
Concept explainers
Consider Lewis formulas A, B, and C:
A B C
Are A, B, and C constitutional isomers, or are they resonance contributors?
Which have a negatively charged carbon?
Which have a positively charged carbon?
Which have a positively charged nitrogen?
Which have a negatively charged nitrogen?
What is the net charge on each?
Which is a more stable structure, A or B? Why?
Which is a more stable structure, B or C? Why?
What is the CNN geometry in each according to VSEPR?
Interpretation:
The given statements for the following Lewis formulas are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Isomers are classified as different compounds having the same molecular formula. Satisfying the octet rule and maximizing the number of bonds usually occur simultaneously.
A more electronegative atom favors a negative charge and a less electronegative atom favors a positive charge. The formal charge of an atom is given by:
Answer to Problem 47P
Solution:
Lewis formulas
Lewis formula
Lewis formula
Lewis formulas
Lewis formulas
Net charge on all Lewis formulas
Lewis formula
Lewis formula
The CNN geometry in Lewis formula
Explanation of Solution
(a) Constitutional isomers or resonance contributors.
In order to be constitutional isomers, Lewis formulas must have the same molecular formula and different connectivity. Given Lewis formulas
Resonance contributors differ only in the distribution of electrons. Given Lewis formulas
Delocalization of electrons is shown using curved arrows as follows:
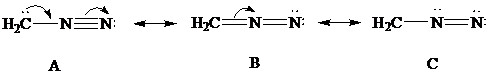
In Lewis formula
In Lewis formula
(b) Negatively charged carbon.
The formal charge on each carbon atom in all the three given Lewis formulas is as follows:
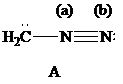
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
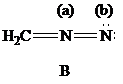
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
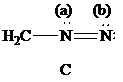
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
Lewis formulas with formal charges are
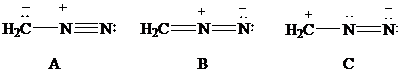
Hence, Lewis formula
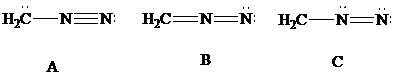
(c) Positively charged carbon.
The formal charge on each carbon atom in all the three given Lewis formulas is as follows:
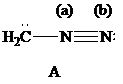
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
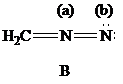
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
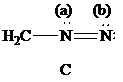
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon |
Lewis formulas with formal charges are
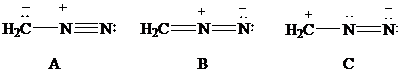
Hence, Lewis formula
(d) Positively charged nitrogen.
The formal charge on each nitrogen atom in all the three given Lewis formulas is as follows:
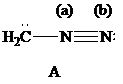
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
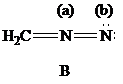
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
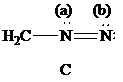
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formulas with formal charges are
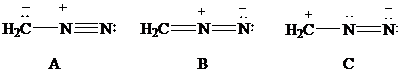
Hence, Lewis formulas
(e) Negatively charged nitrogen.
The formal charge on each nitrogen atom in all the three given Lewis formulas is as follows:
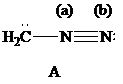
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
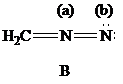
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
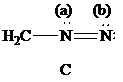
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formulas with formal charges are
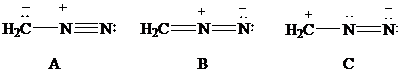
Hence, Lewis formulas
(f) Net charge on each.
The formal charge on each atom for all the three given Lewis formulas is as follows:
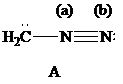
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formula
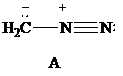
There is one negative charge on carbon and one positive charge on the adjacent nitrogen; hence, net charge on the Lewis formula
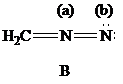
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formula
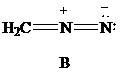
There is one negative charge on the nitrogen atom in the middle and one positive charge on the adjacent nitrogen; hence, net charge on the Lewis formula
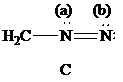
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formula
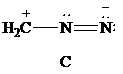
There is one positive charge on carbon and one positive charge on one nitrogen atom; hence, net charge on the Lewis formula
(g) The more stable structures.
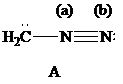
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
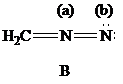
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
The Lewis formulas A and B with formal charges are
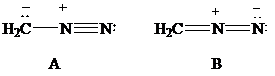
The most stable structure is the contributing structure with the greater number of covalent bonds, which contributes more to the resonance hybrid, as long as the octet rule is not exceeded for second-row elements. The major contributor is the one with the smallest separation of oppositely charged atoms, when two or more structures satisfy the octet rule. The major contributor is the one in which the negative charge resides on the most electronegative atom and the positive charge on the least electronegative element, among the structural formulas that satisfy the octet rule and in which one or more atoms bear a formal charge.
In given Lewis formulas
Out of the given three Lewis formulas, in Lewis formula
Hence, Lewis formula
(h) The more stable structures.
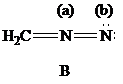
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
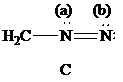
| Atoms | Valence electrons of neutral atom | Electron count | Formal charge |
| Carbon | |||
| Hydrogen | |||
| Nitrogen(a) | |||
| Nitrogen(b) |
Lewis formulas
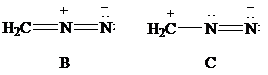
The most stable structure is the contributing structure with the greater number of covalent bonds, which contributes more to the resonance hybrid, as long as the octet rule is not exceeded for second-row elements. The major contributor is the one with the smallest separation of oppositely charged atoms, when two or more structures satisfy the octet rule. The major contributor is the one in which the negative charge resides on the most electronegative atom and the positive charge on the least electronegative element, among the structural formulas that satisfy the octet rule and in which one or more atoms bear a formal charge.
In Lewis formula
Hence, Lewis formula
(i) CNN geometry.
In Lewis formula
In Lewis formula
In Lewis formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Draw a Lewis structure for the N, N-dimethylformamide molecule. The skeletal structure is Various types of evidence lead to the conclusion that there is some double bond character to the CN bond. Draw one or more resonance structures that support this observation.arrow_forward3-127 Amoxicillin is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. Consider the skeletal structure of amoxicillin (y refer to the structure at bottom of page). Where all the bonded atoms are shown but double bonds, triple bonds, and/or lone pairs are missing: (a) Complete the structure of amoxicillin. (b) Identify the various types of geometries present in each central atom using VSEPR theory (e) Determine the various relative bond angles as sociated with each central atom using VSEPR theory. (d) What is the most polar bond in Amoxicillin? (e) Would you predict amoxicillin to be polar or nonpolar? (f) Is amoxicillin expected to possess resonance? Explain why or why not. V Chemical structure for problem 3-127arrow_forwardWrite all possible resonance structures for the following species. Assign a formal charge to each atom. In each case, which resonance structure is the most important? (a) NO2 (nitrogen is central) (b) ClCNarrow_forward
- 3-106 Consider the structure of Penicillin G shown below, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by gram-positive organisms, derived from Penicillium fungi: (a) Identify the various types of geometries present in each central atom using VSEPR theory. (b) Determine the various relative bond angles associated with each central atom using VSEPR theory (c) Which is the most poiar bond in Penicillin G? (d) Would you predict Penicillin G to be polar or nonpolar?arrow_forwardIodine forms a series of fluorides (listed here). Write Lewis structures for each of the four compounds and determine the formal charge of the iodine atom in each molecule: (a) IF (b) IF3 (c) IF5 (d) IF7arrow_forwardFollowing is a structural formula of benzene, C6H6, which we study in Chapter 21. (a) Using VSEPR, predict each HCC and CCC bond angle in benzene. (b) State the hybridization of each carbon in benzene. (c) Predict the shape of a benzene molecule. (d) Draw important resonance contributing structures.arrow_forward
- Can someone expain what it means when it says: draw a better resonance structure than the one shown below" does it mean it wants the highly electronegative atoms O and N to be nuetral? they are "happier neutral? do i draw lewis structure variations and then...?arrow_forwardThe two molecules in the pictrue behave very differently in reactions. Though they are both neutral, it is possible to draw resonance structures to illustrate which atoms will have partial charges. In one of the molecules, a carbon of the double bond is partially positive while in the other it is partially negative. 1. Draw one resonance structure for each molecule below with only one positive and one negative charge in the left box. In the box to the right draw out the original structure with its partial charges, which can be determined from the resonance structures.arrow_forwardDraw resonance structures for the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-. (a) Does HCO3- have the same number of resonance structures as the CO32- ion? Are any less likely than others? (b) What are the formal charges on the O and C atoms in HCO3- ? What is the average formal charge on the O atoms? Compare this with the O atoms in CO32- . (c) Protonation of HCO3- gives H2CO3. How do formal charges predict where the H+ ion will be attached?arrow_forward
- ICl4 Draw the following: 1. Lewis structure 2. Assign formal charges (for elements with non-zero formal charges only). 3. Draw resonance forms (if applicable), pick the most plausible structure (if possible) on the basis of formal charge and electronegativity.arrow_forwardWhich has the higher electronegativity? C or O? Br or Cl? Pb or H? O or H? C or H?arrow_forwardIn the following resonance formula for ozone, O3, what is the formal charge of the central oxygen atom? Select one: a. 0 b. +1 c. -2 d. -1 e. +2arrow_forward

 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





