
Concept explainers
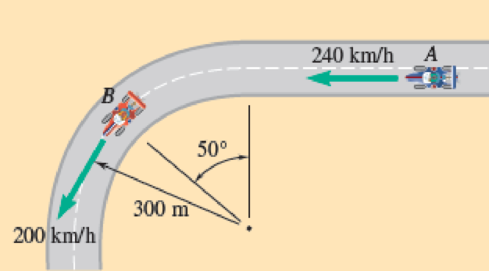
Race car A is traveling on a straight portion of the track while race car B is traveling on a circular portion of the track. At the instant shown, the speed of A is increasing at the rate of 10 m/s2, and the speed of B is decreasing at the rate of 6 m/s2. For the position shown, determine (a) the velocity of B relative to A, (b) the acceleration of B relative to A.
Fig. P11.141
(a)
The relative velocity
Answer to Problem 11.141P
The relative velocity
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The speed
The speed
The speed
The speed
The radius of the circular path
Calculation:
Convert unit kilometer per hour to meter per second.
Consider the velocity
Consider the velocity
Write the velocity of B
Write the velocity of A
Calculate the relative velocity vector
Substitute
Here,
Calculate the relative velocity
Substitute
Calculate the angle
Substitute
Therefore, the relative velocity
(b)
The relative acceleration
Answer to Problem 11.141P
The relative acceleration
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The speed
The speed
The speed
The speed
The radius of the circular path
Calculation:
Calculate the normal acceleration
Substitute
The normal acceleration at an angle:
Write the normal acceleration of B
Substitute
Write the tangential acceleration
Substitute
Write the tangential acceleration
The normal acceleration
Calculate the relative acceleration vector
Rewrite the above equation.
Substitute
Here,
Calculate the relative acceleration
Substitute,
Calculate the angle
Substitute,
Therefore, the relative acceleration
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A snowboarder starts from rest at the top of a double black diamond hill. As she rides down the slope, GPS coordinates are used to determine her displacement as a function of time: x = 0.5t^3 + t^2 + 2t, where x and t are expressed in feet and seconds, respectively. x is measured along the surface of the hill. Determine the position, velocity, and acceleration of the boarder when t = 5 seconds. (x=___ft; v=___ft/s; a=___ft/s^2arrow_forwardTown A is 11 miles west of Town B. A man walks from A to B at the rate of 3 miles per hour, and another man, starting at the same time, walks from B to A at the rate of 4 miles per hour. Determine the following: a) The times after starting, that the men are 2 miles apart. b) Explain the concepts/principles that were considered and the factors that affected the condition of item (a)arrow_forwardCar A is traveling at 40 mi/h when it enters a 30 mi/h speed zone. The driver of car A decelerates at a rate of 16 ft/s2 until reaching a speed of 30 mi/h, which she then maintains. When car B , which was initially 60 ft behind car A and traveling at a constant speed of 45 mi/h, enters the speed zone, its driver decelerates at a rate of 20 ft/s2 until reaching a speed of 28 mi/h. Knowing that the driver of car B maintains a speed of 28 mi/h, determine (a) the closest that car B comes to car A, (b) the time at which car A is 70 ft in front of car B.arrow_forward
- To study the performance of a race car, a high-speed camera is positioned at point A. The camera is mounted on a mechanism which permits it to record the motion of the car as the car travels on straightaway BC. It took 0.5 s for the car to travel from the position θ = 60° to the position θ = 35°. Knowing that b = 24 m, determine the average speed of the car during the 0.5-s interval. The average speed of the car during the 0.5-s interval is ______ km/h.arrow_forwardJack run on a marathon with a speed that can be approximated by the relation v= 6.5(1.2 - 0.05x) ^ 0.3, where v and x are expressed in mi/h and miles respectively. Knowing that x= 0 at t = 0, determine (a.) the distance Jack has run when t =1h, (b) Jack's acceleration in ft/s^2 at t=0, (c.) the time required for him to run 6 mi. helppparrow_forwardTwo road rally checkpoints A and B are located on the same highway and are 8 mi apart. The speed limits for the first 5 mi and the last 3 mi are 60 mi/h and 35 mi/h, respectively. Drivers must stop at each checkpoint, and the specified time between points A and B is 10 min 20 s. Knowing that the driver accelerates and decelerates at the same constant rate, determine the magnitude of her acceleration if she travels at the speed limit as much as possible.arrow_forward
- The acceleration of a particle is defined by the relation a=-k/x. It has been experimentally determined that v= 15 ft/s when x= 0.6 ft and that v= 9 ft/s when x= 1.2 ft. Determine (a) the velocity of the particle when x= 1.5 ft, (b) the position of the particle at which its velocity is zero.arrow_forwardCars A and B are traveling in adjacent highway lanes and at t = 0 s have the position and velocity shown. If vA = 11 km/h , vB = 25 km/h , S = 876 m, and knowing that car A has a constant acceleration of 0.69 m/s2 and that B has a constant deceleration of 0.23 m/s2, determine the relative position of car B with respect to car A at the moment the velocity of car B is zero. Round off your final answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardA Scotch yoke is a mechanism that transforms the circular motion of a crank into the reciprocating motion of a shaft (or vice versa). It has been used in a number of different internal combustion engines and in control valves. In the Scotch yoke shown, the acceleration of Point A is defined by the relation a=-1.5sin(kt) , where a and t are expressed in m/s2 and seconds, respectively, and k=3 rad/s. Knowing that x=0 and v=0.6 m/s when t =0, determine the position of Point A when t=0.5 s.arrow_forward
- The acceleration of a particle is defined by the relation a = –kv^2.5, where k is a constant. The particle starts at x = 0 with a velocity of 16 mm/s, and when x = 14 mm, the velocity is observed to be 8 mm/s. Determine the velocity of the particle when x = 5 mm. in mm/sarrow_forwardA commuter train traveling at 40 mi/h is 3 mi from a station. The train then decelerates so that its speed is 20 mi/h when it is 0.5 mi from the station. Knowing that the train arrives at the station 7.5 min after beginning to decelerate and assuming constant decelerations, determine (a) the time required for the train to travel the first 2.5 mi, (b) the speed of the train as it arrives at the station, (c) the final constant deceleration of the train.arrow_forwardA Scotch yoke is a mechanism that transforms the circular motion of a crank into the reciprocating motion of a shaft (or vice versa). It has been used in a number of different internal combustion engines and in control valves. In the Scotch yoke shown, the acceleration of point A is defined by the relation a = -1.8 sin kt, where a and t are expressed in m/s2 and seconds, respectively, and k = 3 rad/s. Knowing that x= 0 and v = 0.6 m/s when t= 0, determine the velocity and position of point A when t = 0.5 s.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





