
Prescott's Microbiology
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260211887
Author: WILLEY, Sandman, Wood
Publisher: McGraw Hill
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.4, Problem 1MI
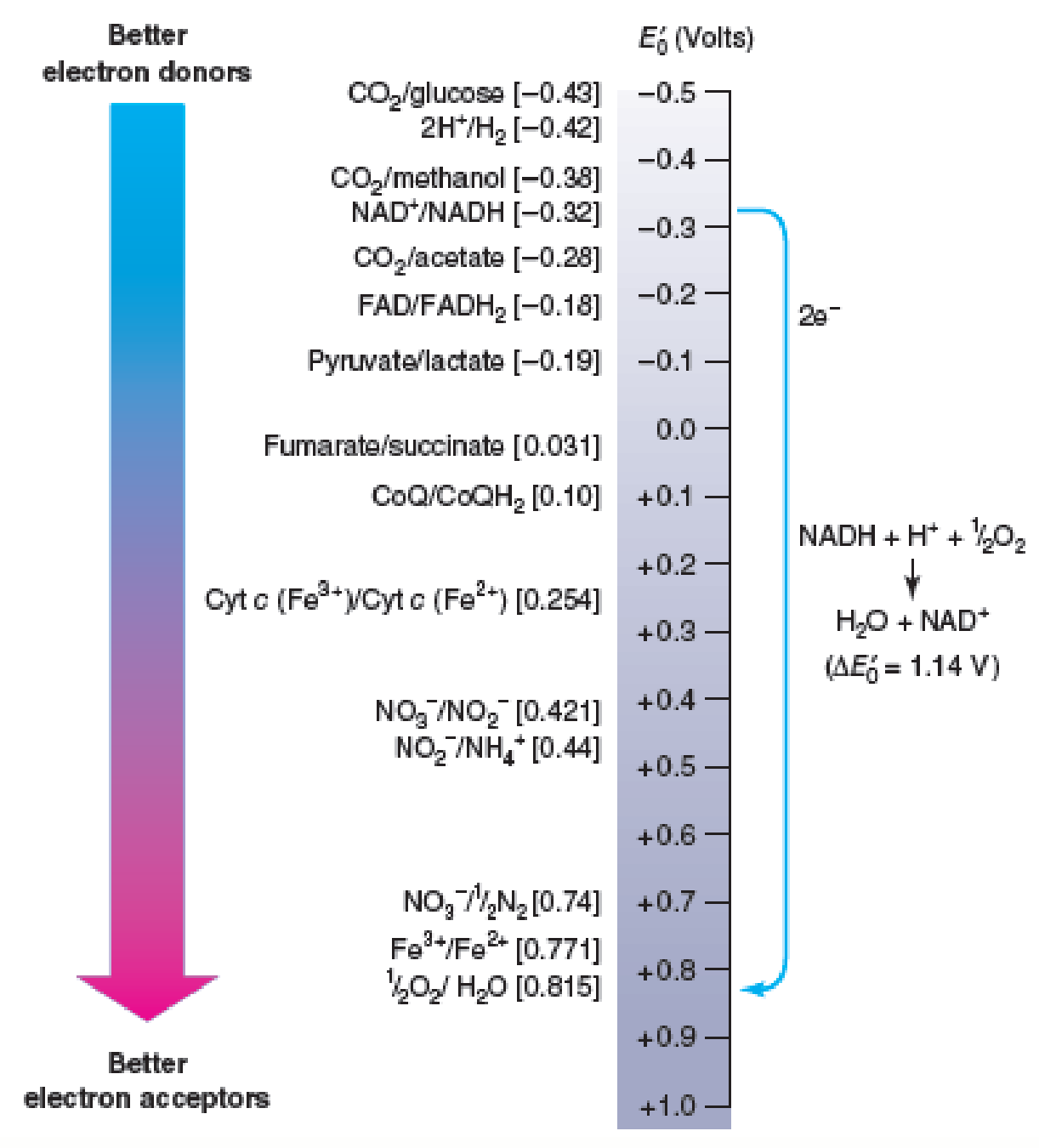
Figure 10.6 Electron Movement and Reduction Potentials. Electrons spontaneously move from donors higher on the tower (more negative potentials) to acceptors lower on the tower (more positive potentials). That is, the donor is always higher on the tower than the acceptor. For example, NADH will donate electrons to oxygen and form water in the process. Some typical conjugate redox pairs are shown on the left, and their reduction potentials are given in brackets.
Refer to figure 10.6 and determine the E′0 for NAD+/NADH and coenzyme Q/CoQH2. Suggest a plausible E′0 value for FMN.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
MAKE A GRAPH FOR ME ON GRAPH PAPER CALL IT ENZYMES VS RATE OF REACTION USING TABLE BELOW
GRAPH paper INSERTED BELOW
rules: data points must be an x or circled dot, must be on grid paper , the independant variable on the x axis and dependant variable on the y axis, must include titles
Regarding the data points:
- H2O2 + MnO2 Control #1: (Control #1, 5)- H2O2 + sand control #2: (Control #2, 0)- Plant versus Animal Liver Catalase: (Liver, 4)- Potato: Plant vs. Animal Catalase: (Potato, 3)- Substance Enzyme Concentration (Used Liver): (Liver Used, 4)- Substance Enzyme Concentration (Used H2O2): (Used H2O2, 1)
- Boiling Water Bath Temperature: (Boiling Water Bath, 5)- Ice Water Bath Temperature: (Ice Water Bath, 2)- HCl, or pH 3: (H 3, 4)- NaOH at pH 12: (pH 12, 2)- pH 7 (H2O): (assuming average of pH readings; pH 7, not specified)
The following explains how to display the graph:
Title: Factors versus Enzyme Activity Rate - Labels on X- and Y-axes: Factors and Rate of Enzyme…
Oxygenic photosynthesis in eukaryotes (in the chloroplasts of green algae and green plants) consumeswhich of the following substrate molecules (to generate glucose, water, and oxygen product molecules)?A. C12H22O11 + H2OB. C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2OC. 6CO2 + 12H2OD. C6H12O6 + C6H12O6E. 6CO2 + 12H2S
Which of the following best indicates a reason why Hisneeds to be a good proton donor (not acceptor) in the catalytic triad mechanism?
So that it can create the alkoxide ion.
So that it can create a hydroxyde ion.
None of the other options is suitable because His's only role is to be a proton acceptor.
So that the first product forms and leaves with the correct number of H's.
So that it can stabilize the transition state.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Prescott's Microbiology
Ch. 10.1 - Figure 10.2 The Relationship of G to the...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 2CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 3CCCh. 10.1 - Prob. 4CCCh. 10.2 - Why is ATP called a high-energy molecule? How is...Ch. 10.2 - Describe the energy cycle and ATPs role in it....Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 1MICh. 10.3 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.4 - Figure 10.6 Electron Movement and Reduction...
Ch. 10.4 - How is the direction of electron flow between...Ch. 10.4 - When electrons flow from the NAD+/NADH conjugate...Ch. 10.4 - Which among the following would be the best...Ch. 10.4 - In general terms, how is G related to E0? What is...Ch. 10.4 - Name and briefly describe the major electron...Ch. 10.6 - Will an enzyme with a relatively high Km have a...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.6 - Prob. 1CCCh. 10.6 - Prob. 2CCCh. 10.6 - How does enzyme activity change with substrate...Ch. 10.6 - What special properties might an enzyme isolated...Ch. 10.6 - What are competitive and noncompetitive...Ch. 10.6 - How are enzymes and ribozymes similar? How do they...Ch. 10.7 - Figure 10.19 Allosteric Regulation. The structure...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 2MICh. 10.7 - Define the terms metabolic channeling and...Ch. 10.7 - Define allosteric enzyme and allosteric effector.Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 3CCCh. 10.7 - Prob. 4CCCh. 10.7 - Prob. 5CCCh. 10 - Prob. 1RCCh. 10 - Prob. 2RCCh. 10 - Prob. 3RCCh. 10 - Examine the structures of macromolecules in...Ch. 10 - Examine the branched pathway shown here for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 3AL
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Image shows reaction for hydrogen ion transport from outside mitochondrion to inside mitochondrion. Part a) What is ∆G ̊ for hydrogen ion transport. Part b) Outside the mitochondria there is a pH of 6.4 and inside mitochondria, there is a pH of 7.4. Calculate Q and ∆G for the reaction shown in the image. Part c) How many hydrogen ions needed per one ATP?arrow_forwardChoose any/all that apply to the proton-motive force and ATP synthesis. The active pumping of protons through ATP synthase against their concentration gradient provides the energy needed for ATP synthesis. The ATP molecules produced from the pair of electrons provided by NADH have greater potential energy than the ATP molecules produced from the pair of electrons provided by FADH2. Each Beta subunit of ATP synthase has a distinct amino acid sequence that accounts for the three different active sites present in the enzyme. Rotation of the Y subunit creates conformational changes in the active sites of ATP synthase that drive the release of ATP from the enzyme. Inhibition of either ATP synthase or ATP translocase will stop flux through the electron-transport chain.arrow_forwardThe production of a hydrogen ion concentration gradient powers the production of ATP in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an organic compound that 'undoes' the hydrogen ion concentration gradient without the production of ATP. It does this by increasing the membrane permeability to hydrogen ions. One use of DNP is as a herbicide.For a brief period in the 1930s, DNP was marketed as a diet pill. Because DNP prevents the production of ATP, the human body will begin to use alternate forms of energy. The result is an increase in the metabolism of fats in the body, thus reducing total body fat. In the presence of DNP, the energy that normally would be converted to ATP for use in the cells is converted to heat instead, causing dangerously high body temperatures.DNP is classified as an illegal substance in Canada and the U.S. although it is still marketed as a commercial chemical. In recent years, several deaths have been reported, primarily in the…arrow_forward
- Referring to the figure below(first picture) explain photosynthetic electron transport. Then compare the process outlined in the figure with figure 1(second picture), What are the similarities and differences?arrow_forwardStarting: Fructose-6- phosphate Ending: Citrate How many NADH and FADH are produced between these in the pathways? How many ATP are generated as you react your starting molecule to your ending molecule? (Assuming all reduced coenzymes go through the ETC to be oxidized).arrow_forwardIn the conversion of acetone to aceto-cyanohydrin, the effect of electron-donating substituents on the tetrahedral intermediate is to: destabilize the charge on oxygen destabilize the carbocation formed make the intermediate more crowded stabilize the charge on oxygenarrow_forward
- Electrons are continuously transferred from higher-energy carriers to lower-energy carriers in the electron transport chain, yet somehow iron is utilized as an electron carrier multiple times. Choose the most likely reason why this is possible. The pH of complex II is slightly higher than the pH of complex III. The reduction potential of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) in complex I is higher than the reduction potential of iron. The redox potential of iron ions can be manipulated by their environment. For instance, the iron in an iron-sulfur cluster will have a different redox potential than the iron in a heme group. The electrons carried by NADH are higher energy than the electrons carried by FADH2.arrow_forwardSmall explanation please. what is a product in the first stage of the Q- cycle? a. two electrons b. Q- cation c. cyt c (oxidized) d. two more protons in the matrix e. Q- radical anionarrow_forwardTrue or False? Electrons after complex III are then sent immediately to complex IV. (during ETC in cellular respiration)arrow_forward
- The oxyanion hole deprotonates an incoming water molecule to convert it to a potent nucleophile. True or False? The oxyanion hole is comprised of hydrogen bonding atoms that project into a space on the active site that will have all H-bonding potential satisfied only during the catalytic cycle of the reaction. True or False? The catalytic triad residues are all next to each other in the primary sequence of trypsin. True or False?arrow_forwardExplain why the coupled reaction ATP → ADP + Pi in the P-class ion pump mechanism does not involve direct hydrolysis of the phosphoanhydride bond.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between resonance energy transfer and photoinduced charge separation? In photoinduced charge separation, an excited electron moves from accessory pigments to the light-harvesting complex. In resonance energy transfer, an excited electron is transferred to a nearby molecule. Photoinduced charge separation of pigments in the light-harvesting complex drives the resonance energy transfer in a reaction center. In resonance energy transfer, the energy of electron excitement is transferred only to an appropriate acceptor. Resonance energy transfer from pigments of a light-harvesting complex drives the photoinduced charge separation in a reaction center.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to the NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods Fifth edition; Author: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B5rUrKLMoas;License: Standard Youtube License