
Concept explainers
The dominant C allele of a gene that controls color in corn produces kernels with color; plants homozygous for a recessive c allele of this gene have colorless or white kernels. What kinds of gametes, and in what proportions, would be produced by the plants in the following crosses? What seed color, and in what proportions, would be expected in the offspring of the crosses?
a.
b.
c.
To review:
On the basis of the data for dominant and recessive traits, the types of gametes formed, the color of the seed and its proportion, for the following crosses:
a. CC x Cc
b. Cc x cc
c. Cc x Cc
Introduction:
According to the law of dominance, the dominant trait is shown in homozygous as well as heterozygous form but the recessive trait is shown only when the homozygous allelic pair is present. The color of the kernels in corn is controlled by gene ‘C’, which is dominant in producing different colors, and gene
Explanation of Solution
a. The cross for CC × Cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype CC (colored) × Cc (colored)
The cross can be made as:
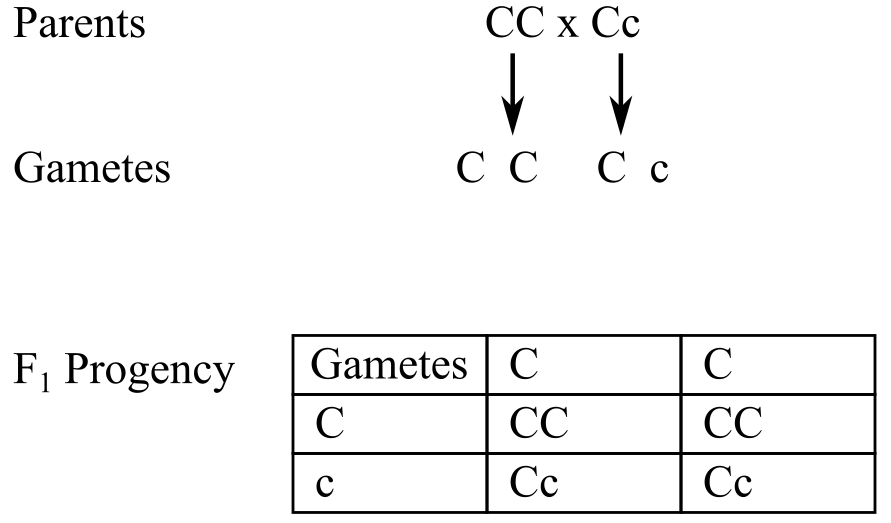
All the progenies will have colored kernels.
The CC plant produces all C gametes. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of homozygous (CC) colored and 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants are produced.
b. The cross for Cc × cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype
The cross can be made as:
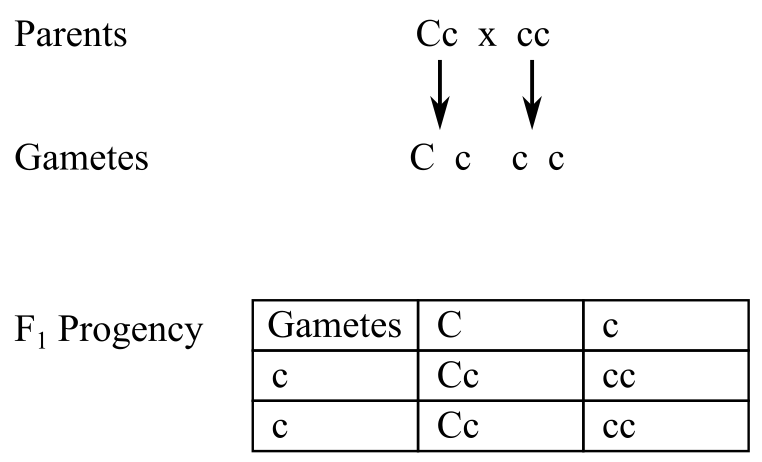
The progenies have the ratio of colored kernels to white kernels as
The Cc plant produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes and the cc parent produces all c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants and 50% (1/2) of homozygous recessive plants are produced.
c. The cross for Cc × Cc can be made as follows:
The parents have the genotype Cc (colored) and Cc (colored).
The cross can be made as:
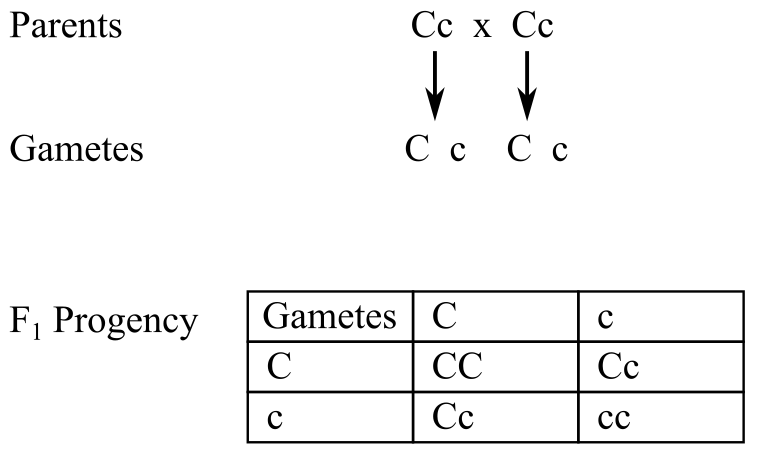
The progenies have the ratio of colored kernels to white kernels as
Both the Cc plants produce 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Looking at the offspring produced, 50% (1/2) of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants, 25% (1/4) of homozygous recessive plants, and 25% (1/4) of homozygous colored plants are produced.
Therefore, it can be concluded that:
a. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Half of homozygous (CC) colored and halh of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants are produced.
b. Cc produces 50% of C and 50% of c gametes and cc produces all c gametes. Half of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants and half of homozygous recessive plants are produced.
c. Both the Cc plants produce 50% of C and 50% of c gametes. Half of heterozygous (Cc) colored plants, 1/4 of homozygous recessive plants, and 1/4 of homozygous colored plants are produced.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
- Imagine that you are performing a cross involving seed texture in garden pea plants. You cross true-breeding round and wrinkled parents to obtain F1 offspring. Which of the following experimental results in terms of numbers of plants are closest to what you expect in the F2 progeny? a. 8lOroundseeds b. 8lOwrinkledseeds c. 405:395 round seeds:wrinkled seeds d. 610:190 round seeds:wrinkled seedsarrow_forwardWhich of the following is an example of a reciprocal cross? A. An F1 offspring is crossed back to one of its parents. B. Two randomly chosen F2 individuals are crossed C. A mother's phenotype in an initial cross is the father's phenotype in a subsequent cross and father's phenotype in the first cross is the mother's phenotype in the subsequent cross. D. An individual with unknown genotype is crossed to a homozygous recessive individual. E. Pollen from the male reproductive structure of one individual is used to fertilize an egg from the female reproductive structure of the same individual.arrow_forwardIn tomatoes, tall (D) is dominant over dwarf (d) and smooth fruit (P) is dominant over pubescent fruit (p), which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. The farmer crosses plants A and B with the same dwarf and pubescent plant and obtains the following numbers of progeny: Q. Explain why different proportions of progeny are produced when plant A and plant B are crossed with the same dwarf pubescent plant.arrow_forward
- In tomatoes, tall plant (D) is dominant over dwarf plant (d) and smooth fruit (H) is dominant over hairy fruit (h). A farmer crosses a tall plant with smooth tomatoes (plant A) with a dwarf and hairy fruit plant (plant B) and obtains the following results: Phenotype Offspring Tall & smooth fruit 3 Tall and hairy fruit 84 Dwarf and smooth fruit 88 Dwarf & hairy fruit 4 Which of the following can be used to represent the genotype of plant A in the question above? (lines represent homologous chromosomes)arrow_forwardA diploid plant has red flowers, heavy seeds and large leaves. The plant is a heterozygous for the following three genes:flower color (gene “F”),seed weight (gene “S”),and leaf size (gene “L”). This plant is testcrossed to a plant, which has white flowers, light seeds, and small leaves, the progeny of the testcross is as follows: 222 Red, heavy, large 228 White, light, small 224 Red, heavy, small 226 White, light, large 24 Red, light, large 26 White, heavy, small 25 White, heavy, large 25 Red, light, small Based on this results, which of the following statement is correct? Question 9 options: All three genes are on different chromosomes. Genes S and L are linked, while F assorts independently. Genes F and S are linked, while L assorts independently. Genes F and L are linked, while S assorts independently.arrow_forwardMany of the color varieties of summer squash are determined by two different interacting genes A and B: AA or Aa gives white colored squash, aaBB or aaBb gives yellow squash, and aabb produces green squash. A plant producing white squash is crossed with a plant producing green squash. One half of the offspring produces white squash; the other half produces green squash. What is the genotype of the parent plant producing white squash? AAbb AABB AaBb Aabb AaBBarrow_forward
- three recessive genes a, b, and c in the model plant Arabidopsis are found to be linked on chromosome 4. A three point test cross is done with a homozygous recessive plant with a heterozygous for all three genes. Following is the number of progenies a b C 65 A B c 56 A B C 1267 a b c 1310 A b C 550 a B c 515 a B C 470 A b c 489 Total = 4,722 Determine the middle locus by your choice of method and after that calculate the map distance between the genes in map unit (m.u.).arrow_forwardBateson and Punnett crossed two white-flowered lines and saw all purple flowers in the F1 generation. They concluded this was an example of complementary gene interactions because a cross of the F1 plants yielded what ratio in the F2 generation? A) 8 purple to 8 white B) 16 purple to 0 white C) 0 purple to 16 white D) 7 purple to 9 white E) 9 purple to 7 whitearrow_forwardThe crossing of two orange-flowering plants results in ~2/3 orange-flower progeny and ~1/3 white-flower progeny. The crossing of two orange-flowering F1 plants generates the same progeny ratios as observed for the parental cross, while the crossing of white-flowering F1 plants only produces white-flowering progeny. What is a likely explanation for these results?arrow_forward
- The genes for tall vine D and yellow seed G, are dominant over their respective alleles for dwarf d and green g. What phenotypes are expected from each of the following crosses? Include phenotypic and genotypic ratio. Use Punnet square to show the ff. Crosses. a. Heterozygous tall, homozygous yellow X Homozygous Tall, heterozygous yellow. b. Homozygous Dwarf, heterozygous yellow X Heterozygous tall, homozygous greenarrow_forwardTwo pure-breeding strains of flies are mated, and the F1 are intercrossed. The first strain has curled wings and black bodies. The second strain has straight wings and brown bodies. The F2 progeny are 271 straight wings with brown bodies, 31 curled wings with black bodies, 94 curled wings with brown bodies and 90 straight wings with black bodies. If instead of the above, assume the wing shape gene and the body color gene are completely linked. From parents that are curled winged with brown bodies mated to straight winged with black bodies, what would be the outcome of an F1 intercross? (Specify the phenotypes and the frequency of each expected).arrow_forwardA plant geneticist is examining the mode of inheritance of flower color in two closely related species of exotic plants. The first species may have two pure-breeding lines—one produces a distinct red flower; and the other produces flowers with no color at all, or very pale yellow flowers. However, she cannot be sure. A cross of these varieties produces all pink-flowered progeny. The second species exhibits similar pure-breeding varieties; that is, one variety produces red flowers; and the other produces an albino or very pale yellow flower. A cross of these two varieties, however, produces orange-flowered progeny exclusively. Analyze the mode of inheritance of flower color in these two plant species.arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
