
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Density of the liquid carbon dioxide is greater or less than solid carbon dioxide has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
All three phases of
(a)
Answer to Problem 37PS
The density of liquid
Explanation of Solution
The phase diagram of
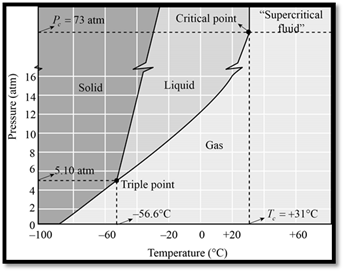
Figure 1
When seeing the phase diagram of
(b)
Interpretation:
Phase at which carbon dioxide at 5tm and
Concept introduction:
All three phases of
(b)
Answer to Problem 37PS
Explanation of Solution
The phase diagram of
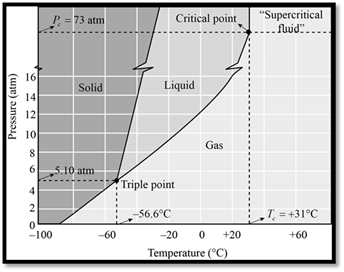
Figure 1
When seeing the phase diagram of
In the phase diagram of
(b)
Interpretation:
Carbon dioxide can be liquefied at
Concept introduction:
All three phases of
(b)
Answer to Problem 37PS
Explanation of Solution
The phase diagram of
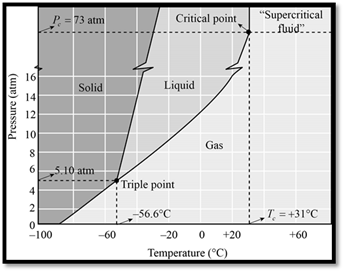
Figure 1
When seeing the phase diagram of
In the phase diagram of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- The normal boiling point of SO2 is 263.1 K and that of NH3 is 239.7 K. At −40 °C, would you predict that ammonia has a vapor pressure greater than, less than, or equal to that of sulfur dioxide? Explain.arrow_forwardButane is a gas at room temperature; however, if you look closely at a butane lighter you see it contains liquid butane. Explain how it is possible to have liquid butane present.arrow_forwardAssociate each of the solids BN, P4S3, Pb, and CaCl2 with one of the following sets of properties. a A bluish white, lustrous solid melting at 327C; the solid is soft and malleable. b A white solid melting at 772C; the solid is an electrical nonconductor but dissolves in water to give a conducting solution. c A yellowish green solid melting at 172C. d A very hard, colorless substance melting at about 3000C.arrow_forward
- Draw and explain pressure-density phase diagram for CO2.arrow_forwardIn the phase diagram shown, segment AD corresponds to the conditions of temperature and pressure under which the solid and gas of the substance are in equilibrium. Select one:A)RealB) Falsearrow_forwardThe molar enthalpy of vaporization of carbon disulfide is 26.74 kJ/mol , and its normal boiling point is 46°C . What is the vapor pressure of CS 2 at 0°C ?arrow_forward
- Since the vapor pressure of diethylether at 18 ° C is 401 mmHg, calculate the pressure at 32 ° C (delta Hbuh = 26.0 kJ / mol, R = 8.314 J / K.mol)arrow_forwardA 10.0 g sample of liquid water is sealed in a 1515 mL flask and allowed to come to equilibrium with its vapor at 27 °C. What is the mass of H2O (g) present when equilibrium is established?arrow_forwardList the following substances in order of decreasing boiling point:CO2, Ne, CH3OH, KF Rank substances from the highest boiling point to the lowest one. To rank substances as equivalent, overlap them.arrow_forward
- The vapor pressure of benzene is 224 mmHg at 45 °C and 648 mmHg at 75 °C.(a) Find the enthalpy of vaporization of benzene, ∆Hvap (kJ/mol), assuming it is constant. You may also assume that ZV − ZL ≃ 1. B)arrow_forwardHow much heat is required to evaporate 100.0 g of liquid ammonia, NH3, at its boiling point if its enthalpy of vaporization is 4.8 kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe vapor pressure of ethanol (C2H5OH) at 19 °C is 40.0torr. A 1.00-g sample of ethanol is placed in a 2.00 L containerat 19 °C. If the container is closed and the ethanolis allowed to reach equilibrium with its vapor, how manygrams of liquid ethanol remain?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning


