 6,000 | |
| Add: Common Stock Issued | 30,000 | |
| Ending Common Stock | 36,000 | |
| Beginning |
8,000 | |
| Add: Net Income | 4,000 | |
| Less: Dividends | (2,000) | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | 10,000 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 46,000 | |
Table (3)
Balance sheet for the year 2 is prepared as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Assets: | ||
| Cash | 32,000 | |
| Land | 24,000 | |
| Total Assets: | 56,000 | |
| Liabilities: | ||
| Notes Payable | 10,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | 10,000 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Common Stock | 36,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 10,000 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 46,000 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | 56,000 | |
Table (4)
Statement of cash flows for the year 2 is prepared as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers | 20,000 | |
| Cash Payment for Utilities Expense | (1,000) | |
| Cash Payments for Other Operating Expense | (15,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 4,000 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| Cash Paid to Purchase Land | (12,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities | (12,000) | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Stock Issue | 30,000 | |
| Cash Receipts from Loan | 10,000 | |
| Cash Payments for Dividends | (2,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | 38,000 | |
| Net Increase in Cash | 30,000 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | 2,000 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | 32,000 | |
Table (5)
c.
Ascertain the percentage of assets provided by the retained earnings and find out the amount of cash in the retained earnings account.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings:
Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth.
Calculate the percentage of assets provided by retained earnings:
Retained earnings are used to purchase assets or to pay liabilities and therefore, the amount of cash in the retained earnings accounts cannot be determined
Therefore, the percentage of assets provided by retained earnings is 17.9%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





