
Concept explainers
The three-dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position
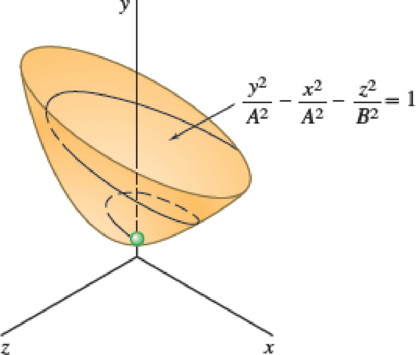
Fig. P11.96
(a)
The magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec.
Answer to Problem 11.96P
The magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec are
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The three dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position vector is
The curve described by the particle lies on the hyperboloid is
The value of A and B are 3 and 1 respectively.
Calculation:
Write the three dimensional motion of a particle position vector equation.
Here, x is
Consider x:
Consider y:
Consider z:
Calculate the
Substitute
Check whether the position vector equation satisfied the curve equation or not.
Substitute
Hence, the equation is satisfied.
Rewrite the Equation (1).
Substitute 3 for A and 1 for B in Equation (1).
Write the expression for velocity using the relation:
Substitute
Calculate velocity vector
Substitute 0 for t in Equation (5).
Here,
Calculate the magnitude of velocity (v) using the relation:
Substitute
Write the expression for acceleration vector using the relation:
Substitute
Substitute 0 sec for t.
Here,
Calculate the magnitude
Substitute 0 is
Therefore, the magnitude of the velocity (v) and acceleration (a) when time is 0 sec are
(b)
The smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other.
Answer to Problem 11.96P
The smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The three dimensional motion of a particle is defined by the position vector is
The curve described by the particle lies on the hyperboloid is
The value of A and B are 3 and 1 respectively.
Calculation:
Write the equation if the position vector and velocity vector are perpendicular:
Substitute
Using trial and error method the smallest root is (t) is 4.38 sec.
Therefore, the smallest nonzero value of t for which the position vector and the velocity are perpendicular to each other is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A particle travels to the right along a straight line with a velocity v = [5/(4+s)]m/s where s is in meters. Determine its position when t = 6 s if s = 5 m when t = 0.arrow_forward1. The motion of a particle is defined by the relation x = t^3 - 9t^2 + 24t - 8, where x and t are expressed in inches and seconds, respectively. Determine: 1. when the velocity is zero in seconds, 2. the position in inches, 3. and the total distance traveled in inches when the acceleration is zero.arrow_forwardA particle travels along a straight line with a velocity of v = (7t -4t^2) m/s, where t is in seconds.Determine the position of the particle when t = 5s. Note that s = 0 when t = 0. Determine the total distance traveled by the particle after 8 seconds.arrow_forward
- a particle is moving along a straight line such that its position is defined by 2=10t^2+20 where t is in seconds and s in mm. determine thedisplacement )in mm) of the particle during the timeinterval from t=1s. to t=5s.arrow_forwardIf the x and y components of a particle’s velocity are vx = (32t) m/s and vy = 8m/s, determine the equation of the path y = f(x), if x = 0 and y = 0 when t = 0.arrow_forward1.The car is traveling at 48 km/h when the traffic light 90mahead turns yellow. The driver takes one second to reactbefore he applies the brakes.(a) After he applies the brakes, what constant rate ofdeceleration will cause the car to come to a stop just asit reached the light?(b) How long does it take the car to travel the 90 m?arrow_forward
- A particle strikes the smooth surface with a velocity of 30 m/s. If e = 0.8, (Vx) 2 is _____ after the collision. zero equal to (Vx) 1 less than (Vx) 1 greater than (Vx) 1arrow_forwardIn a basketball game, the point guard A intends to throw a pass to the shooting guard B, who is breaking toward the basket at a constant speed of 12 ft/sec. If the shooting guard is to catch the ball at a height of 7 ft at C while in full stride to execute a layup, determine the speed v, and launch angle 6 with which the point guard should throw the ball. A Vo 7~ e 5/arrow_forwardA race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 70 m. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is travelling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s2. Three seconds later, determine the followingarrow_forward
- A particle travels along a straight line with a velocity of v = (4t - 3t^2) m/s, where t is in seconds. Determine the position of the particle when t = 4 s. s = 0 when t = 0.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle, measured from a rectangular coordinate system (X, Y, Z)is given by ? = [t3i + 8t2j + (5t + 2) k ]m/s, where t is given in seconds. If the particle is at the origin (x = 0, y = 0, z = 0) when t = 0 s, determine: (a) The intensity of the particle velocity when t = 4 s (b) The intensity of the particle acceleration when t = 4 s (c) The position of the particle in coordinates (x, y, z) when t = 4 sarrow_forwardThe motion of a particle is defined by the relation x = (at + b)4 where x and t are expressed in centimeter and seconds, respectively. Determine the velocity (in cm/s) of the particle at t = 2.41 seconds if a = 5 and b = 8.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





