
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The use of prefix
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
The given IUPAC name is
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The use of prefix
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
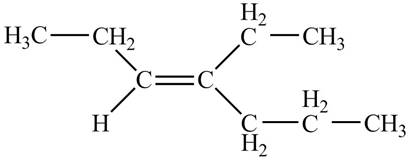
Figure 1
The structure corresponding to
(b)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to the given
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
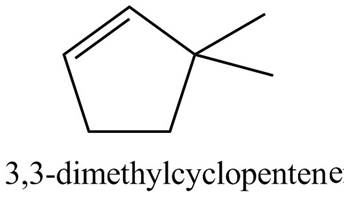
Figure 2
The structure corresponding to
(c)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
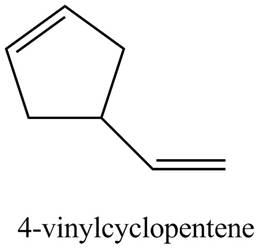
Figure 3
The structure corresponding to
(d)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The use of prefix
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The use of prefix
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
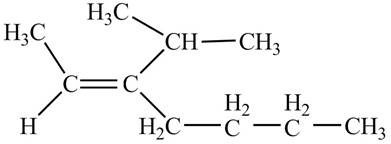
Figure 4
The structure corresponding to
(e)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the two correct structure of
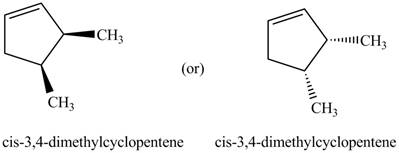
Figure 5
The structure corresponding to
(f)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
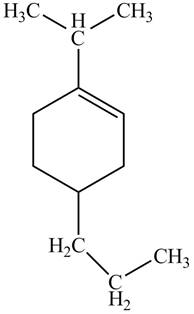
Figure 6
The structure corresponding to
(g)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
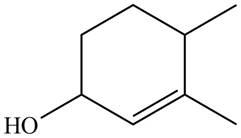
Figure 7
The structure corresponding to
(h)
Interpretation: The structure corresponding to
Concept introduction: The systematic naming of organic compound is given by IUPAC nomenclature. The naming of organic compound is done such that the structure of organic compound is correctly interpreted from the name.
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are:
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
Answer to Problem 10.39P
The structure corresponding to
Explanation of Solution
Rules for writing structural formula from IUPAC are
1. First identify the word root for the given compound.
2. The suffix used in the compound like –ene.
3. Identify the position, location, and number of the substituent bonded to the carbon chain.
The given name is
Thus, the correct structure of
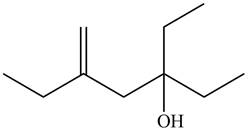
Figure 8
The structure corresponding to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- draw out a step by step mechansim with arrows to get from the compound on the lefts to get the compound on the right and explainarrow_forwardAssign the stereochemical configuration (E or Z) for the alkene below. Show your work, indicating clearly which groups are assigned high priority (e.g., through assigning the groups numbers, circling only the high priority groups, or labeling groups as high or low).arrow_forwardShow how HC ≡ CH, CH3CH2Br, and (CH3)2CHCH2CHBr can be used to prepare CH3CH2C ≡ CCH2CH2CH(CH3)2. Show all reagents, and use curved arrows to show movement of electron pairs.arrow_forward
- Rank the following alkenes from least to most stable. Then explain why you picked this order.arrow_forwardWhen you react ammonia with a halogenated Alkane will you get only one organic product? Why or why notarrow_forwardKMnO4, warm, conc'd reacts with hept-1-ene to yield __________. CO2, hex-1-ene CO2, hexanoic acid Formic acid, pentanoic acid Ethanoic acid, pentanal Formic acid, hexanonearrow_forward
- The 1,2‑dibromide is synthesized from an alkene starting material. Draw the alkene starting material. Clearly, show stereochemistry of the alkene.arrow_forwardPlease solve correctly: Optio for Q1. a.)2-hexyne b.)3-methyl-1-pentyne c.)3-hexyne d.)1-hexyne e.)4-methy-1-pentyne Q2) a.)Alkenes react with nucleophiles and bases. b.)Alkenes react with electrophiles. c.)In the reactions of alkenes, the p bond is not always broken. d.)Alkenes contain double bonds from two sp-hybridized carbon atoms.arrow_forwardShow how HC≡CH, CH3CH2Br, and (CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br can be used to prepare CH3CH2C≡CCH2CH2CH(CH3)2. Show all reagents, and use curved arrows to show movement of electron pairs.arrow_forward
- Show all steps and reagents needed to convert cyclohexane into each compound: (a) the two enantiomers of trans-1,2- dibromocyclohexane; and (b) 1,2-epoxycyclohexane.arrow_forwardA hydrocarbon of unknown structure has the formula C8H10. On catalytichydrogenation over the Lindlar catalyst, 1 equivalent of H2 is absorbed. Onhydrogenation over a palladium catalyst, 3 equivalents of H2 are absorbed.(a) How rnany degrees of unsaturation are present in the unknown?(b) How many triple bonds are present?(c) How many double bonds are present?(d) How many rings ar e present?(e) Draw a structure that fits the data.arrow_forwardPlease explain carbocations and the increasing stabilityarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
