
Concept explainers
Answer the following questions about aldosterone, a compound that helps to control the absorption of Na+and Cl- ions in the kidneys and, as a result, affects water retention.
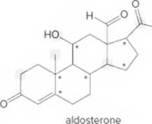
- Identify the
functional groups . - Draw in all lone pairs on O atoms.
- How many C’s does aldosterone contain?
- How many H’s are present at each C labeled with an asterisk (*)?
- Give the shape around each atom labeled in gray.
- Label all polar bonds.
(a)
Interpretation:
The functional group in aldosterone should be midentified.
Concept Introduction:
Functional groups are the atoms or group of atoms that gives chemical properties to an organic compound and also chemical reactivity centre. Examples of functional groups are aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, double bond.
Answer to Problem 83P
In aldosterone, functional groups present are alcohol, aldehyde, ketone and alkene.
Explanation of Solution
Functional groups are the atoms or group of atoms that gives chemical properties to an organic compound and also chemical reactivity centre. Structures of different functional groups are as follows:
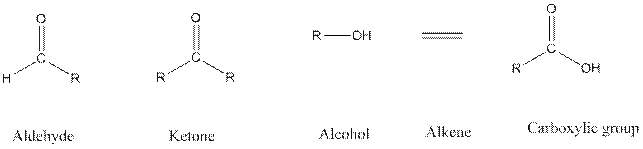
R represents any alkyl chain.
In functional group ketone carbonyl carbon is bonded to two alkyl groups, in aldehyde carbonyl carbon is attached to one alkyl group and one hydrogen atom, in alcohol functional group an −OH is bonded to an alkyl group.
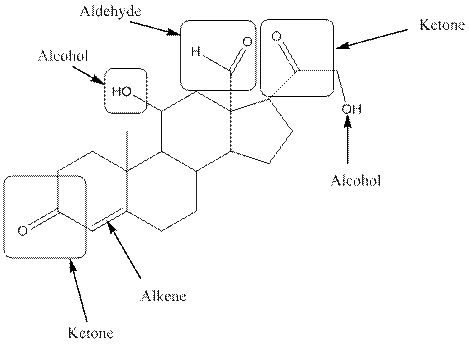
The compound aldosterone consists of two alcohol frunctional group, two ketone functional groups and one aldehyde functional group and one alkene. So, four types of functional group, that is, alcohol, aldehyde, ketone and alkene.
(b)
Interpretation:
All the lone pairs on oxygen atom of aldosterone should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxygen atom has six valence electrons. The electrons which are used in bond formation are called bonding electrons. The electrons that remain on an atom after bond formation are called lone pair electrons.
Answer to Problem 83P
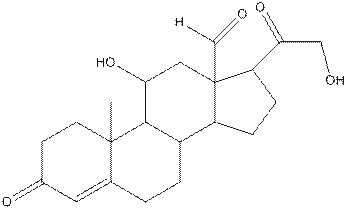
The structure of aldosterone having all lone pairs on oxygen atom is,
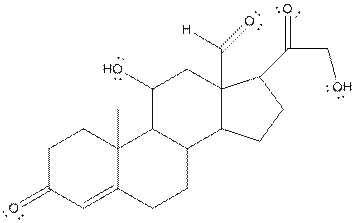
Explanation of Solution
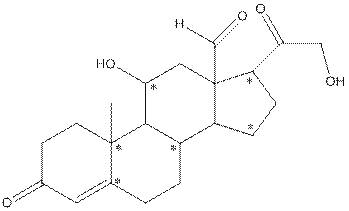
The structure of aldosterone is as follows:
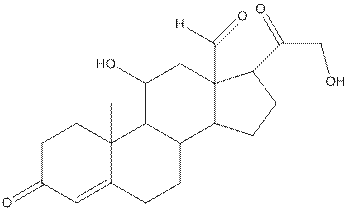
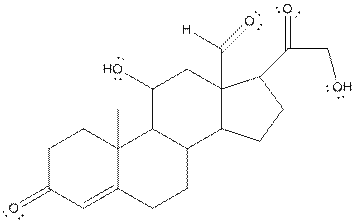
In the compound, three double bonded oxygen atoms present. Oxygen has six valence electrons. Two electrons in all double bonded oxygen atoms are used for formation of double bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pair. Also the compound contains three single bonded oxygen atoms. One electron is used for making O-H bond and one electron is used for making O-C bond. Remaining four electrons present as two lone pairs on each single bonded oxygen atom. Hence, the structure having all lone pairs on oxygen atom is,
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of carbon atoms in the structure of aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
Answer to Problem 83P
Twenty one carbon atoms present in the aldosterone.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of aldosterone is given as follows:
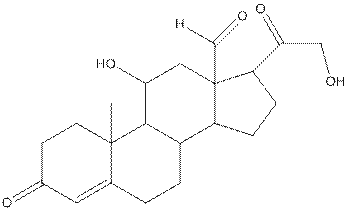
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
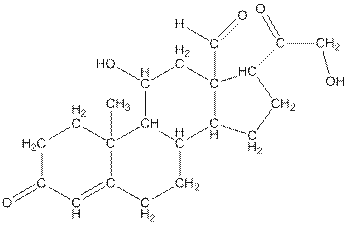
Hence, twenty one carbon atoms present in the compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of hydrogen atoms present in the * carbon atoms in aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
Answer to Problem 83P
The * carbon atoms have total five hydrogen atoms.
Explanation of Solution
In skeletal structure the terminals represent methyl
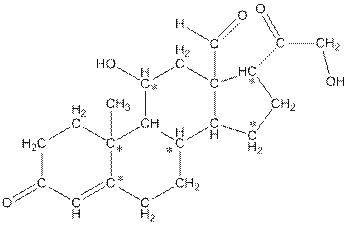
Hence, the * carbon atoms have total five hydrogen atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
The shape around each indicated carbon atom in aldosterone should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The following table should be used while determining the shape around an atom.
| Number of groups | Number of atoms | Number of lone pairs | Shape | Bond angle |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | Linear | |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | Bent |
Answer to Problem 83P
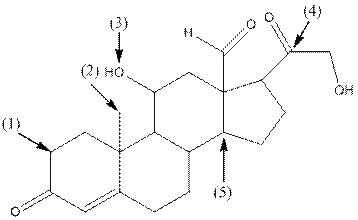
- Shape around carbon (1) is tetrahedral, shape around carbon (2) is tetrahedral, shape around oxygen (3) is bent, shape around carbon (4) is trigonal planar and shape around carbon (5) is tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
The complete structure of aldosterone is as follows:
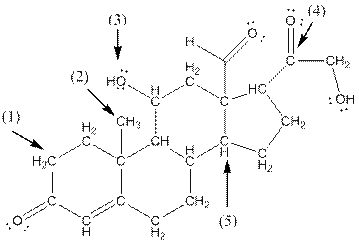
- Carbon (1) has four groups ( two hydrogen and two carbon) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (1) is tetrahedral.
- Carbon (2) has four groups (three hydrogen and one carbon) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (2) is tetrahedral.
- Oxygen (3) has two groups (one carbon and one hydrogen) and two lone pairs surrounding it. So, shape around oxygen (3) is bent.
- Carbon (4) has three groups (two carbon and one oxygen) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (4) is trigonal planar.
- Carbon (5) has four groups (three carbon and one hydrogen) surrounding it. So, shape around carbon (5) is tetrahedral.
(f)
Interpretation:
All the polar bonds in aldosterone should be labeled.
Concept Introduction:
The unequal sharing of valence electrons in a bond is called polar bond. Polar bond result when the bond formed between two atoms in which one atom is more electronegative than the other one. One example of polar bond is
Structure of HCl is as follows:

In
Answer to Problem 83P
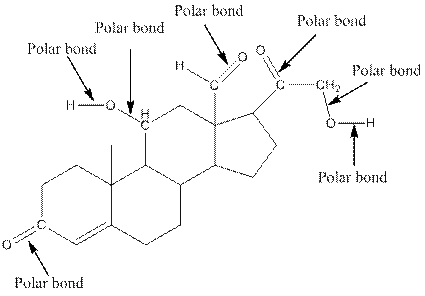
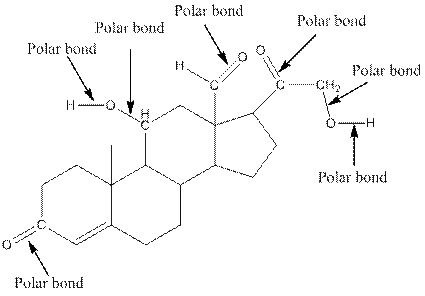
The structure of aldosterone with all polar bonds is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
In organic compound, most of the polar bonds formed between carbon and heteroatoms like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. To identify the polar bonds in the compound aldosterone, find the bonds between carbon and oxygen or oxygen and hydrogen because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. In aldostrone, five polar bonds are formed between carbon and oxygen (oxygen is more electronegative than carbon) and two polar bonds present between oxygen and hydrogen (oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen). Thus, the polar bonds are:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- 10-27 What is meant by the term functional group?arrow_forwardHow many electron pairs are shared when a triple bond exists between two carbon atoms? What must he the geometric arrangement around the carbon atoms in a triple bond? Draw the Lewis structure of a simple molecule that contains a triple bond.arrow_forwardDraw the organic compound based on the following and answer the questions that follows. a. what organic compound is the structure? b. how many substituents are present in the structure? c. how many functional groups are present in the structure? 1. All carbons are sp3 hybrid. 2.C9, C10 and C11 are primary carbons. 3. C1, C4 and C5 are tertiary carbons. 4. C12 connects C11 and C4. 5. C3 and C6 have one hydroxyl substituent each. 6. C1 to C8 are connected end to end.arrow_forward
- Draw structures that fit each description and name the functional group in each molecule: (a) two constitutional isomers with molecular formula C5H10O that contain different functional groups; (b) two constitutional isomers with molecular formula C6H10O that contain the same functional group.arrow_forwardWhich functional group or groups are not present in the compound shown in Figure 1. * A- Alcohol B- Amide C- Ether D- Alkyne E- All these functional groups are present in the compound.arrow_forward1. How many total covalent bonds are present in the compound? (Please refer to the first image attached.) A. 8 B. 10 C. 12 D. 16 2. What is the correct IUPAC name for this compound? (Please refer to the second image attached.) A. 2,5,5-Trimethylhexane B. 2,2,5-Trimethylhexane C. 2,2,5-methylhexane D. 2,5,5-methylhexane 3. Which of the following is a tertiary alcohol? A. 2-Pentanol B. 2-Methyl-2-butanol C. 1-Butanol D. 2-Methyl-1-pentanolarrow_forward
- Identify each other functional groups that are boxed out in the compounds below. Put your answers on the lines next to the boxed functional groups.arrow_forwardChange 1,2-ethanediol into 1,2 ethenediol (HOCHCHOH) by removing one hydrogen atom from each carbon atom and replacing with a double bond between the carbon atoms. Be sure to add the second rod to represent the double bond. Draw a Lewis structure for 1,2-ethenediol. A. Identify the electron-pair and molecular geometry around each carbon and oxygen atom. B. What are the bond angles for H-C-C? For C-C-O? For C-O-H? C. Draw two different structures of the molecule in which the –OH group on the two carbon atoms occupy different orientations with respect to each other.arrow_forward1. Give any organic pharmaceutical drug or any organic molecule useful in the medical profession. ONE MOLECULE ONLY. Make sure that the molecule has at least three different functional groups. If your molecule has more than three, the better. 2. Draw the molecule (by hand, or you can copy the molecular drawing from a source, cite the source). 3. BRIEFLY discuss the use of your chosen molecule. 4. Identify ALL functional groups present in your molecule.arrow_forward
- Circle any and all functional groups present in the following organic molecules. After identifying the functional groups, identify which class(es) of compound(s) the molecule belongs to. Molecule Name Molecules Classes of Compounds? Acetaminophen in pictures Acetic Acid Aspirin Isopropyl Alcohol Ethyl Alcohol Benzoic Acid Chloroform Formaldehyde Glycine Dimethylether Serine Methylsalicylate Acetonearrow_forwardFollowing is the structure of cortisone, a corticosteroid that increases the blood glucose level and stimulates the synthesis of glycogen in the liver. What functional groups are in cortisone? Group of answer choices a. ketone group, aldehyde group, and carboxyl group, b.hydroxyl group, carboxyl group, and ether group c. hydroxyl group, ketone group, and alkene group d. ester group, amide group, and alkene grouparrow_forwardComplete the table by checking the box next to each nitrogen-containing functional group the molecule contains.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



