
To calculate:
The
Answer to Problem 1SPPA
Without pollution control, equilibrium Output (QP) is 400,
Explanation of Solution
An externality refers to the cost and benefits that the third-party bears and it has no control over it. However, externalities can be negative and positive. The externalities that cost to the third party are considered as negative externality while if it benefits the third party then it is considered as positive externalities.
The price, output, marginal private cost (MPC) and marginal external cost (MEC) schedules are given as follows:
| Price (P) | Output (Q) | MPC | MEC | MSC |
| 4 | 500 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 8 | 400 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| 12 | 300 | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| 16 | 200 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| 20 | 100 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Without pollution control, the coal burning utility would take output and price decisions according to the following condition:
MB=MPC
Where
MB is marginal benefit,
MPC is marginal private cost.
The marginal benefit is equal to the output (demand). That is, coal burning utility would produce the output level where MB curve intersects MPC curve. Hence, without pollution control,
Equilibrium output (QP) is 400, equilibrium price (PP) is 8 cents and marginal external cost (MEC) is 8 cents.
The diagram below shows the plot of marginal benefit/ demand (MB), marginal private cost (MPC) and marginal
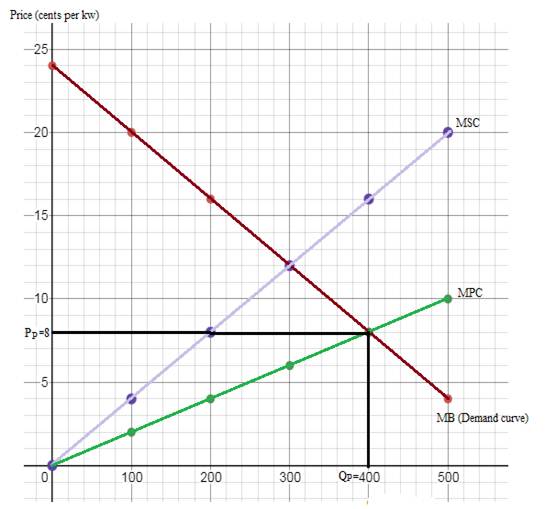
Externalities:
Externality is the negative or positive effect of an action by an economic agent on another.
Marginal benefit:
Marginal benefit of an economic activity is the extra benefit received by undertaking an additional unit of that economic activity. It is also the demand curve.
Marginal cost:
Marginal cost of an economic activity is the extra cost incurred by undertaking an additional unit of that economic activity.
External cost:
When externality is negative, it is regarded as external cost.
Social cost:
Social cost is the sum of private cost and external cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Foundations of Economics, Student Value Edition (8th Edition)
- Show the market for cigarettes in equilibrium, assuming that there are no laws banning smoking in public. Label the equilibrium private market price and quantity as Pm and Qm. Add whatever is needed to the model to show the impact of the negative externality from second-hand smoking. (Hint: In this case it is the consumers, not the sellers, who are creating the negative externality.) Label the social optimal output and price as Fe and Qe. On the graph, shade in the deadweight loss at the market output.arrow_forwardTable 12.12, shows the supply and demand conditions for a firm that will play trumpets on the streets when requested. QS1 is the quantity supplied without social costs. QS2 is the quantity supplied with social costs. What is the negative externality in this situation? Identify the equilibrium price and quantity when we account only for private costs, and then when we account for social costs. How does accounting for the externality affect the equilibrium price and quantity?arrow_forwardIdentify the following situations as an example of a negative or a positive externality: You are a birder (bird watcher), and your neighbor has put up several birdhouses in the yard as well as planting trees and flowers that attract birds. Your neighbor paints his house a hideous color. Investments in private education raise your countrys standard of living. Trash dumped upstream flows downstream right past your home. Your roommate is a smoker, but you are a nonsmoker.arrow_forward
- The rows in Table 12.7 show three market-oriented tools for reducing pollution. The columns of the table show three complaints about command-and-control regulation. Fill in the table by stating briefly how each market-oriented tool addresses each of the three concerns.arrow_forwardRefer to Table 12.2. The externality created by the refrigerator production was 100. However, once we accounted for both the private and additional external costs, the market price increased by only 50. If the external costs were 100 why did the price only increase by 50 when we accounted for all costs?arrow_forwardTable 12.5 provides the supply and demand conditions for a manufacturing film. The third column represents a supply curve without accounting for the social cost of pollution. The fourth column represents the supply curve when the film is required to account for the social cost of pollution. Identify the equilibrium before the social cost of production is included and after the social cost of production is included.arrow_forward
- Classify the following pollution-control policies as command-and-control or market incentive based. A state emissions tax on the quantity of carbon emitted by each firm. The federal government requires domestic auto companies to improve car emissions by 2020. The EPA sets national standards for water quality. A city sells permits to films that allow them to emit a specified quantity of pollution. The federal government pays fishermen to preserve salmon.arrow_forwardDraw a standard supply and demand diagram for televisions, and indicate the equilibrium price and output. a. Assuming that the production of televisions generates external costs, illustrate the effect of the producers being forced to pay a tax equal to the external costs generated, and indicate the equilibrium output. b. If instead of generating external costs, television production generates external benefits, illustrate the effect of the producers being given a subsidy equal to the external benefits generated, and indicate the equilibrium output.arrow_forward

 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
 Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





