
Chemical/Bio Engineering
Figure P12.12 depicts a chemical exchange process consisting of a series of reactors in which a gas fl owing from left to right is passed over a liquid fl owing from right to left. The transfer of a chemical from the gas into the liquid occurs at a rate that is proportional to the difference between the gas and liquid concentrations in each reactor. At steady state, a mass balance for the first reactor can be written for the gas as
and for the liquid as
Where
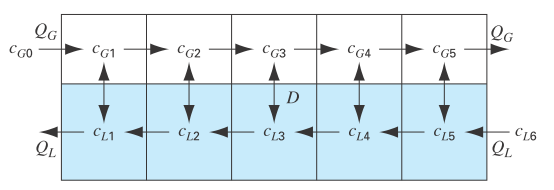
FIGURE P12.12
To calculate: The flow rate of the flow through every pipe if the flow equation through he reactors is provided by following system of equations:
For gas it is provided as:
And for liquid it is provided as:
Answer to Problem 12P
Solution: The concentration of liquid and gases in the reactor is:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The system of reactors is provided as follows:
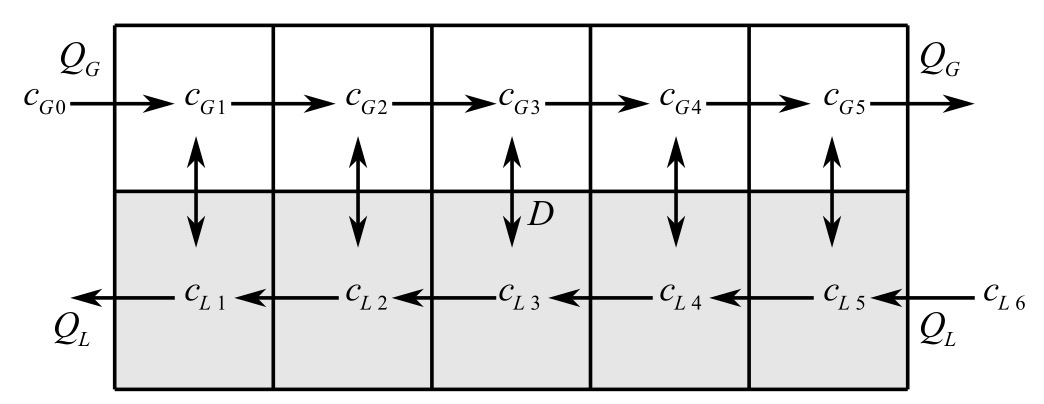
Flow rate and the concentration are provided as:
Formula used:
Write system of linear equations in matrix form.
And,
The term
Calculation:
Consider the figure below,

Here,
For reactor 1, the system is in steady state. Therefore, themass balance equation for the gas reactor 1.
Substitute
For reactor 2, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the gas reactor 2 is,
Substitute
For reactor 3, the system is in steady state, therefore, the mass balance equation for the gas reactor 3 is,
Substitute
For reactor 4, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the gas reactor 4 is,
Substitute
For reactor 5, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the gas reactor 5 is,
Substitute
For reactor 1, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the liquid reactor 1 is,
Substitute
For reactor 2, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the liquid reactor 2 is,
Substitute
For reactor 3, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the liquid reactor 3 is,
Substitute
For reactor 4, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the liquid reactor 4 is,
Substitute
For reactor 5, the system is in steady state. Therefore, the mass balance for the liquid reactor 5 is,
Substitute
Now, recollect all the linear equations for mass balance equation of gases and liquids.
There are too many linear equations which is complex to solving manually. So, write the equation in the form ofmatrices that is augmented form as shown below:
With the help of the linear system of equations provided above, the coefficient matrix A is,
With the help of the linear system of equations provided above, the column matrix X is:
And With the help of the linear system of equations provided above, the column matrix D is,
Write the system of equation in the augmented form.,
Solve the matrix
MATLAB is used to perform the calculation, type the following code into MATLAB cmd.
Once you press eneter, the resut is obtained as follows:
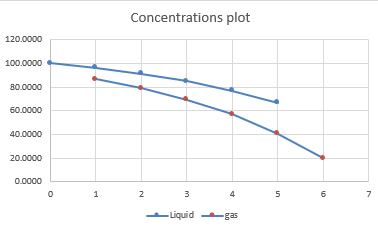
Hence, the values of concentrations passing through the reactors is shown in the below table:
The plot of concentration of liquid and gas is provided as:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Fundamentals of Differential Equations (9th Edition)
Basic Technical Mathematics
STATS:DATA+MODELS-W/DVD
Intermediate Algebra (8th Edition)
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
