
In Exercises 1–3, use the following service times (in seconds) observed at lunchtime at different fast-food restaurant drive-up windows. Assume that the service times for such restaurants are
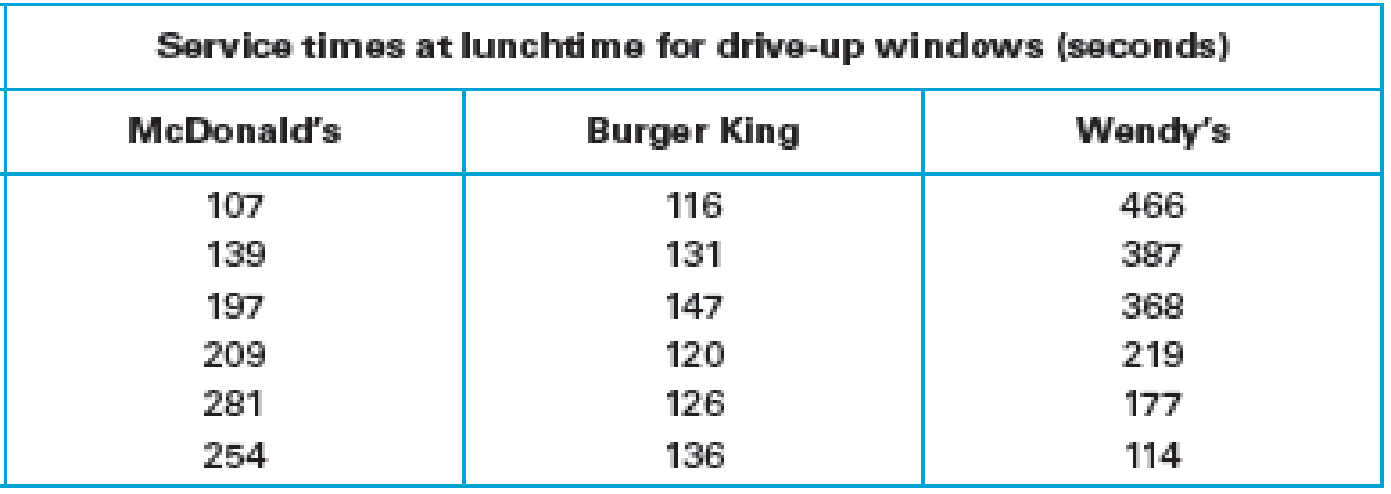
- 1. McDonald’s. Using only the service times from McDonald’s, construct a 95% confidence
interval estimate of the population mean.
Using the service times from McDonald’s obtain a 95% confidence interval to estimate the populations mean.
Answer to Problem 1CRE
The 95% confidence interval to estimate the population mean is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The data related to the service times at lunchtime for drive-up windows at McDonald’s.
t-distribution:
A random variable X is said to follow t distribution with degrees of freedom
The value of random variable X can be defined as,
Test statistic:
The test statistic is obtained as,
Level of significance:
The level of significance is
For two tail test the level of significance is,
The sample size is
Degrees of freedom:
The degrees of freedom for t distribution is
Hence, the degrees of freedom for
Critical value:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value from the TABLE 10.1: Critical t values, is obtained as:
- Locate the degrees of freedom of 5 from the 1st column of TABLE 10.1.
- Locate the area from the column of “0.05 area in two tails” corresponding to the degrees of freedom of 5.
The critical value is 2.571.
Mean:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure using EXCEL to obtain Mean is given below:
- Enter the name McDonald’s in the first cell A1 of an EXCEL sheet.
- Enter the data value in that sheet corresponding to the heading McDonald’s from cell A2 to A7.
- In cell A8 enter the formula “=AVERAGE(A2:A7)”.
- Click Enter.
The output is given below:
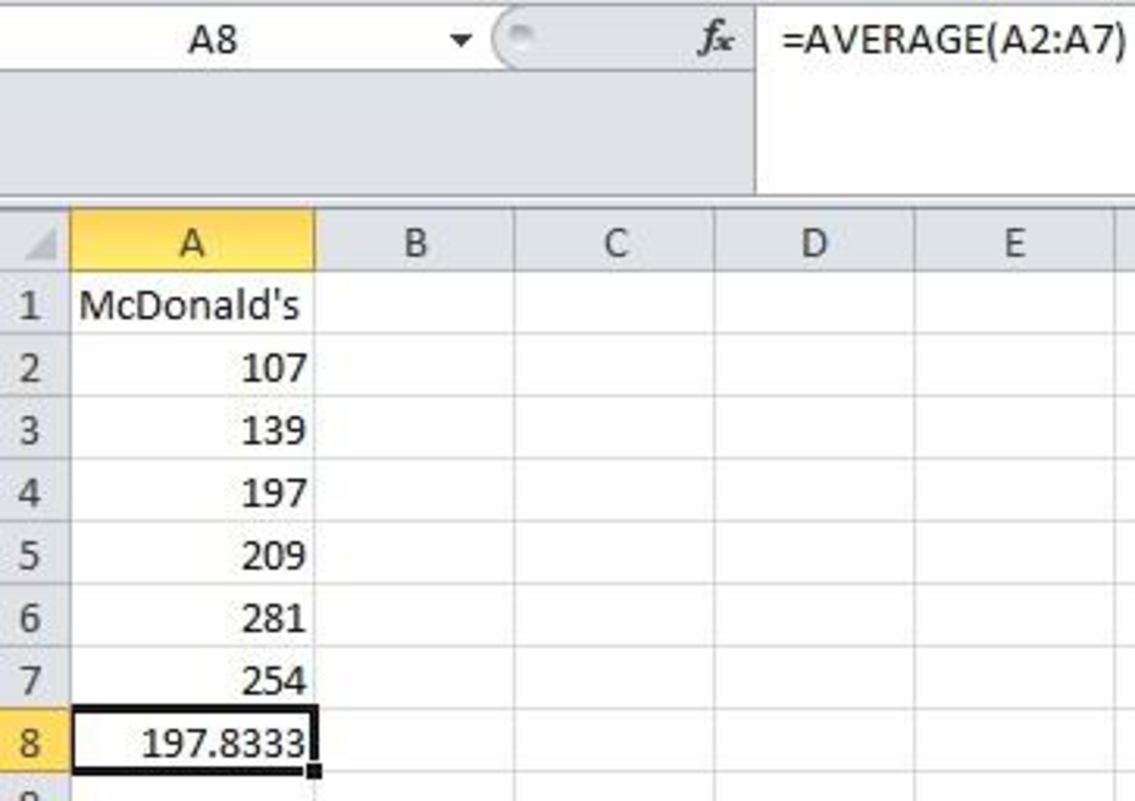
Thus, the sample mean
Standard deviation:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure using EXCEL to obtain Standard deviation is given below:
- Enter the name McDonald’s in the first cell A1 of an EXCEL sheet.
- Enter the data value in that sheet corresponding to the heading McDonald’s from cell A2 to A7.
- In cell A8 enter the formula “=STDEVA(A2:A7)”.
- Click Enter.
The output is given below:
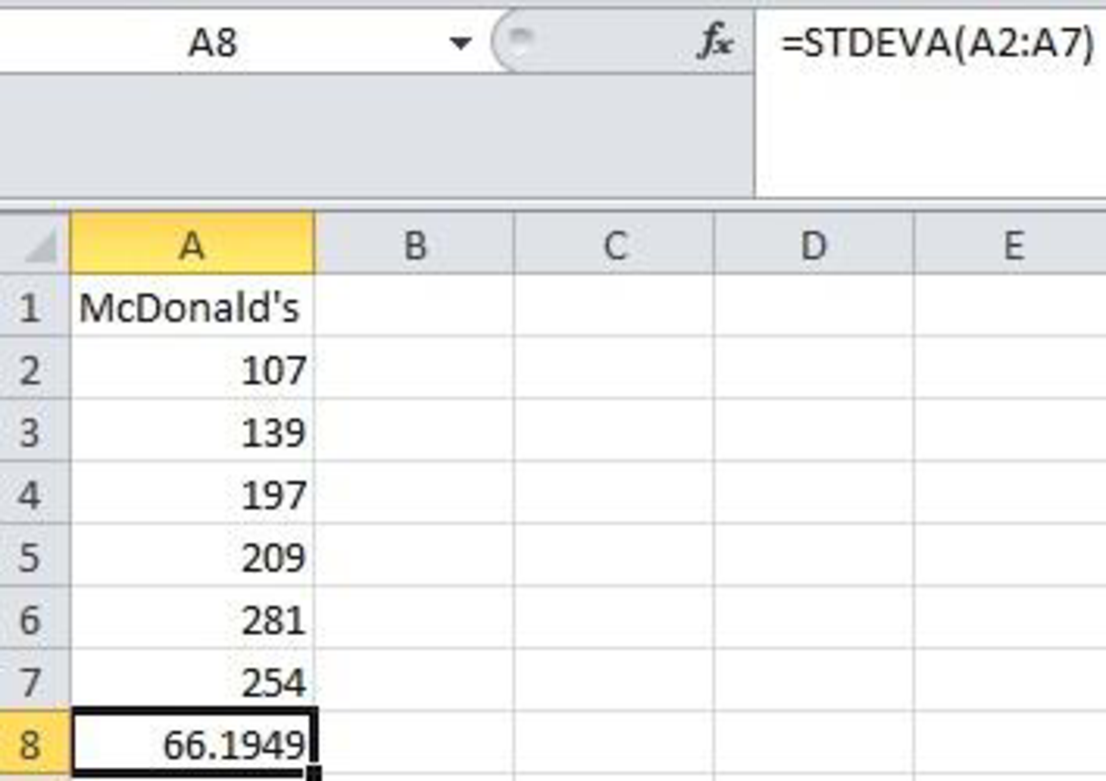
Thus, the sample standard deviation
Margin of error:
The margin of error, E is defined as,
The critical value is obtained as 2.571, the sample standard deviation is
Thus, the margin of error is,
Therefore, the margin of error is approximately 69.46
Confidence interval:
The 95% confidence interval around a sample mean to estimate the true value of population mean,
Hence the confidence interval is,
Thus, the 95% confidence interval to estimate the population mean is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Student's Solutions Manual For Statistical Reasoning For Everyday Life Format: Paperback
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





