
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a. 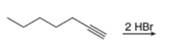 f.
f. 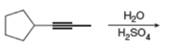
b. 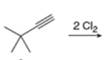 h.
h. 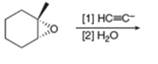
d. 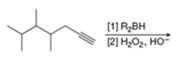 i.
i. 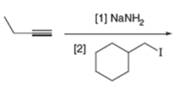
e. 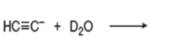 j.
j. 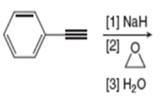
(a)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The addition of an electrophile to an alkyne is followed by Markovnikoff’s rule and anti-stereoselectivity.
The addition of a halogen to an alkyne chain leads to the formation of corresponding alkene or alkane. The reaction which includes the addition of bromine atoms to the alkyne chain is known as bromination. Bromination can be done by using the reagents like
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Figure 1
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(b)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The addition of an electrophile to an alkyne is followed by Markovnikoff’s rule and anti-stereoselectivity.
The addition of a halogen to an alkyne chain leads to the formation of corresponding alkene or alkane. The reaction which includes the addition of bromine atoms to the alkyne chain is known as bromination. Bromination can be done by using the reagents like
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
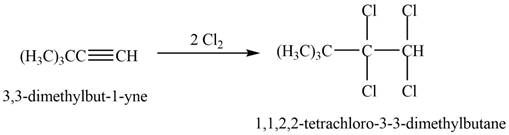
Figure 2
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(c)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The addition of a halogen to an alkyne chain leads to the formation of corresponding alkene or alkane. The reaction which includes the addition of bromine atoms to the alkyne chain is known as bromination.
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
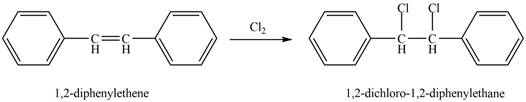
Figure 3
The reaction of
The reaction of
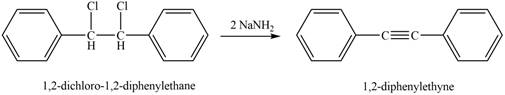
Figure 4
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(d)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A stepwise procedure of transforming an alkyne into a carbonyl group is known hydroboration-oxidation reaction. In a hydroboration-oxidation reaction, a terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is heptanal.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
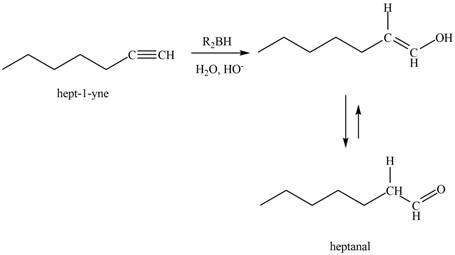
Figure 5
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is heptanal.
(e)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is deuteroacetylene.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
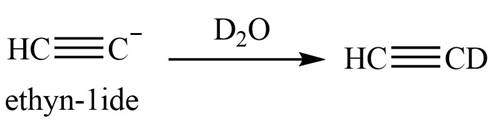
Figure 6
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is deuteroacetylene.
(f)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
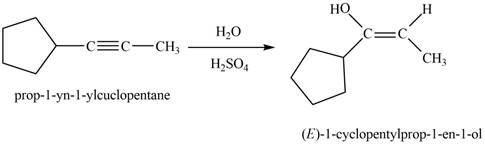
Figure 7
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(g)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
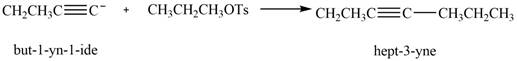
Figure 8
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(h)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
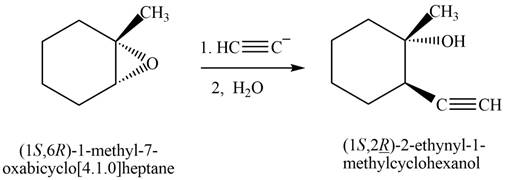
Figure 9
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(i)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
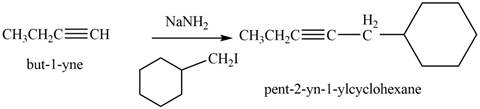
Figure 10
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
(j)
Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Answer to Problem 11.38P
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of ethynylbenzene with
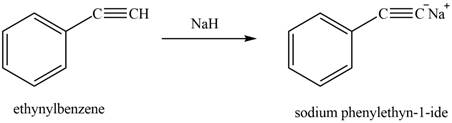
Figure 11
The reaction of ethynylbenzene with
The reaction of
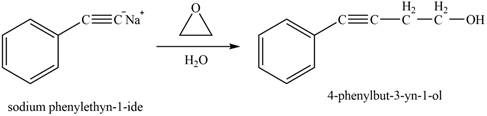
Figure 12
The reaction of
The product that is formed by the reaction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (5th Edition) (Standalone Book)
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
