
a) NaBH4 and H3O+
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
NaBH4, either in water or in alcohol reduce
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 58AP
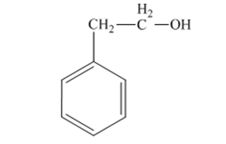
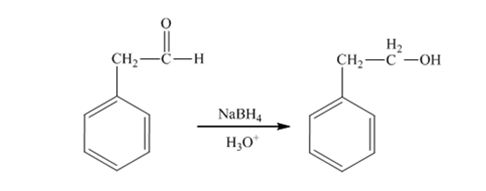
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 2-phenylethanol.
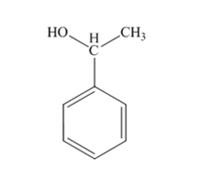
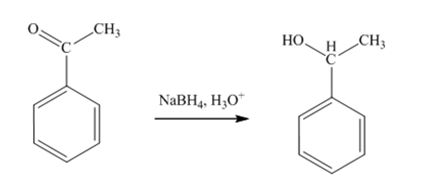
The product produced when acetophenone is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 1-phenylethanol.
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde, being an aldehyde is reduced by NaBH4 to a primary alcohol, 2-phenylethanol.
Acetophenone, being a ketone is reduced by NaBH4 to a secondary alcohol, 1-phenylethanol.
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 2-phenylethanol.

The product produced when acetophenone is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 1-phenylethanol.

b) Dess-Martin reagent
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with Dess-Martin reagent are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones are not oxidized by Dess-Martin reagent.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with Dess-Martin reagent.
Answer to Problem 58AP
Phenylacetaldehyde does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Acetophenone does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes and ketones are not oxidized by Dess-Martin reagent.
Phenylacetaldehyde does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Acetophenone does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
c) NH2OH, HCl catalyst
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxyl amne in the presence of an acid catalyst to yield aloximes and ketoximes respectively.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
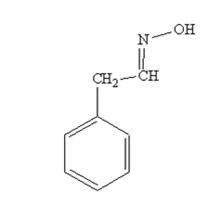
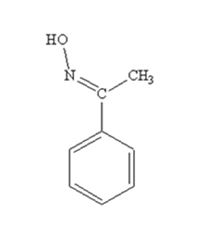
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
Explanation of Solution
phenylacetaldehyde reacts with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalystto yield phenylacetaldoxime.
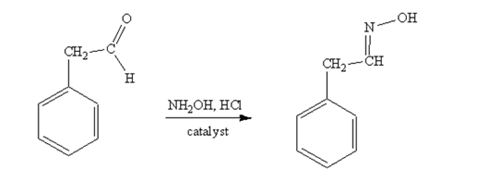
Acetophenone reacts with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to give acetophenoneoxime.
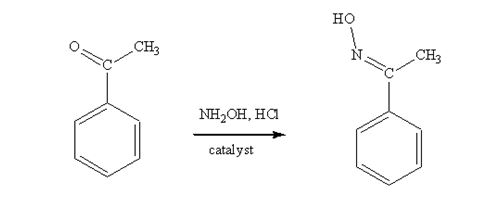
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

d) CH3MgBr and H3O+
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
On treatment with Grignard reagents followed by acidification, aldehydes other than formaldehyde yield secondary alcohols and ketones give tertiary alcohols.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is
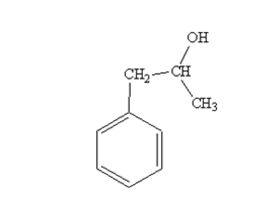
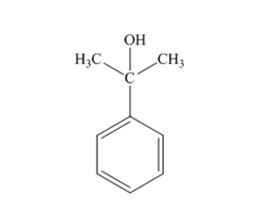
The products produced when acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is
Explanation of Solution
When phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ the product produced is 1-phenyl-2-propanol, a secondary alcohol.
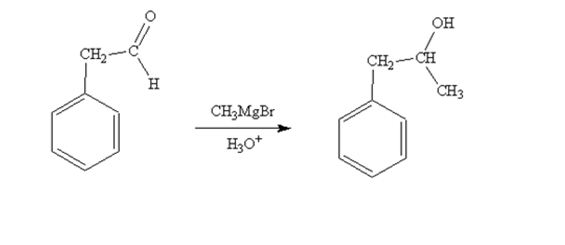
When acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ the product produced is 2-phenyl-2-propanol, a tertiary alcohol.
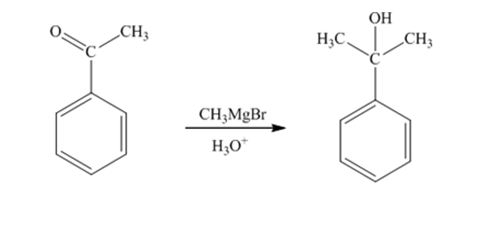
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is

The products produced when acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is

e) CH3OH, HCl catalyst
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes react reversibley with two equivalents of an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to yield acetals and ketones react to give ketals.
To give:
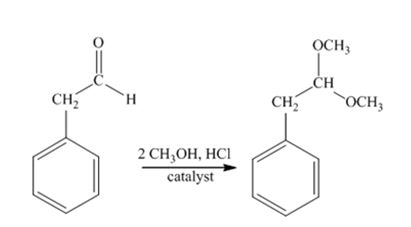
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
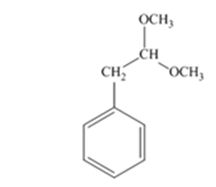
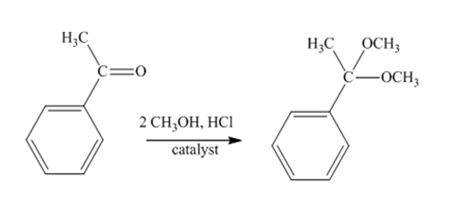
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
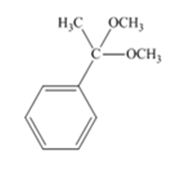
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to yield an acetal.
Acetophenone reacts with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to yield a ketal.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

f) NH2NH2, KOH
Interpretation:
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2NH2 in the presence of KOH are to be given.
Concept introduction:
The aldehydes and ketones undergo Wolff-Kishner reduction to yield
To give:
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NH2NH2 and KOH.
Answer to Problem 58AP
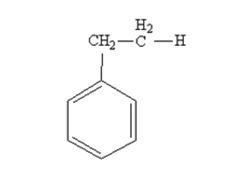
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is
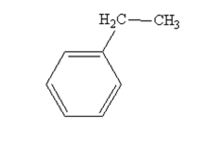
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is
Explanation of Solution
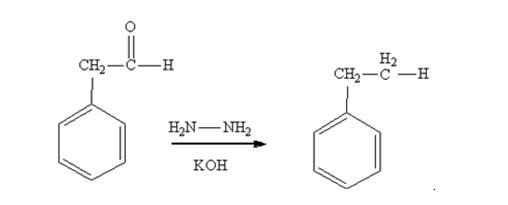
Phenylacetaldehyde is reduced by NH2NH2 and KOH to ethylbenzene.
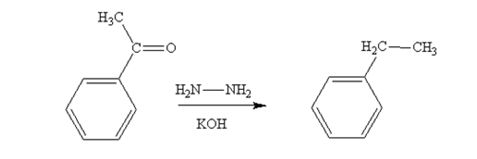
Acetophenone also is reduced by NH2NH2 and KOH to ethylbenzene.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is

g) (C6H5)3P=CH2
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 are to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction given is Wittig reaction. Aldehydes and ketones are converted into
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2.
Answer to Problem 58AP
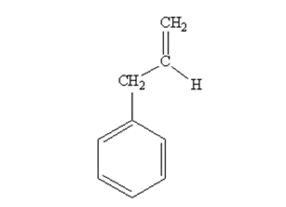
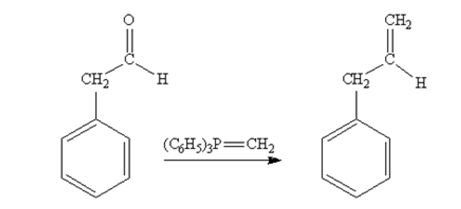
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is
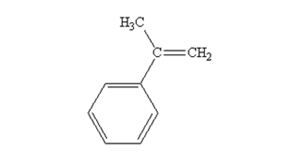
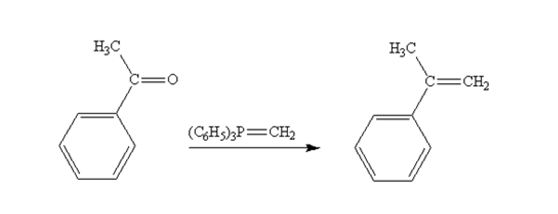
The product produced when acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with with (C6H5)3P=CH2 to yield 3-phenylpropene.
Acetophenone reacts with with (C6H5)3P=CH2 to yield 2-phenylpropene.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is

The product produced when acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is

h) HCN, KCN
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with HCN, KCN are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with HCN, KCN to yield their cyanohydrins.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN is
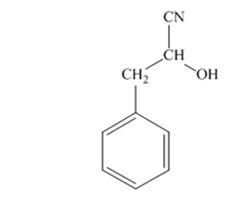
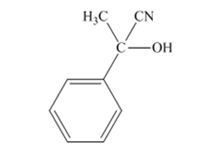
The products produced when acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN is
Explanation of Solution
When phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN, it gives phenylacetaldehydecyanohydrin.
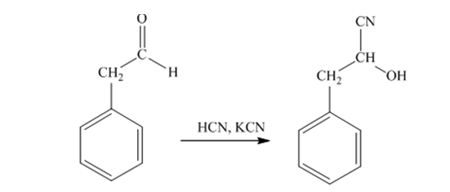
When acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN, it gives acetophenonecyanohydrin.
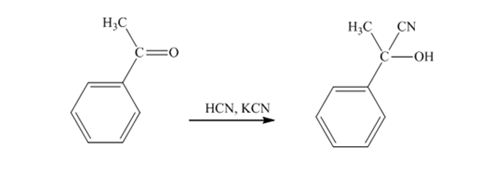
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN is

The products produced when acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Consider the series of the trans effect: CO, CN-, C2H4 > PR3, H-, CH3- > C6H5- > NO2-, SCN-, I- > Br- >Cl- > py > NH3 > H20 What would be the major product of the following reaction? Select one:arrow_forwardpredict the major product of the reaction sequence below and how many stereoisomers would be producedarrow_forwardpredict the major product of the reaction sequence below and how many stereoisomers of the major product would be producedarrow_forward
- Identify the major product/S of these reactions:arrow_forwardWrite down the mechanism of the reactions given below and find the resulting product.arrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions: [PtCl4]2- + NO2- → (a) (a) + NH3 → (b) [PtCl3NH3]- + NO2- →(c) (c) + NO2- → (d) [PtCl(NH3)3]+ + NO2- → (e) (e) + NO2- → (f) [PtCl4]2- + I- → (g) (g) + I- → (h) [PtI4]- + Cl- →(i) (i) + Cl- → (j)arrow_forward
- Conformation control of reaction mechansims. Consider the reaction below: Provide all possible elimination products from this reaction and identify the major elimination product. Provide mechanisms (with curved arrows) that clearly explain the reaction outcome.arrow_forwardPlease give a detailed stepwise mechanism for the following reactions of Q.1 and Q.2. All arrows, charges, intermediates, and resonance structures must be shown.arrow_forward3-Bromo-1-butene and 1-bromo-2-butene undergo SN1 reaction at nearly the same rate, even though one is a secondary halide and the other is primary. Explain.arrow_forward
