
Concept explainers
Review. While Lost-a-Lot ponders his next move in the situation described in Problem 11 and illustrated in Figure P12.11, the enemy attacks! An incoming projectile breaks off the stone ledge so that the end of the drawbridge can be lowered past the wall where it usually rests. In addition, a fragment of the projectile bounces up and cuts the drawbridge cable! The hinge between the castle wall and the bridge is frictionless, and the bridge swings down freely until it is vertical and smacks into the vertical castle wall below the castle entrance. (a) How long does Lost-a-Lot stay in contact with the bridge while it swings downward? (b) Find the
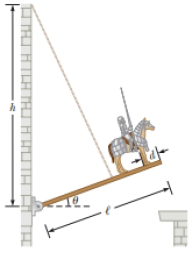
(a)
The time that Lost a Lot stay in contact with the bridge while it swings downward.
Answer to Problem 12P
The time that Lost a Lot stay in contact with the bridge while it swings downward is
Explanation of Solution
The length of the uniform bridge is
There is no time interval as the Lost a Lot stay in contact with the bridge while it swings downward because the horse feet loose contact with the down bridge as soon as it begins to move because the vertical acceleration act on the feet is greater than the acceleration due to gravity due to that the horse is in the air and moves upward with a vertical component of acceleration.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time that Lost a Lot stay in contact with the bridge while it swings downward is
(b)
The angular acceleration of the bridge just as it starts to move.
Answer to Problem 12P
The angular acceleration of the bridge just as it starts to move is
Explanation of Solution
The mass moment of inertial along the centroid is,
The total moment along the centroid is,
Here,
Total moment along the centroid is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angular acceleration of the bridge just as it starts to move is
(c)
The angular speed of the bridge when it strikes the wall below the hinge.
Answer to Problem 12P
The angular speed of the bridge when it strikes the wall below the hinge is
Explanation of Solution
The total height of the wall from the point of hinge is,
Here,
From the conservation of energy, the total potential energy will be equal to the rotational energy is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angular speed of the bridge when it strikes the wall below the hinge is
(d)
The force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately after the cable breaks.
Answer to Problem 12P
The force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately after the cable breaks is
Explanation of Solution
From Figure (1), the tangential acceleration is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the tangential acceleration is
The acceleration along the horizontal is,
Here,
The acceleration along the vertical is,
Here,
Force along the horizontal direction is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the force along the horizontal is
Force along the vertical is,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the vertical force is
The force exerted by the hinge on the bridge is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately after the cable breaks is
(e)
The force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately before strikes the cable wall.
Answer to Problem 12P
The force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately before strikes the cable wall is
Explanation of Solution
The acceleration along the vertical is,
From Newton’s second law, the total force along the vertical is,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the force exerted by the hinge on the bridge immediately before strikes the cable wall is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Figure P12.38 shows a light truss formed from three struts lying in a plane and joined by three smooth hinge pins at their ends. The truss supports a downward force of F=1000N applied at the point B. The truss has negligible weight. The piers at A and C are smooth. (a) Given 1 = 30.0 and 2 = 45.0, find nA and nC. (b) One can show that the force any strut exerts on a pin must be directed along the length of the strut as a force of tension or compression. Use that fact to identify the directions of the forces that the struts exert on the pins joining them. Find the force of tension or of compression in each of the three bars. Figure P12.38arrow_forwardWhy is the following situation impossible? A worker in a factory pulls a cabinet across the floor using a rope as shown in Figure P12.36a. The rope make an angle = 37.0 with the floor and is tied h1 = 10.0 cm from the bottom of the cabinet. The uniform rectangular cabinet has height = 100 cm and width w = 60.0 cm, and it weighs 400 N. The cabinet slides with constant speed when a force F = 300 N is applied through the rope. The worker tires of walking backward. He fastens the rope to a point on the cabinet h2 = 65.0 cm off the floor and lays the rope over his shoulder so that he can walk forward and pull as shown in Figure P12.36b. In this way, the rope again makes an angle of = 37.0 with the horizontal and again has a tension of 300 N. Using this technique, the worker is able to slide the cabinet over a long distance on the floor without tiring. Figure P12.36 Problems 36 and 44.arrow_forwardReview. One end of a light spring with force constant k = 100 N/m is attached to a vertical wall. A light string is tied to the other end of the horizontal spring. As shown in Figure P12.57, the string changes from horizontal to vertical as it passes over a pulley of mass M in the shape of a solid disk of radius R = 2.00 cm. The pulley is free to turn on a fixed, smooth axle. The vertical section of the string supports an object of mass m = 200 g. The string does not slip at its contact with the pulley. The object is pulled downward a small distance and released. (a) What is the angular frequency of oscillation of the object in terms of the mass M? (b) What is the highest possible value of the angular frequency of oscillation of the object? (c) What is the highest possible value of the angular frequency of oscillation of the object if the pulley radius is doubled to R = 4.00 cm? Figure P12.57arrow_forward
- A horizontal, rigid bar of negligible weight is fixed against a vertical wall at one end and supported by a vertical string at the other end. The bar has a length of 50.0 cm and is used to support a hanging block of weight 400.0 N from a point 30.0 cm from the wall as shown in Figure P14.81. The string is made from a material with a tensile strength of 1.2 108 N/m2. Determine the largest diameter of the string for which it would still break. FIGURE P14.81arrow_forwardWhen a person stands on tiptoe on one foot (a strenuous position), the position of the foot is as shown in Figure P12.32a. The total gravitational force Fg on the body is supported by the normal force n exerted by the floor on the toes of one foot. A mechanical model of the situation is shown in Figure P12.32b, where T is the force exerted on the foot by the Achilles tendon and R is the force exerted on the foot by the tibia. Find the values of T, R, and when Fg = 700 N. Figure P12.32arrow_forwardA stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P12.40, with AC = BC = . A painter of mass m stands on the ladder a distance d from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately. Figure P12.40 Problems 40 and 41.arrow_forward
- When a circus performer performing on the rings executes the iron cross, he maintains the position at rest shown in Figure P12.37a. In this maneuver, the gymnasts feet (not shown) are off the floor. The primary muscles involved in supporting this position are the latissimus dorsi (lats) and the pectoralis major (pecs). One of the rings exerts an upward force Fk on a hand as show n in Figure P12.37b. The force Fs, is exerted by the shoulder joint on the arm. The latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major muscles exert a total force Fm on the arm. (a) Using the information in the figure, find the magnitude of the force Fm for an athlete of weight 750 N. (b) Suppose a performer in training cannot perform the iron cross but can hold a position similar to the figure in which the arms make a 45 angle with the horizontal rather than being horizontal. Why is this position easier for the performer? Figure P12.37arrow_forwardA uniform rod of weight Fg and length L is supported at its ends by a frictionless trough as shown in Figure P12.49. (a) Show that the center of gravity of the rod must be vertically over point O when the rod is in equilibrium. (b) Determine the equilibrium value of the angle . (c) Is the equilibrium of the rod stable or unstable? Figure P12.49arrow_forwardA uniform beam of length L and mass m shown in Figure P12.8 is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. Its upper end is connected to a wall by a rope, and its lower end rests on a rough, horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the beam and surface is s. Assume the angle is such that the static friction force is at its maximum value. (a) Draw a force diagram for the beam. (b) Using the condition of rotational equilibrium, find an expression for the tension T in the rope in terms of m, g, and . (c) Using the condition of translational equilibrium, find a second expression for T in terms of s, m, and g. (d) Using the results from parts (a) through (c), obtain an expression for s involving only the angle . (e) What happens if the ladder is lifted upward and its base is placed back on the ground slightly to the left of its position in Figure P12.8? Explain. Figure P12.8arrow_forward
- Figure P12.13 shows a claw hammer being used to pull a nail out of a horizontal board. The mass of the hammer is 1.00 kg. A force of 150 N is exerted horizontally as shown, and the nail does not yet move relative to the board. Find (a) the force exerted by the hammer claws on the nail and (b) the force exerted by the surface on the point of contact with the hammer head. Assume the force the hammer exerts on the nail is parallel to the nail. Figure P12.13arrow_forwardA bridge of length 50.0 m and mass 8.00 104 kg is supported on a smooth pier at each end as shown in Figure P12.25. A truck of mass 3.00 104 kg is located 15.0 m from one end. What are the forces on the bridge at the points of support? Figure P12.25arrow_forwardA 500-N uniform rectangular sign 4.00 m wide and 3.00 m high is suspended from a horizontal, 6.00-m-long, uniform. 100-N rod as indicated in Figure P12.47. The left end of the rod is supported by a hinge, and the right end is supported by a thin cable making a 30.0 angle with the vertical. (a) Find the tension T in the cable. (b) Find the horizontal and vertical components of force exerted on the left end of the rod by the hinge. Figure P12.47arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



