
Concept explainers
Carbon–carbon bond dissociation enthalpies have been measured for many
Without referring to Table
has the lower carbon–carbon bond-dissociation enthalpy, and explain the reason for your
choice.
Ethane or propane
Propane or
Cyclobutane or cyclopentane
Interpretation:
In each of the given pairs, the alkane having lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy is to be identified and the reason for this is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Species that contain unpaired electrons are called free radicals.
Alkyl radicals are described by the presence of carbon with three bonds. The alkyl radicals are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary on the basis of the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the carbon atom bearing unpaired electron.
Similar to carbocation’s, free radicals are stabilized by alkyl substituents. The stability order of alkyl radicals is
In a hemolytic cleavage, each atom of the bond keeps one of the electrons in the bond.
The bond dissociation energy represents the stability of radical formed.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
a) Propane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
b)
c)
d) Cyclopentane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
Explanation of Solution
a) The given alkanes are ethane and propane.
The cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical.
The ethyl radical is a primary radical and is more stable than the methyl radical. Hence propane produces more stable radicals than ethane upon homolytic cleavage. Lower energy is required to generate free radicals in propane. Thus, propane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than ethane.
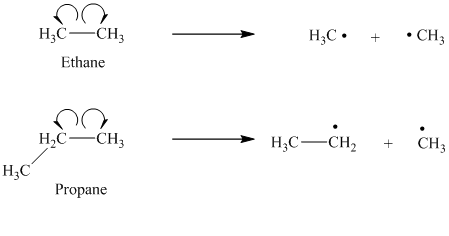
b) The given alkanes are propane and
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical. The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The isopropyl radical is a secondary radical and is more stable than the ethyl radical, which is a primary radical. Hence
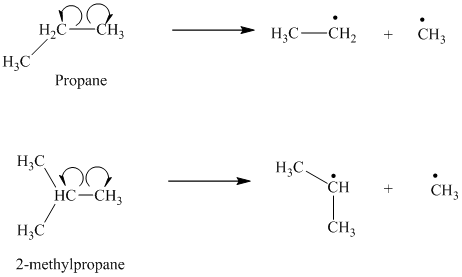
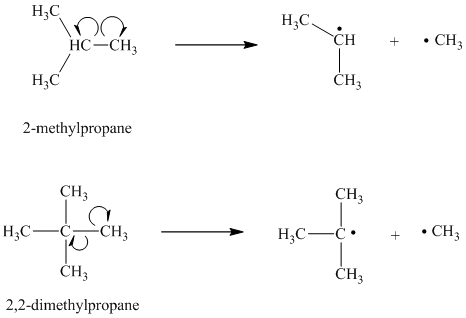
c) The given alkanes are
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The tertiary butyl radical is a tertiary radical and is more stable than the isopropyl radical, which is a secondary radical. Hence
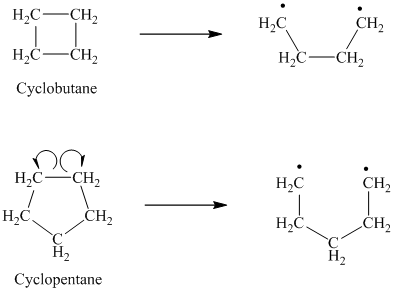
d) The given alkanes are cyclobutane and cyclopentane.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclobutane produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclopentane also produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
In the radicals produced by cyclopentane, there is one alkyl substituent more as compared to the radicals in cyclobutane. The more the alkyl substituents, the more stable is the radical. Hence, in cyclopentane, the radicals are slightly more stable as compared to cyclobutane. Hence, cyclopentane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than cyclobutane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEXT PACKAGED - 2 YE
- Following are structural formulas for 1,4-dioxane and piperidine. 1,4-Dioxane is a widely used solvent for organic compounds. Piperidine is found in small amounts in black pepper (Piper nigrum). (a) Complete the Lewis structure of each compound by showing all unshared electron pairs. (b) Predict bond angles about each carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atom. (c) Describe the most stable conformation of each ring and compare these conformations with the chair conformation of cyclohexane.arrow_forwardFind the butanol combustion enthalpy using bond energy and calculate the value of the change in heat of combustion due to the addition of a CH2 unit in the given alcoholarrow_forwardBased on your knowledge of boiling point trends in alkanes, predict which compound has the higher boiling point, butane or 2-methylpropane (isobutane). Based on your knowledge of boiling point trends in alkanes, predict which compound has the higher boiling point, butane or 2-methylpropane (isobutane). a. isobutane would have a higher boiling point, since the greater the surface area, the higher the boiling point. b. Butane would have a higher boiling point, since the greater the surface area, the higher the boiling point. c. Butane would have a higher boiling point, since the smaller the surface area, the higher the boiling point. d. Isobutane would have a higher boiling point, since the smaller the surface area, the higher the boiling point.arrow_forward
- Using the table of bond dissociation enthalpies , calculate ▲H° for bromination of propane to give 2-bromopropane and hydrogen bromide.arrow_forwardThe molar heat of combustion of gaseous cyclopropane is -2089 kJ/mol; that for gaseous cyclopentane is -3317 kJ/mol. Calculate the heat of combustion per CH2 group in the two cases, and account for the difference.arrow_forwardThe molar heat of combustion of gaseous cyclopropane is -2089 Kj/mol, that for gaseous cyclopentene is -3317 Kj/mol. Calculate the heat of combustion per CH2 group in the two cases and account for the differencearrow_forward
- Arrange the following compounds in order of decreasing heat of combustion: pentane, 2-methylbutane, 2,2-dimethylpropane, hexane.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the organic product of the reaction between cyclohexene and H2SO4, H2O. Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. Separate multiple products using the + sign In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one.arrow_forwardEstimate the heat released when 1-butene(CH3CH2CHCH2) reacts with bromine to give CH3CH2CHBrCH2Br. Bond enthalpies are CH : 412 kJ/mol; CC : 348 kJ/mol;CC : 612 kJ/mol; CBr : 276 kJ/mol;BrBr : 193 kJ/mol. 1.317 kJ/mol 2.507 kJ/mol 3.95 kJ/mol 4.288 kJ/mol 5.181 kJ/molarrow_forward
- Draw Lewis structures and condensed structural formulas for the four alcohols with the molecular formula C4H10O. Classify each alcohol as primary, secondary, or tertiary.arrow_forwardExplain the role strain plays on stability and reactivity of a cyclic alkane such as cyclopropane.arrow_forwardThe reaction between methanol and hydrochloric acid yields chloromethane and water. What is the enthalpy for the reaction using the given bond energies (kJ mol-1)? C-Cl = 326 H-O = 463 H-Cl = 431 C-O = 335 -511 kJ mol-1 -59 kJ mol-1 -23 kJ mol-1 -42 kJ mol-1 The reaction between methanol and hydrochloric acid yields chloromethane and water. What is the enthalpy for the reaction using the given bond energies (kJ mol-1)? C-Cl = 326 H-O = 463 H-Cl = 431 C-O = 335 -511 kJ mol-1 -59 kJ mol-1 -23 kJ mol-1 -42 kJ mol-1arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


