
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
If the given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement istrue.
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds. The combustion reaction takes place in the presence of air. The combustion of alkenes produces carbon dioxide and water.
Hence, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition reaction of alkenes is one double bond of alkene and one single bond of a second reactant break, and three new single bonds are formed such that the addition of the second reactant occurs at the carbon atoms of the double bond. Hence, the two new single bonds are formed at the doubly bonded carbon atoms. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Regioselectivity means the preference of making or breaking of bonds over all other possibilities. Markovnikov's rule states that in the addition of a halogen acid to an alkene, hydrogen goes to the carbon atom in a double bond that bears a higher number of hydrogen atoms. Thus, it indicates the position of the attack. Hence, Markovnikov's rule refers to the regioselectivity of the carbon-carbon double bond. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Markovnikov's rule states that addition of a halogen acid (HX, x = Cl, Br or I) to an alkene, hydrogen goes to the carbon atom in the double bond that bears a higher number of hydrogen atoms. In additionof HCI, HBr, and HI to an alkene, hydrogen attaches to the carbon of the double bond that already has a greater number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
A carbocation is a carbon atom with three bonds and is deficient in one pair of the electrons, thus, acquiring a positive charge. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The carbocation is derived from ethylene by the attack of a proton as depicted in the equation is CH3 CH2 +.
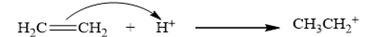
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The mechanism of the addition of HX to an alkene is a two-step reaction.
Step 1: The formation of the carbocation. In the first step of the reaction, the proton is added to the double bond, and the carbocation is generated as carbocation intermediate.
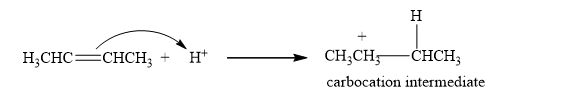
Step 2: The Nucleophilic attack. Then, a halide ion which is a nucleophile attacks the carbocation, forming an additional product.
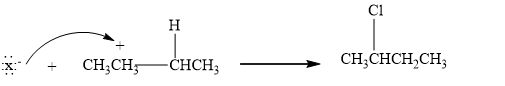
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of water is known as hydration. According to Markovnikov's rule, in acid, the catalyzed addition of water to an alkene water molecule is added to the carbon-carbon double bond. Furthermore, in the presence of acid, the alkene is converted to alcohol. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of Br2 to a carbon-carbon double bond takes place at room temperature. Thus, if a compound fails to react with Br2, then the compound does not contain a double bond. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of H2 is known as reduction. During a reaction with molecular H2, all of the alkenes, are converted to alkanes. Hence, hydrogen is added to the double bond of an alkene. Thus, the given statement is true.
(k)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Catalytic reduction is the process in which a substance is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. The catalytic reduction of cyclohexene is the addition of H2 across the double bond that is present in the cyclic ring. The resultant product is cyclohexane, not hexane. Thus, the given statement is false.
(l)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The acid catalyzed hydration of alkene is completed in three steps. The first step includes the addition of a proton (from acid) to the double bond that results in the formation of a carbocation, and hydrogen attaches to one of the doubly bonded carbons. In the second step, an oxygen atom of a water molecule attacks the positively charged carbon, and the water molecule attaches to it, forming an intermediate called an oxonium ion. In the third step, the proton is regenerated again by losing H+ from the oxonium ion, Therefore, in the final product, OH comes from a water molecule, while H comes from the acid used as a catalyst. Thus, the given statement is false.
(m)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation is characterized as a gain in oxygen or a loss of hydrogen or a molecule. The alkene on the acid-catalyzed hydration is converted into alcohol. Thus, the conversion of CH2 = CH2 to ethanol is an addition reaction in which a molecule of water is added to the double bond. Thus, there is neither a loss of hydrogen nor a gain of oxygen. Hence, this is an addition reaction and not an oxidation reaction, so, the given statement is false.
(n)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
According to Markovnikov's rule, in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkene, water is added to the double bond of alkene such that the addition of the H and OH groups occur. Furthermore, it says that H is added to the carbon with more of the hydrogen atoms. The acid catalyzed hydration of 1-butene and 2-butene both result in the formation of 2-butanol. Hence the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Summarize the nomenclature rules for alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic compounds. Correct the following false statements regarding nomenclature of hydrocarbons. a. The root name for a hydrocarbon is based on the shortest continuous chain of carbon atoms. b. The suffix used to name all hydrocarbons is -ane. c. Substituent groups are numbered so as to give the largest numbers possible. d. No number is required to indicate the positions of double or triple bonds in alkenes and alkynes. e. Substituent groups get the lowest number possible in alkenes and alkynes. f. The ortho- term in aromatic hydrocarbons indicates the presence of two substituent groups bonded to carbon- 1 and carbon-3 in benzene.arrow_forwardDodecane, C12H26, is an unbranched alkane Predict the following: Will it dissolve in water? Will it dissolve in hexane? Will it burn when ignited? Is it a liquid, solid, or gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure? Is it more or less dense than water?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





